This document discusses modular programming and provides examples. It covers:
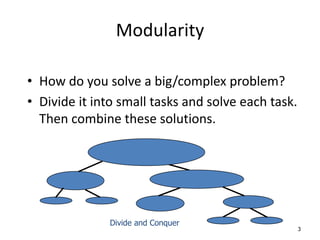
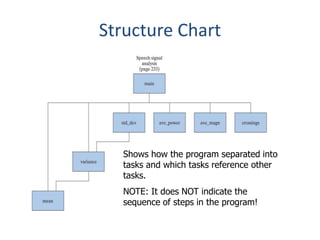
1) Modularity involves dividing complex problems into smaller tasks and combining the solutions. Structure charts show how programs are divided into modules.
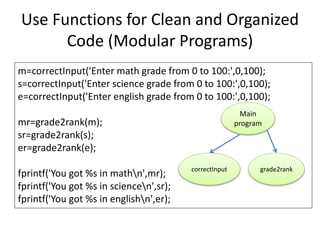
2) Best practices for modules include dedicating each to a single task and providing input/output parameters and error messages.
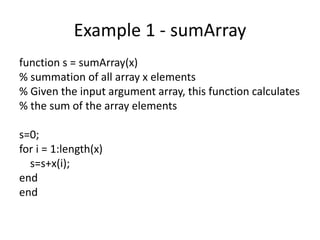
3) Examples demonstrate creating functions for calculating statistics, removing duplicates, and converting grades to ranks to divide programs into clean, organized modules.



![Example 1 - stat
function [mean, stdev] = stat(x)
% Mean and Standard deviation of an array
% Given the input argument array, this function calculates
% the mean (first output argument) and
% the standard deviation (second argument)
% of the array
% developed by XYZ on April 30, 2014
n=length(x);
mean=sumArray(x)/n;
stdev = sqrt(ssd(x,mean)/n);
end
stat
sumArray ssd](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csci101lect08bmatlabprograms-200319121953/85/Csci101-lect08b-matlab_programs-6-320.jpg)






![function – DisplayTime, DisplayTimeArray
function DisplayTime(h,m)
fprintf(‘%02d:%02dn’,h,m);
end
>>DisplayTime(5,10);
05:10
function DisplayTimeArray(t)
for i=1:length(t)
fprintf(‘%02d:%02dn’,t(i,1),t(i,2));
end
end
>>DisplayTimeArray([5 10; 11 30]);
05:10
11:30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csci101lect08bmatlabprograms-200319121953/85/Csci101-lect08b-matlab_programs-15-320.jpg)