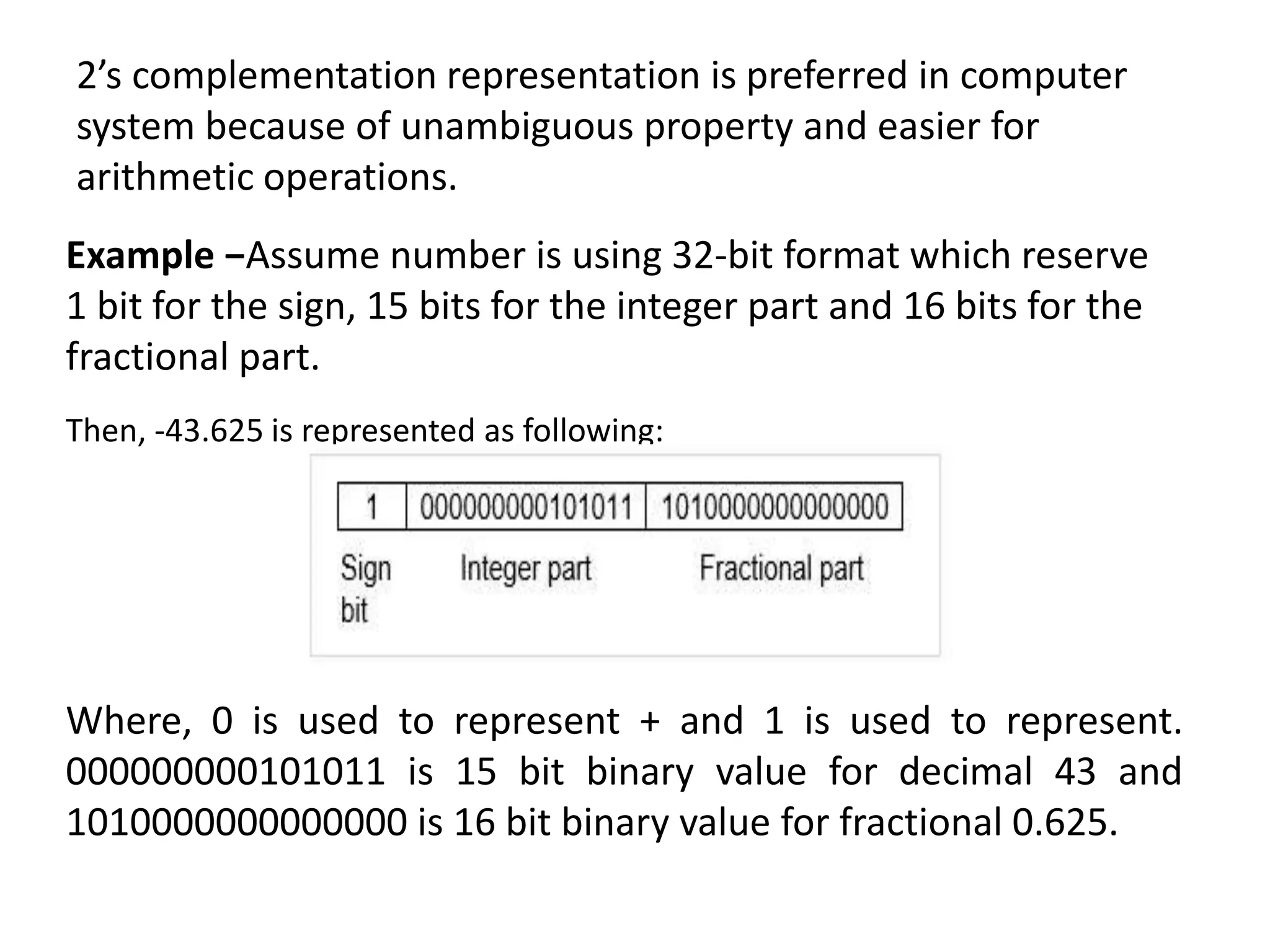
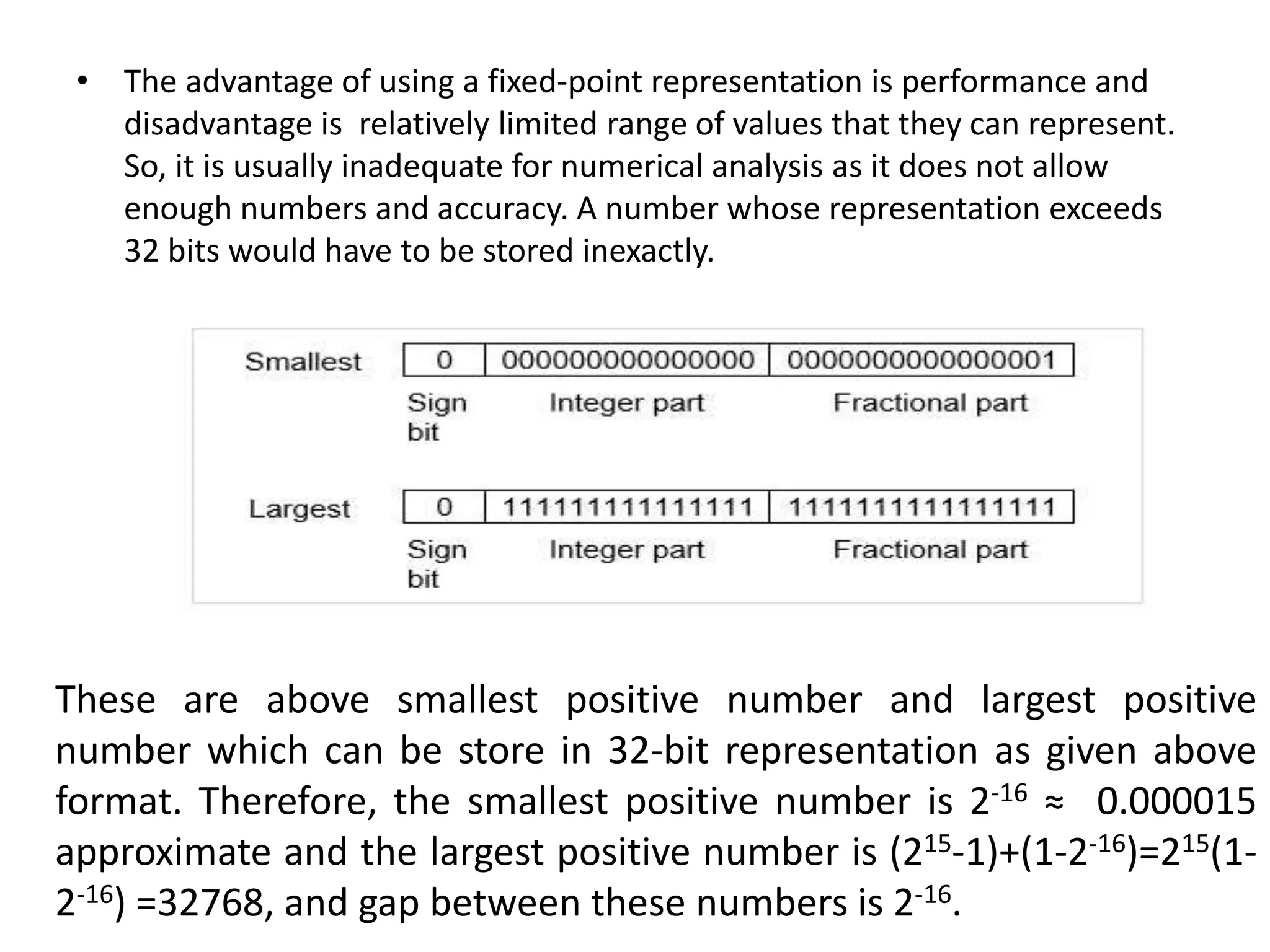
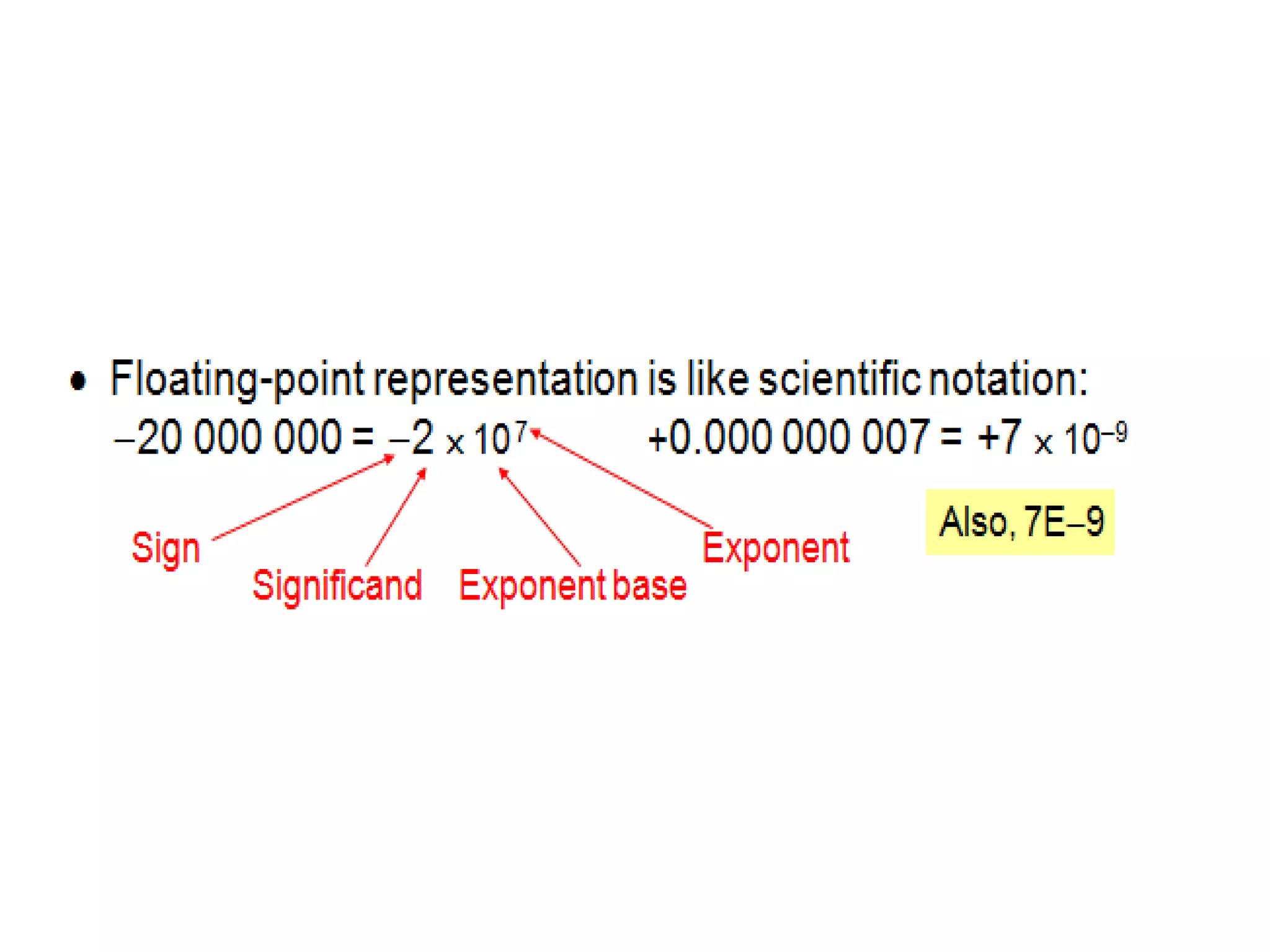
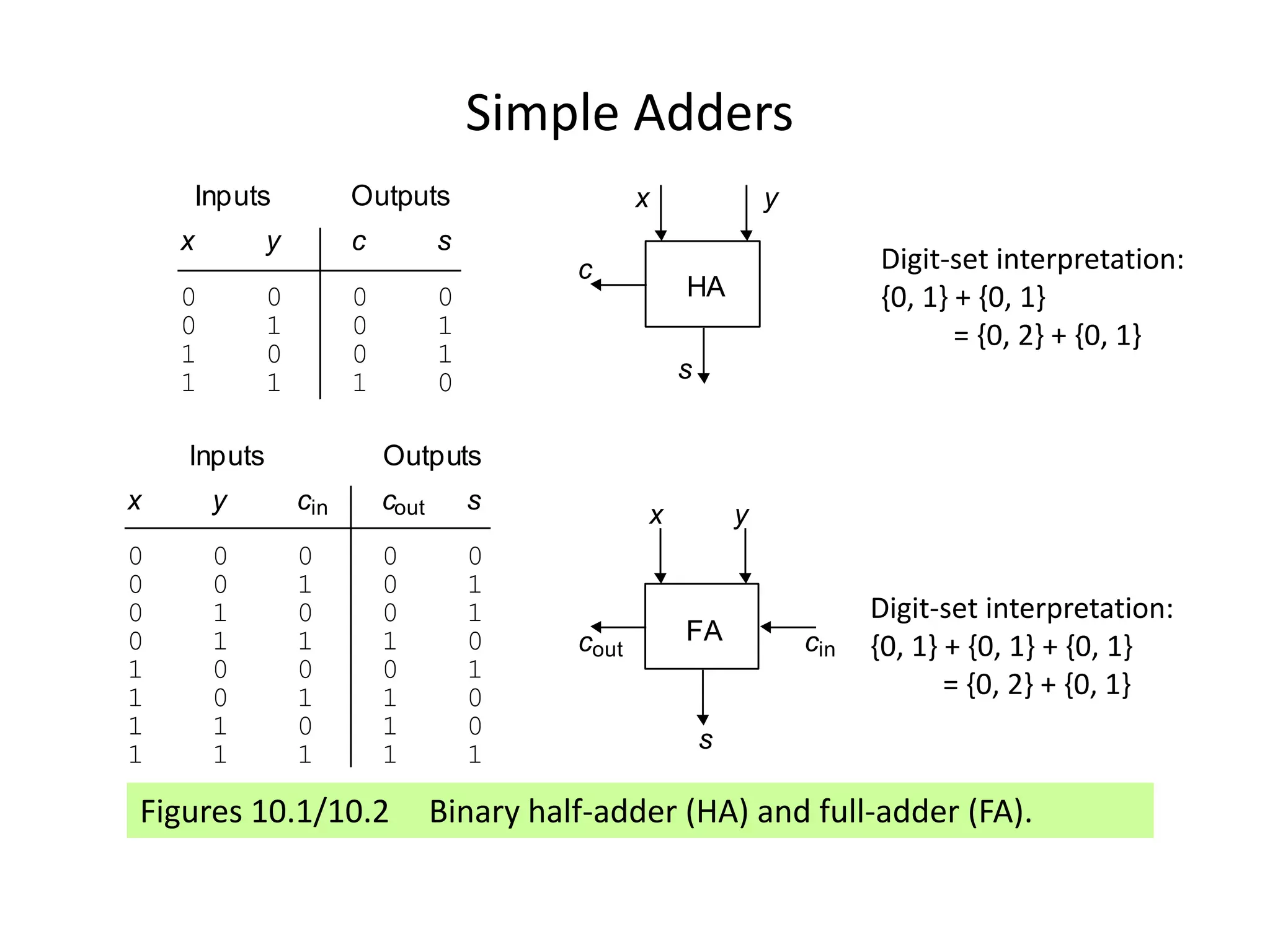
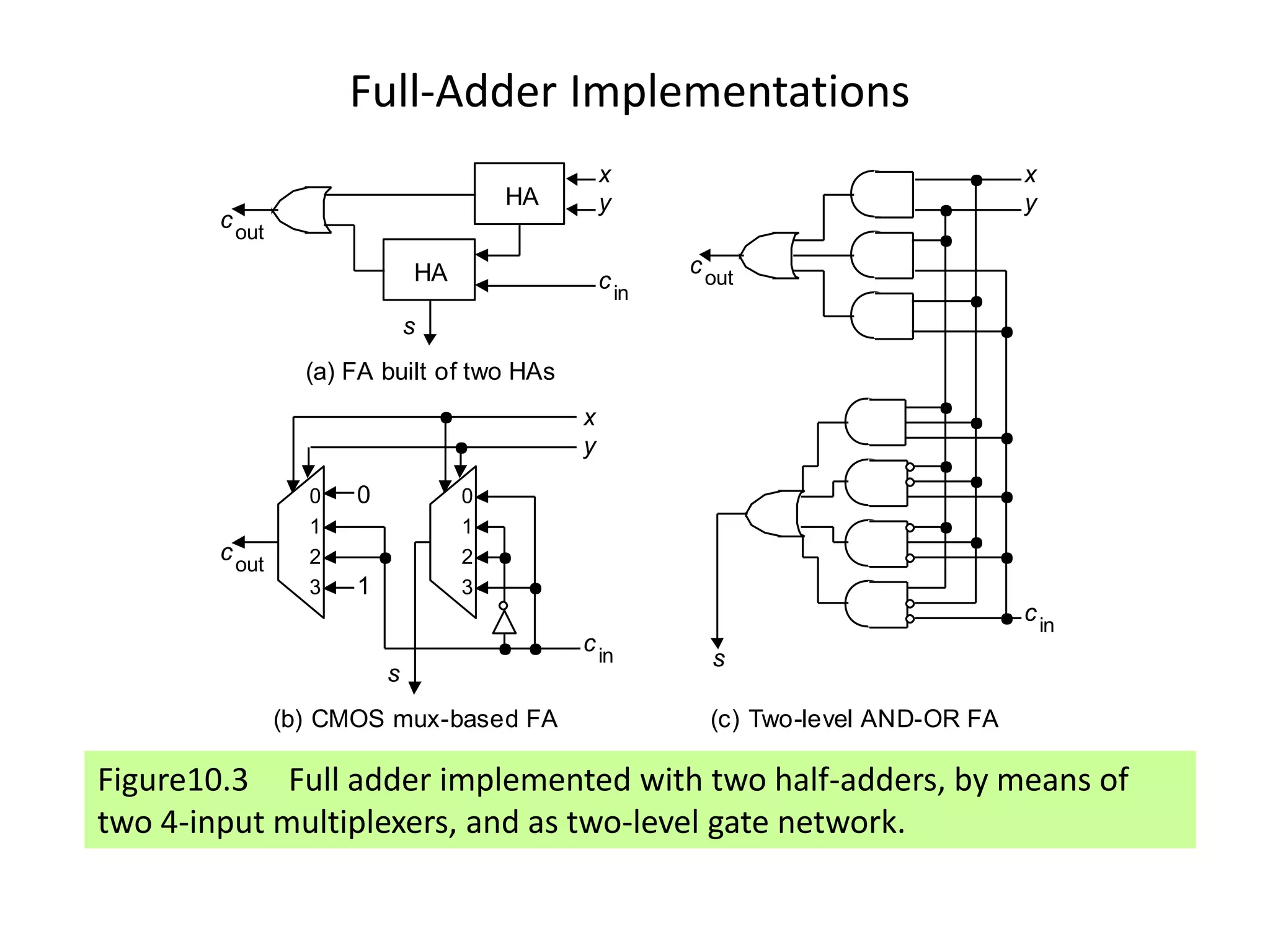
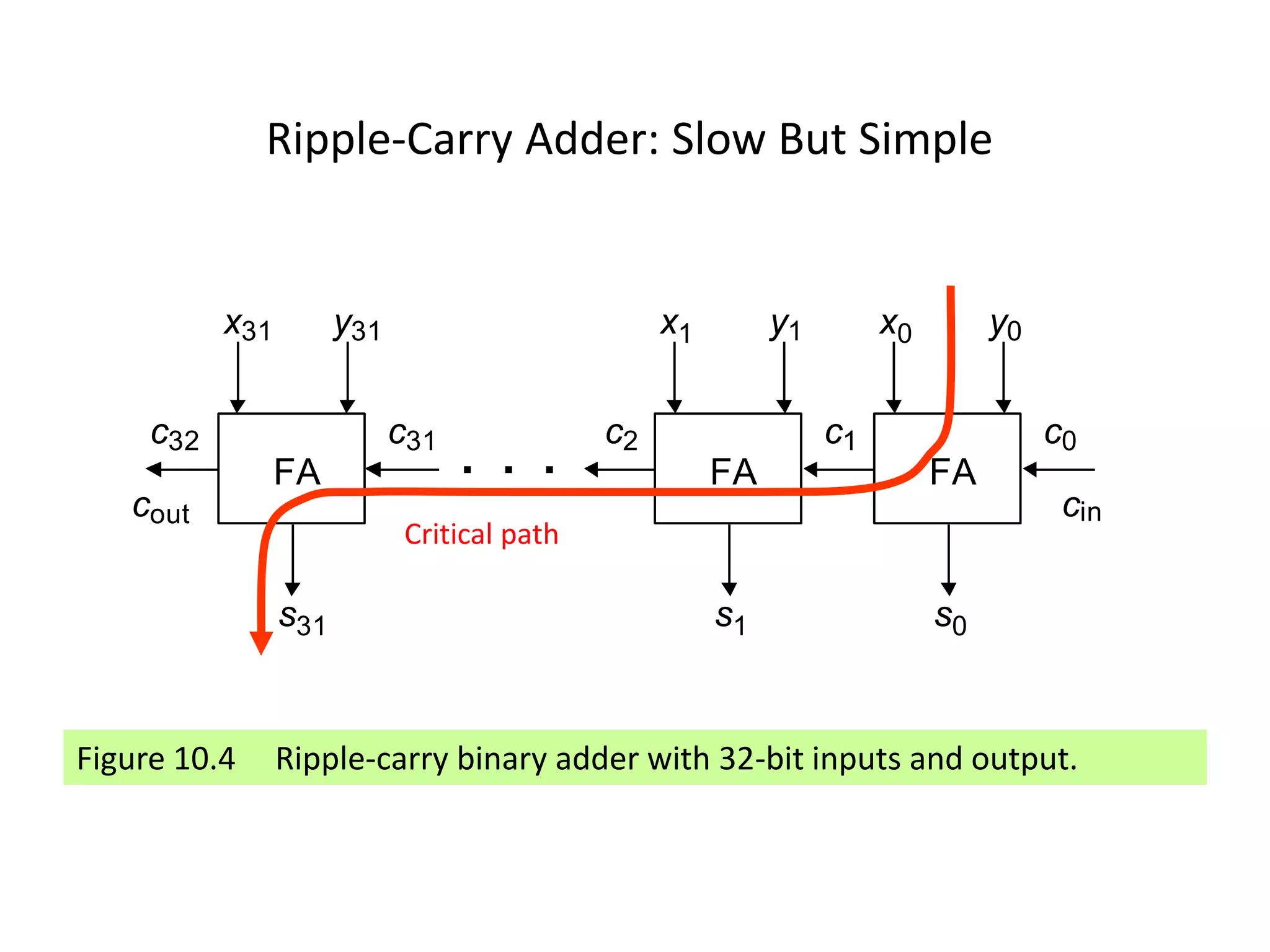
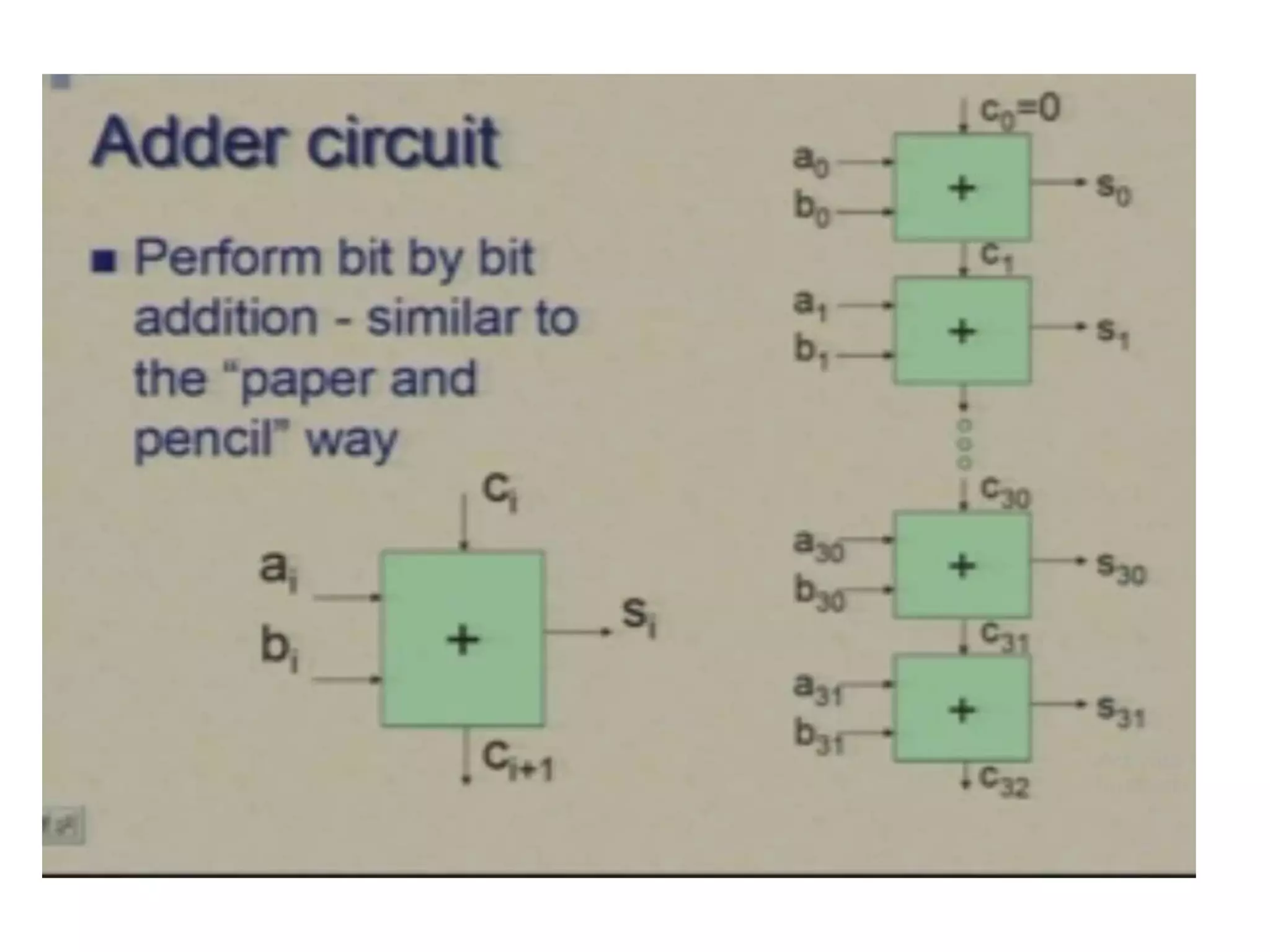
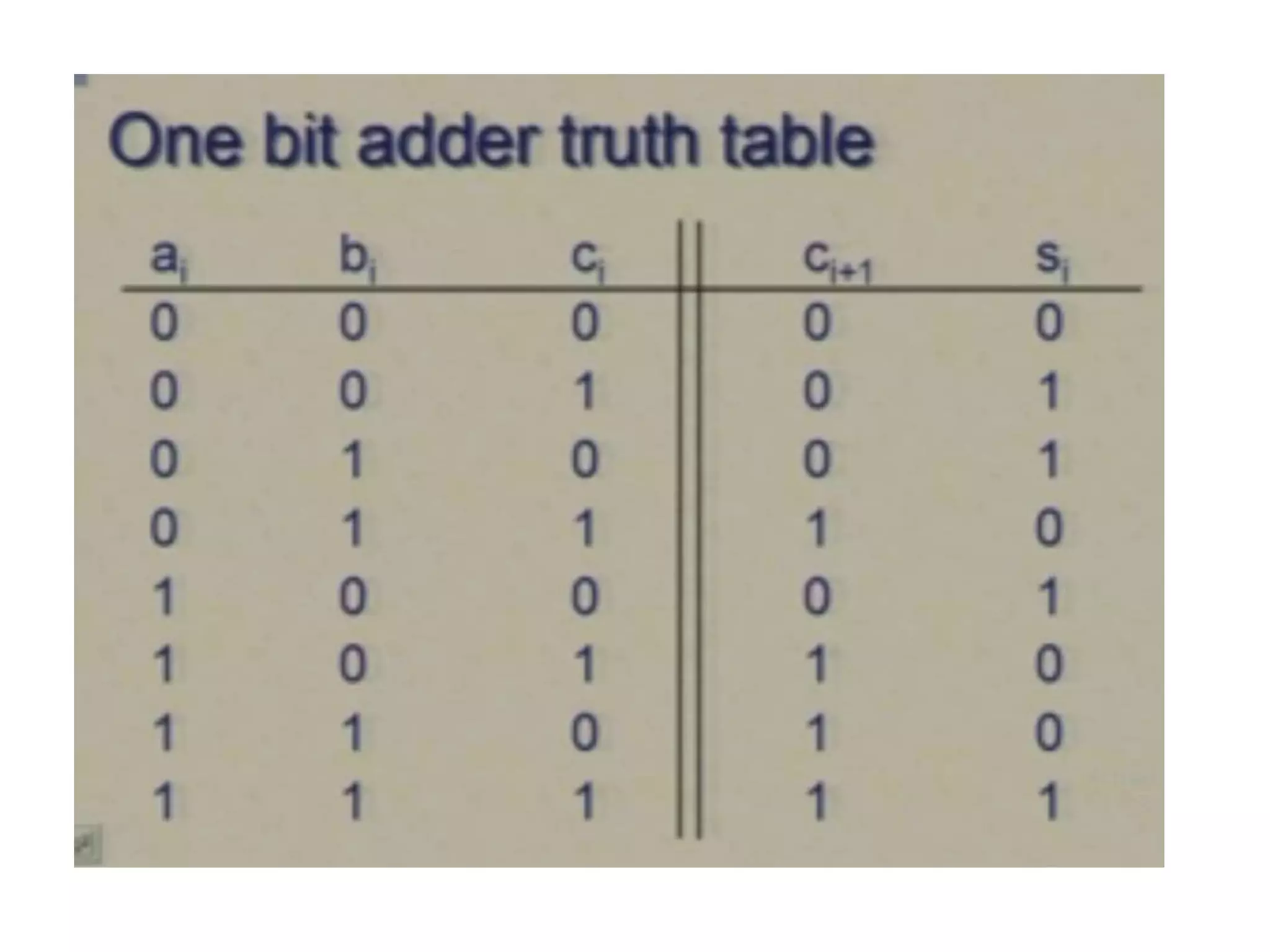
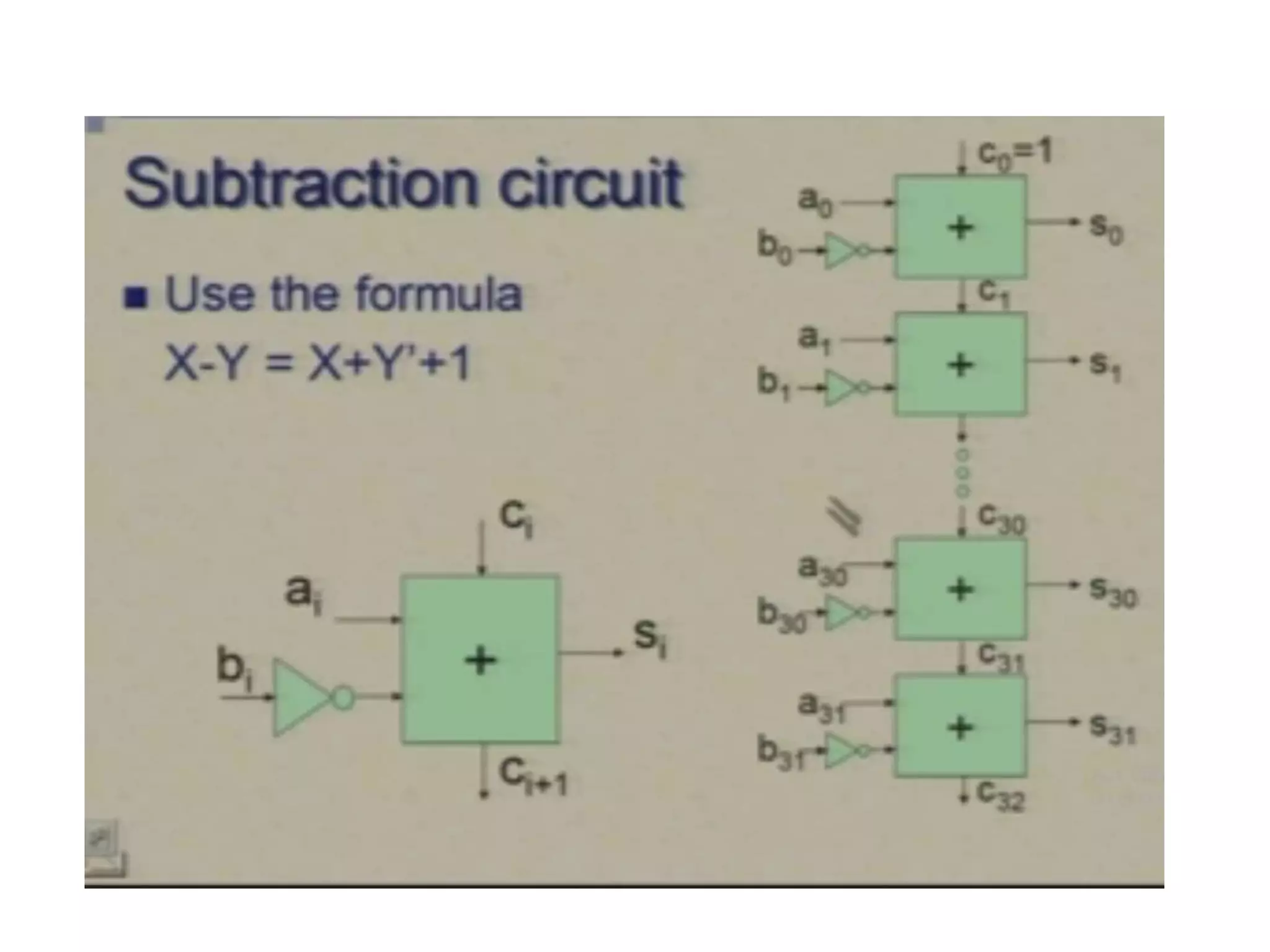
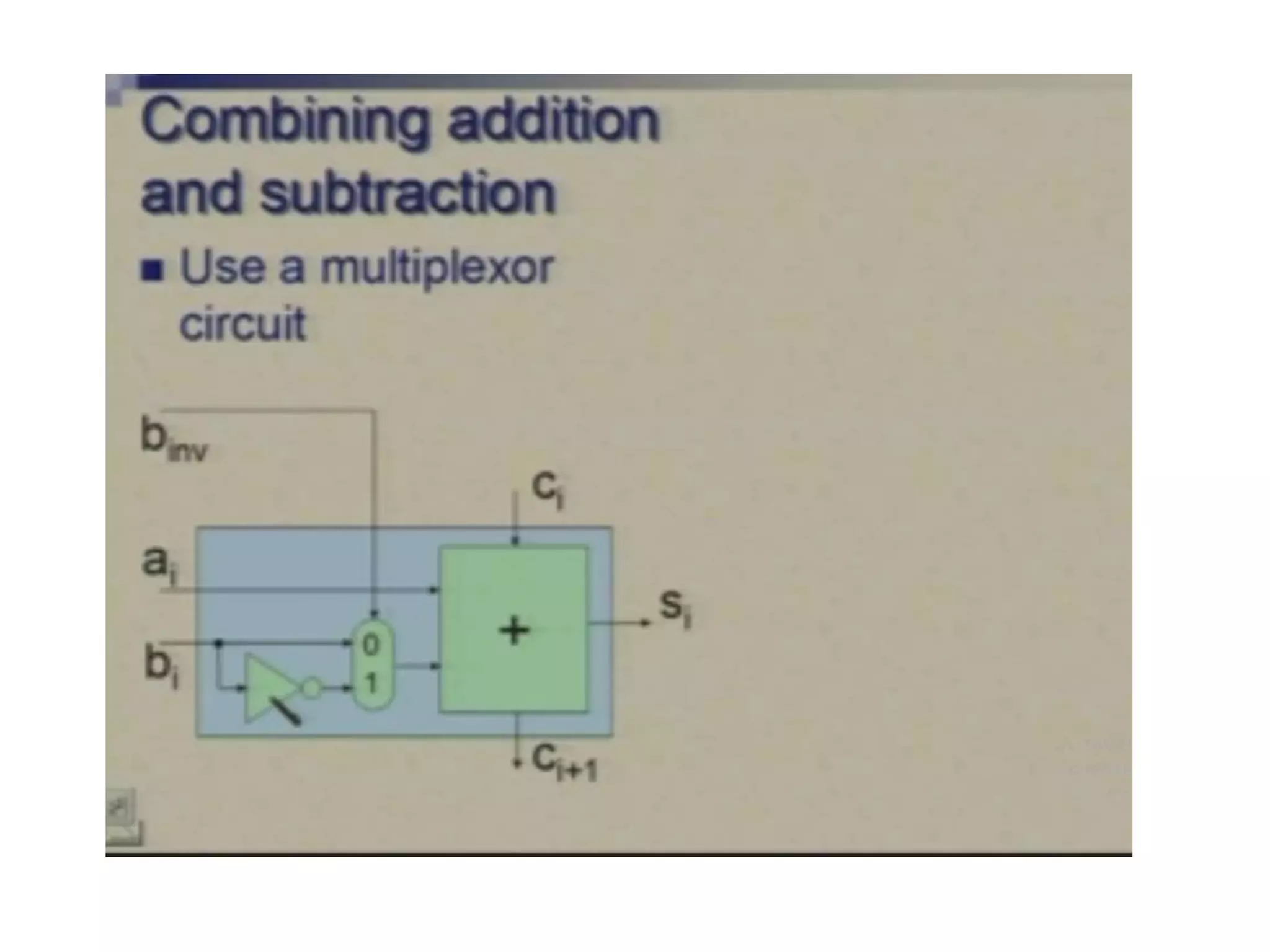
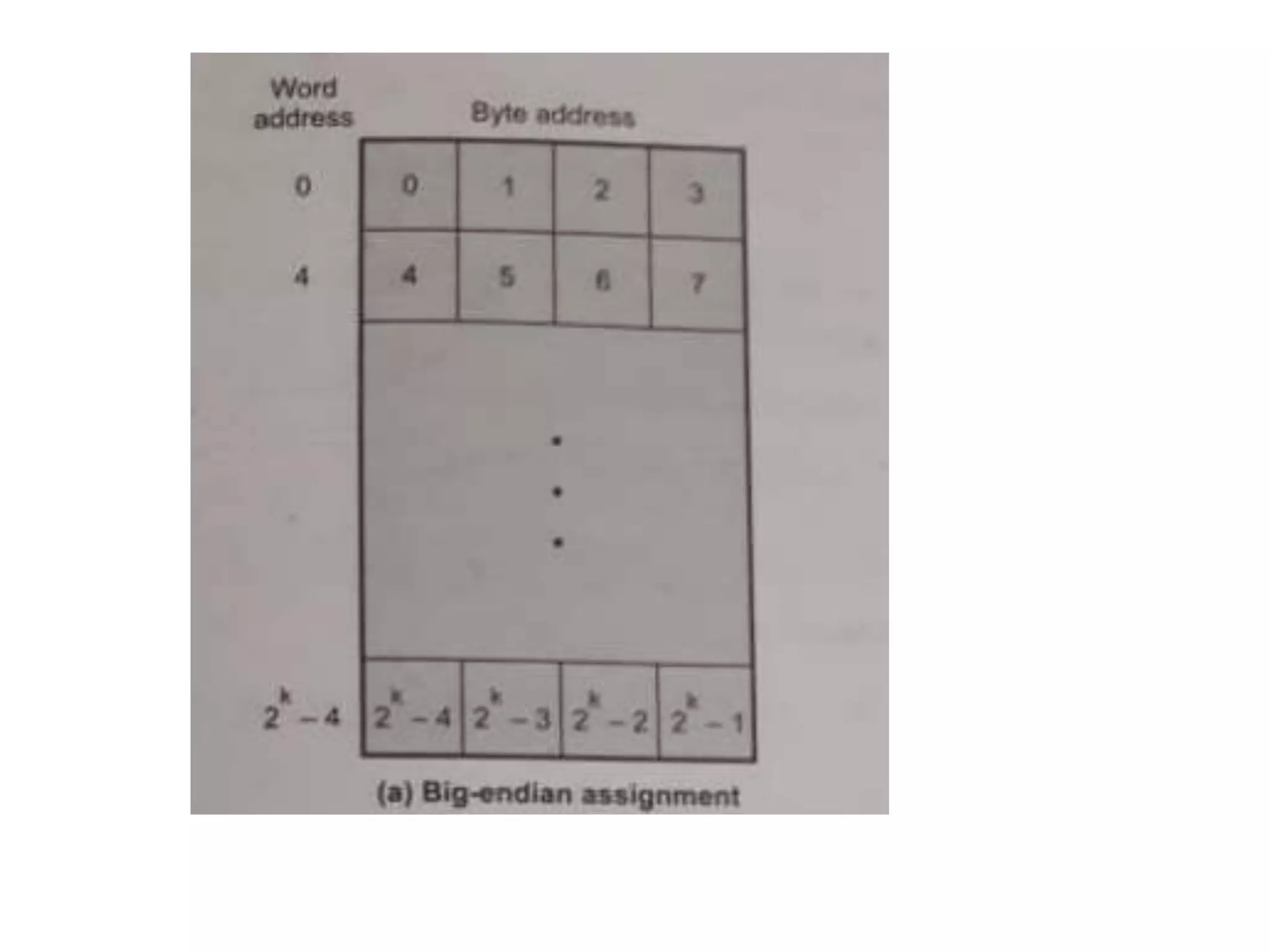
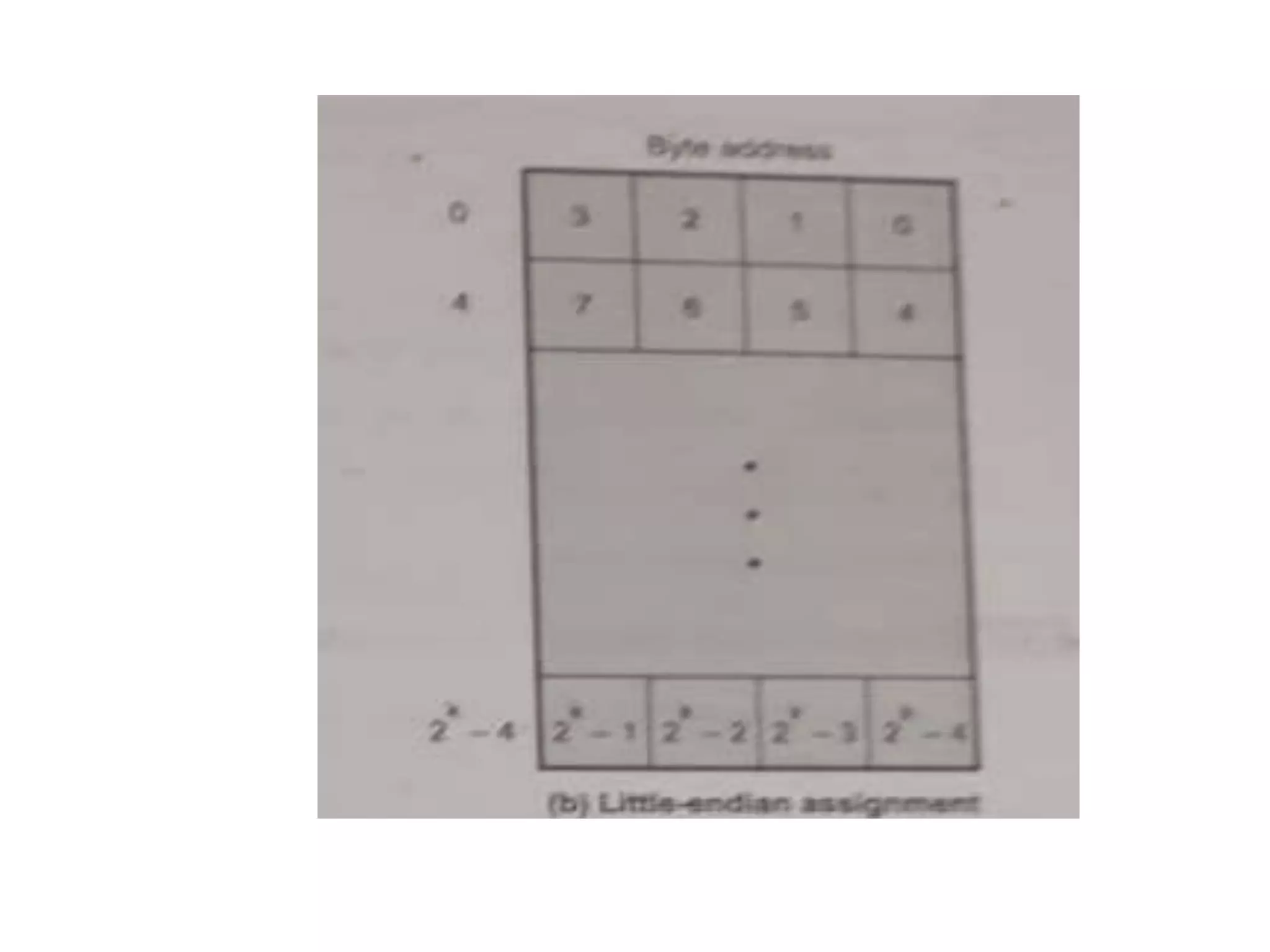
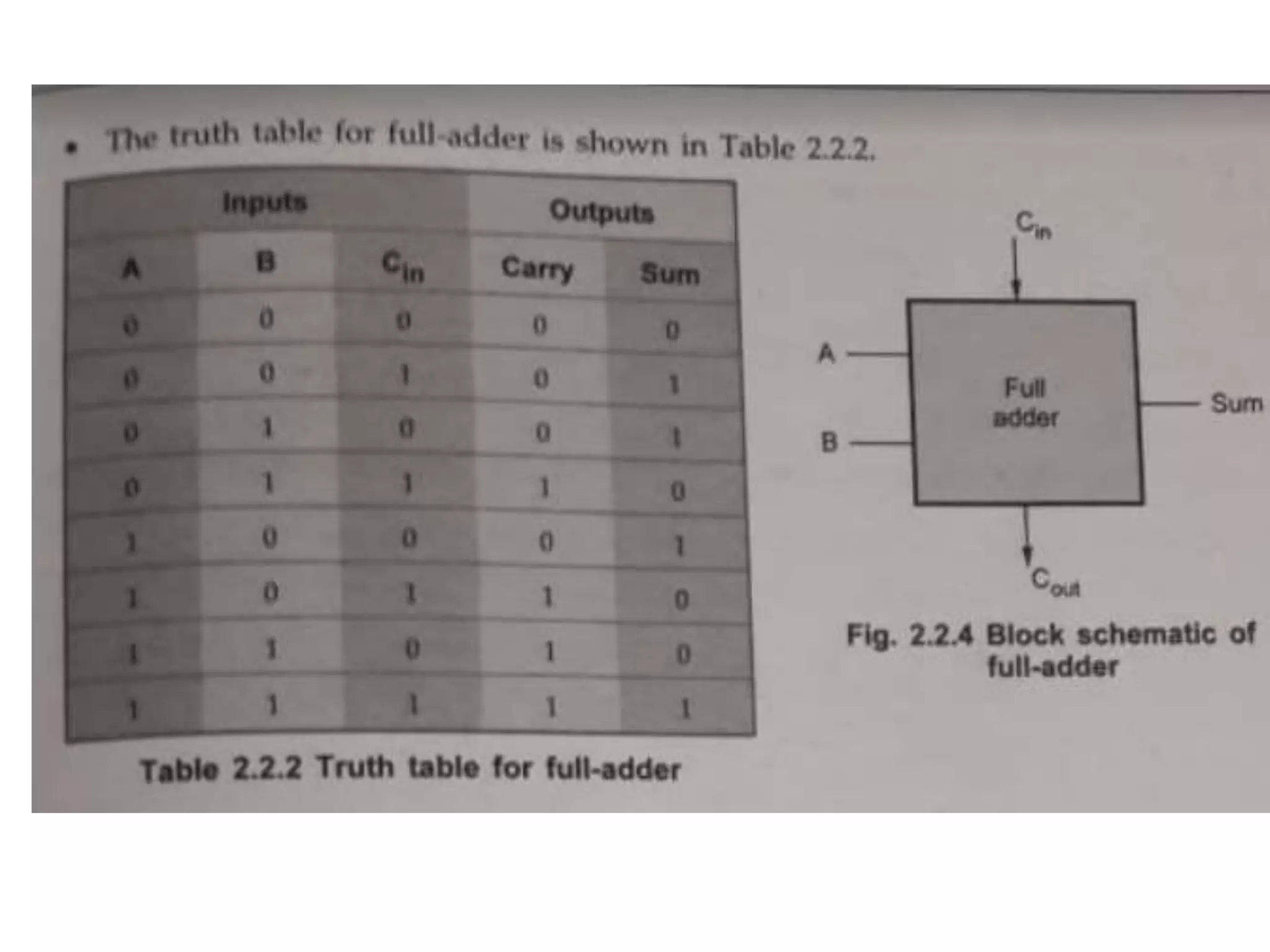
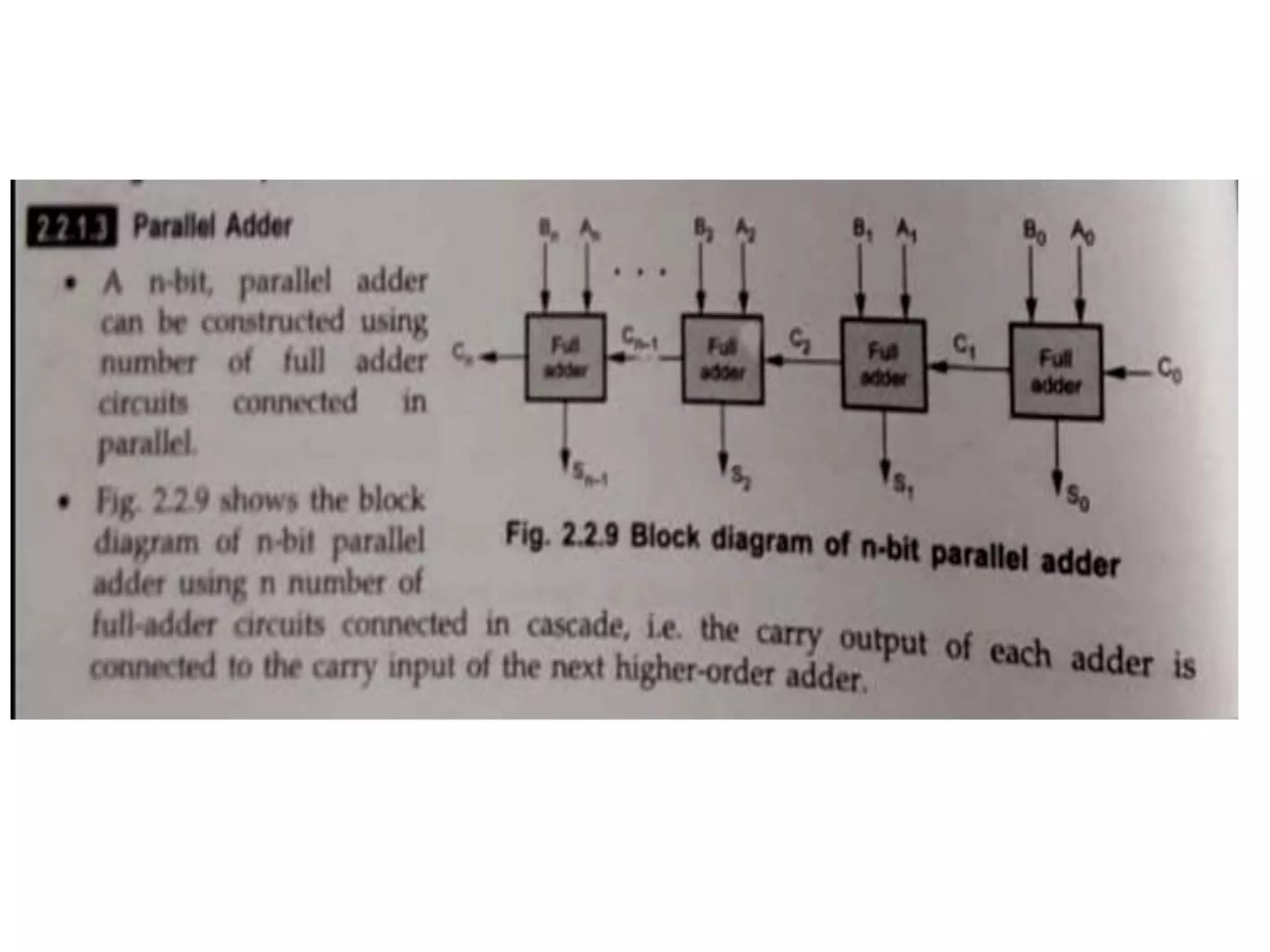
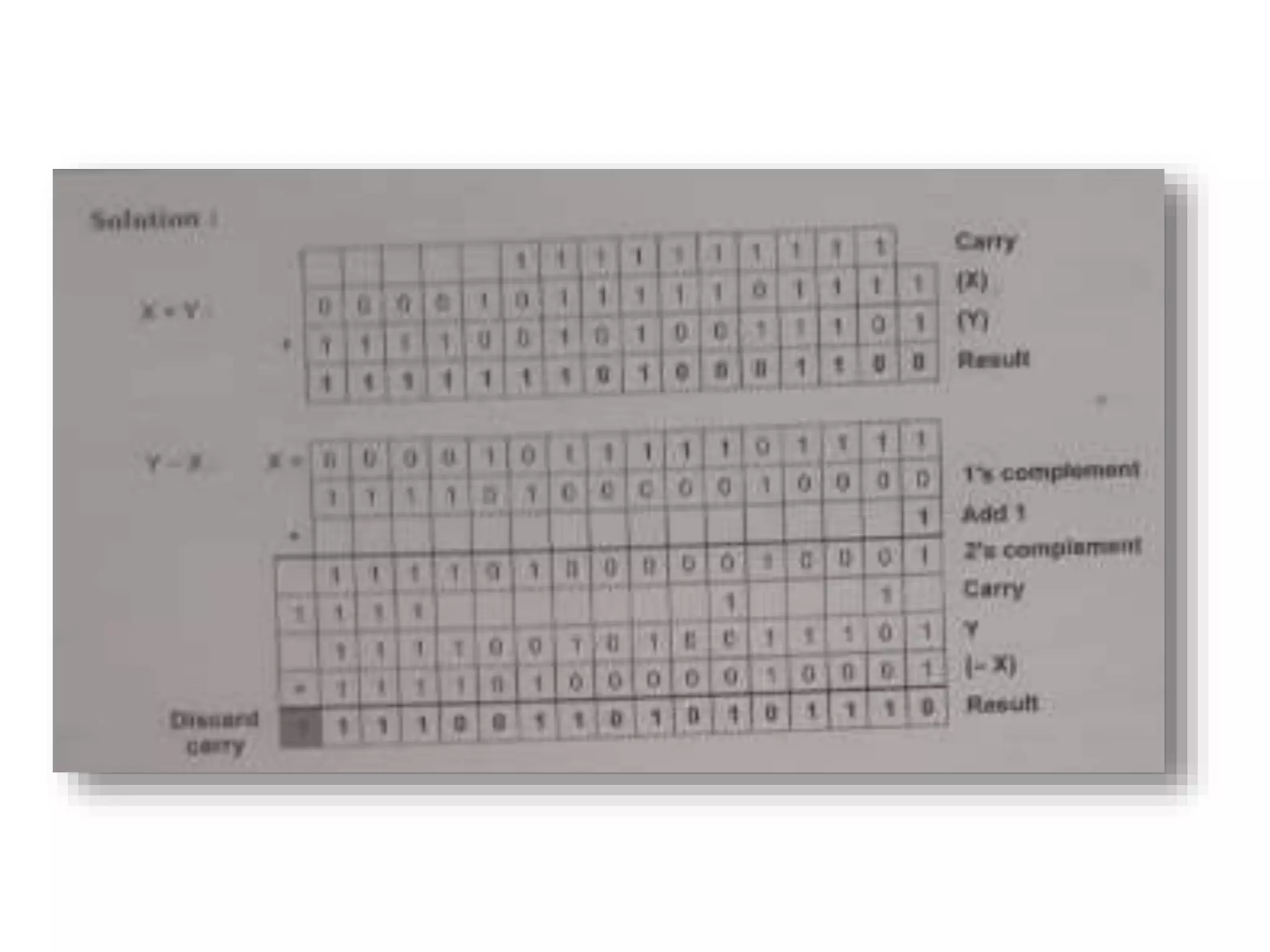
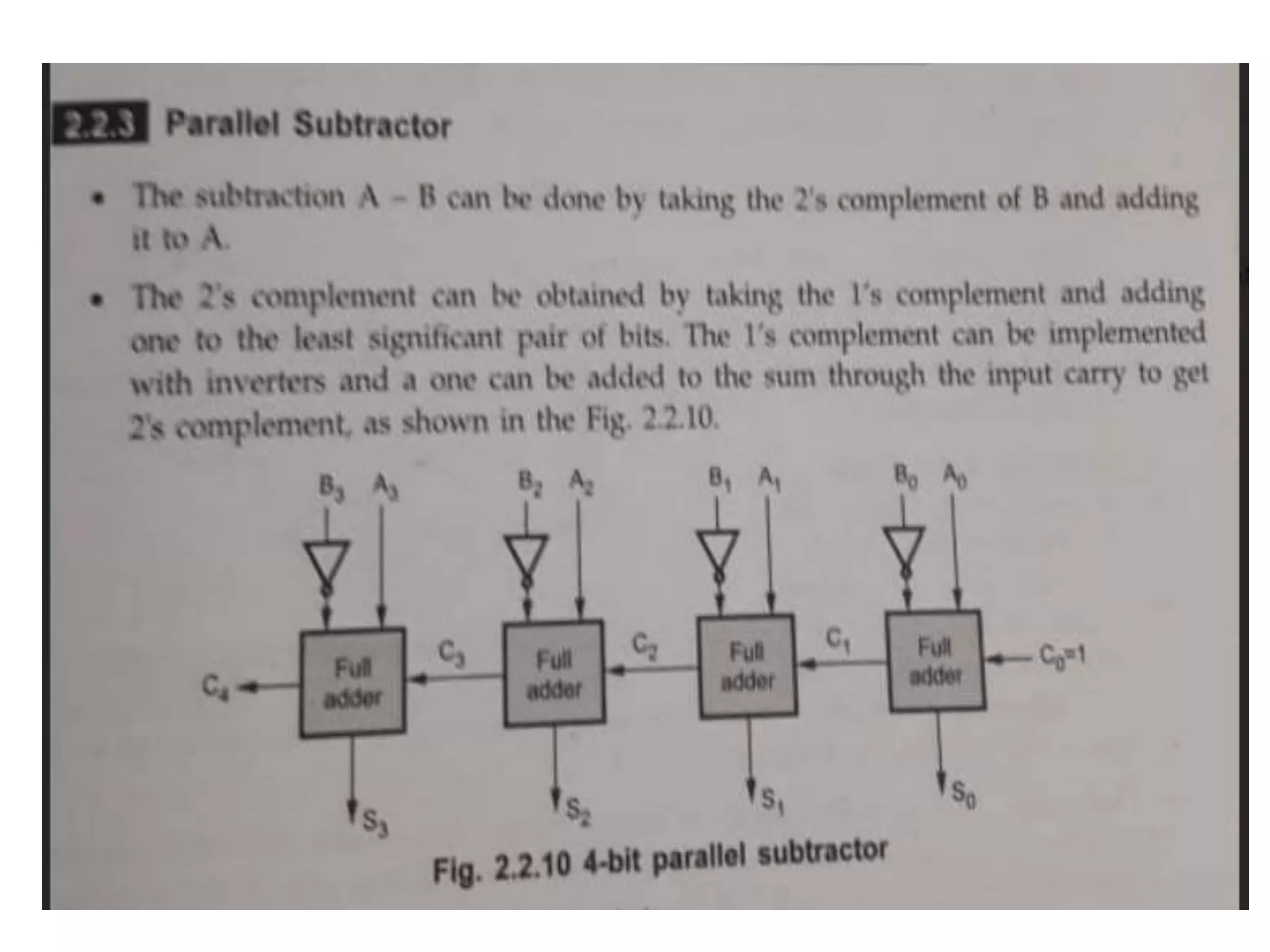
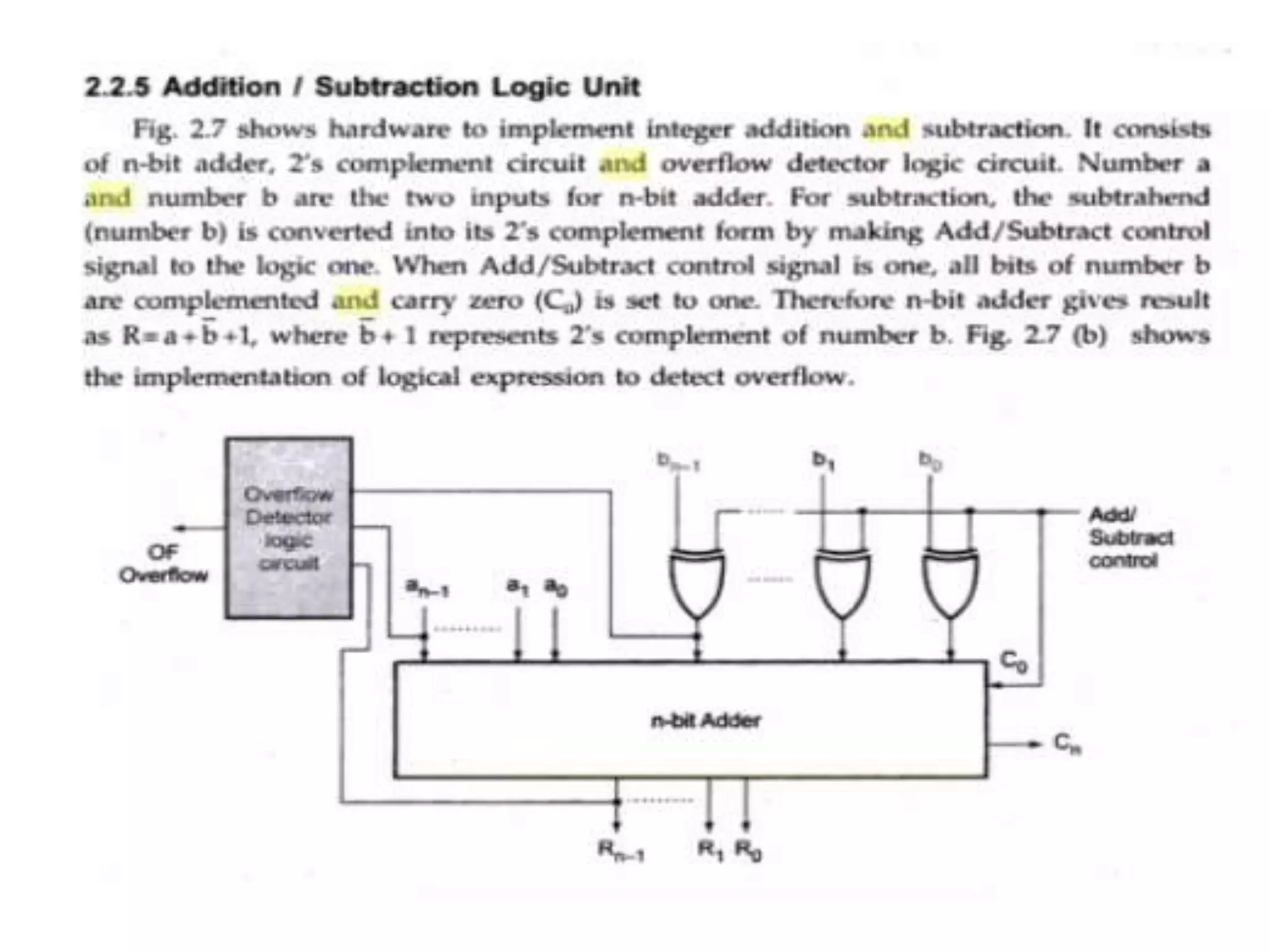
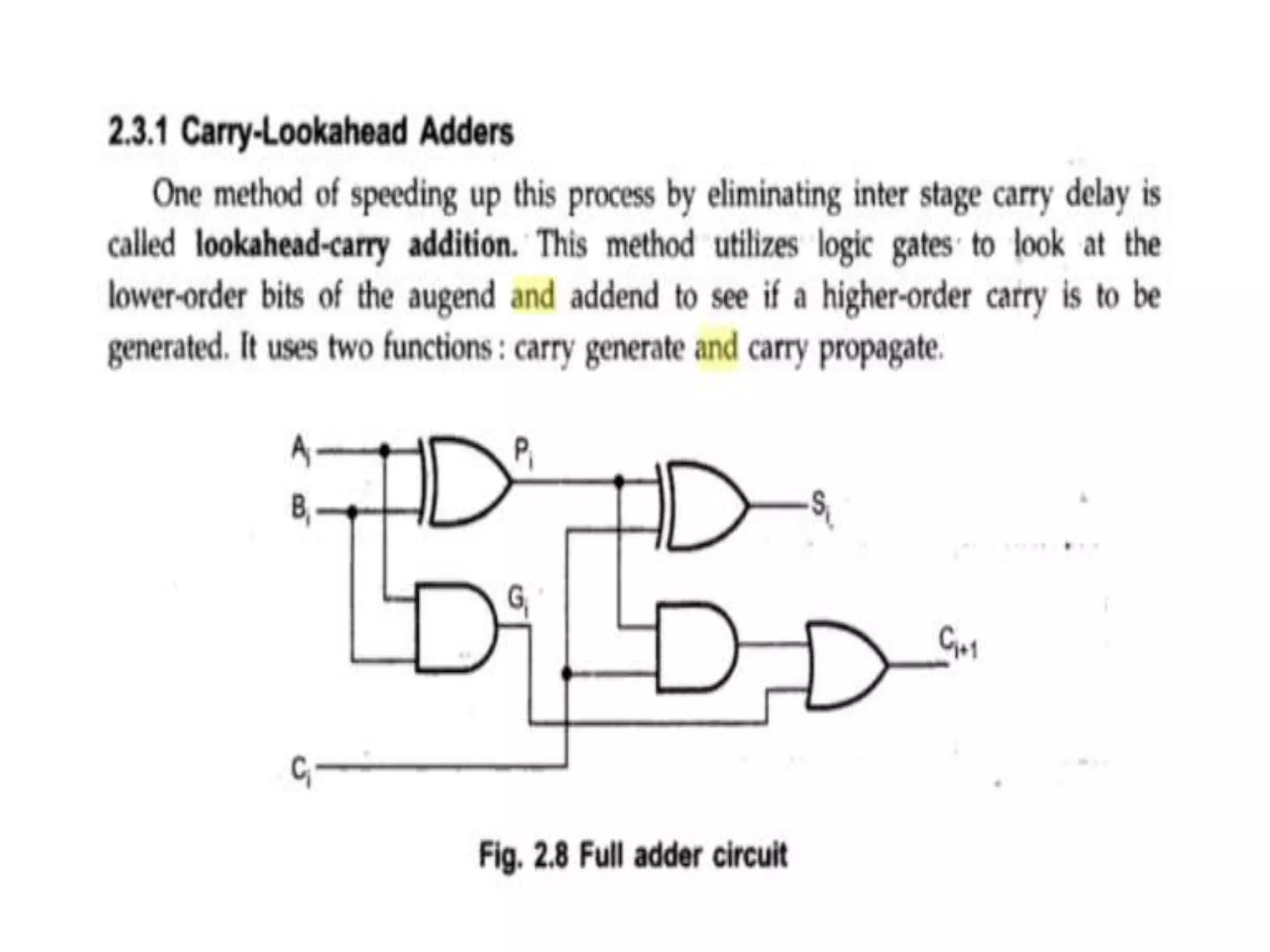
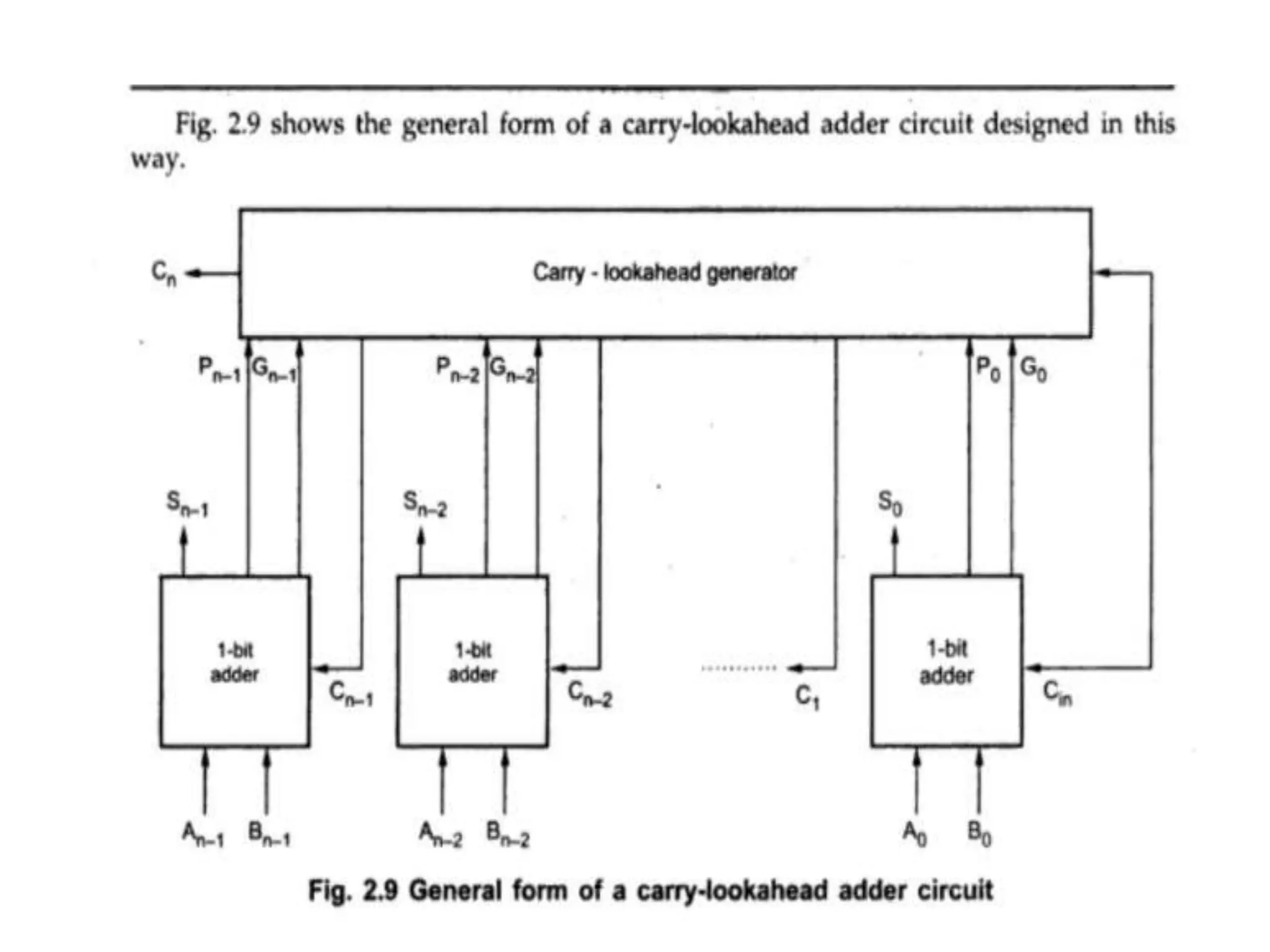
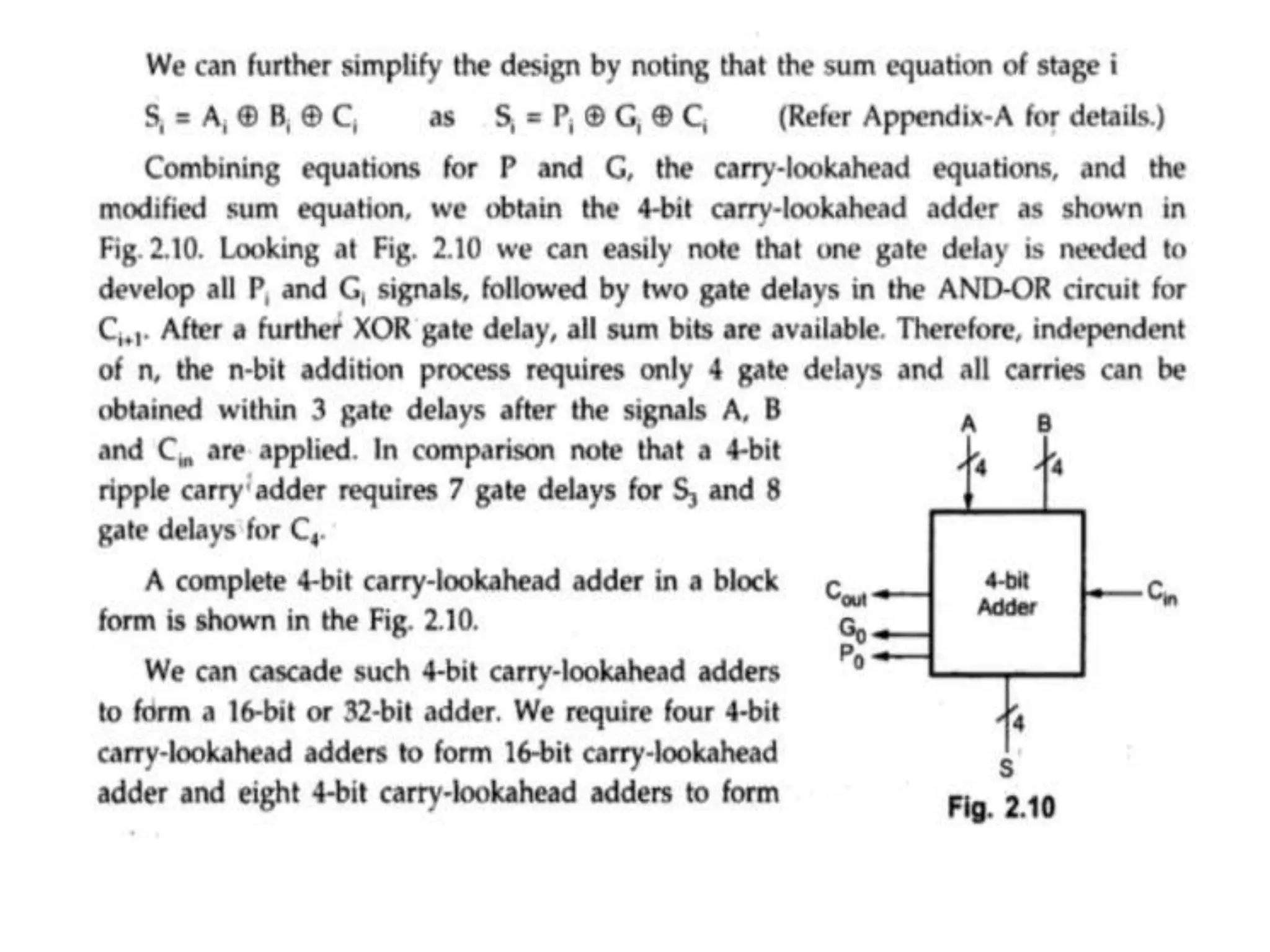
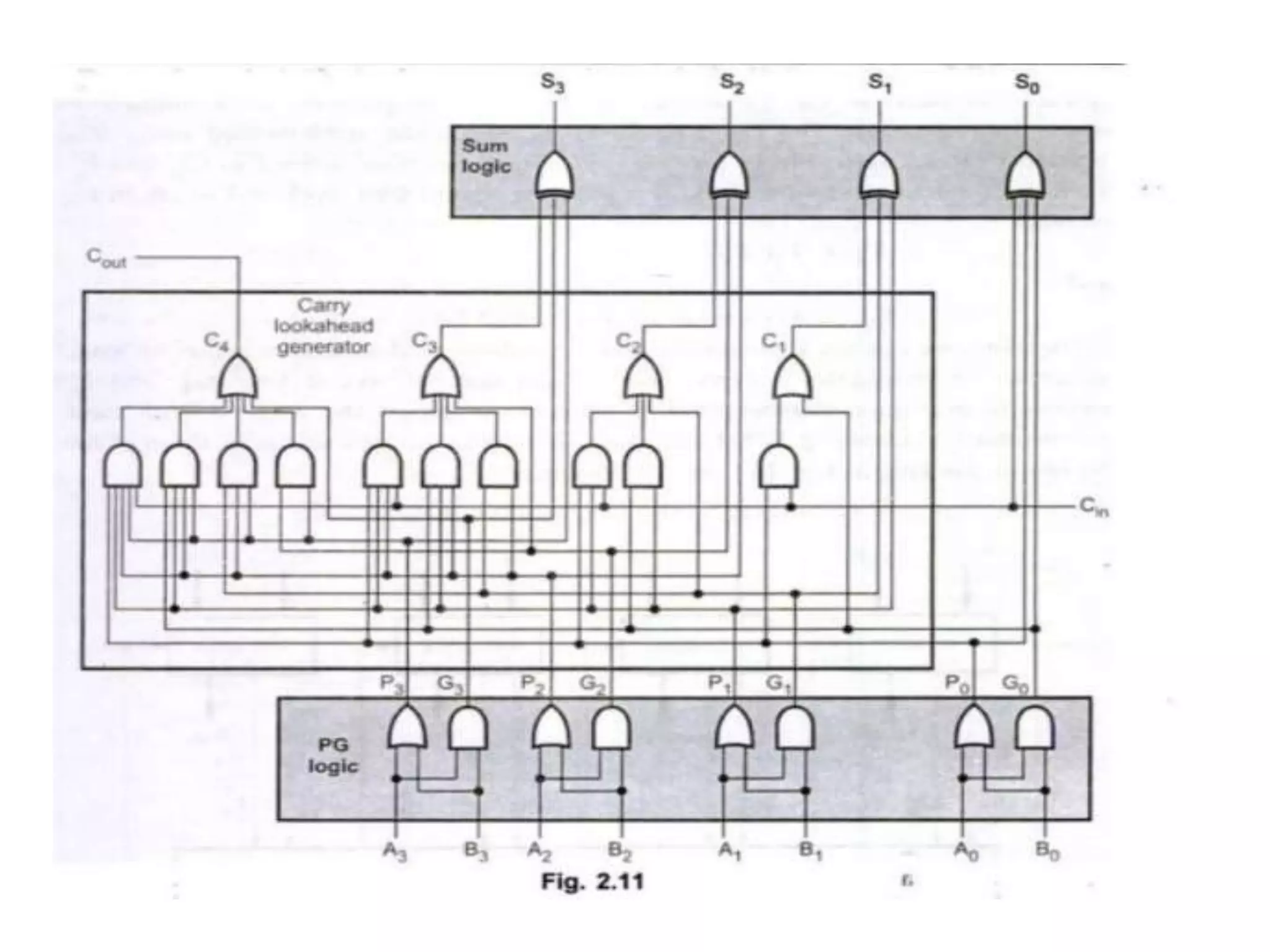
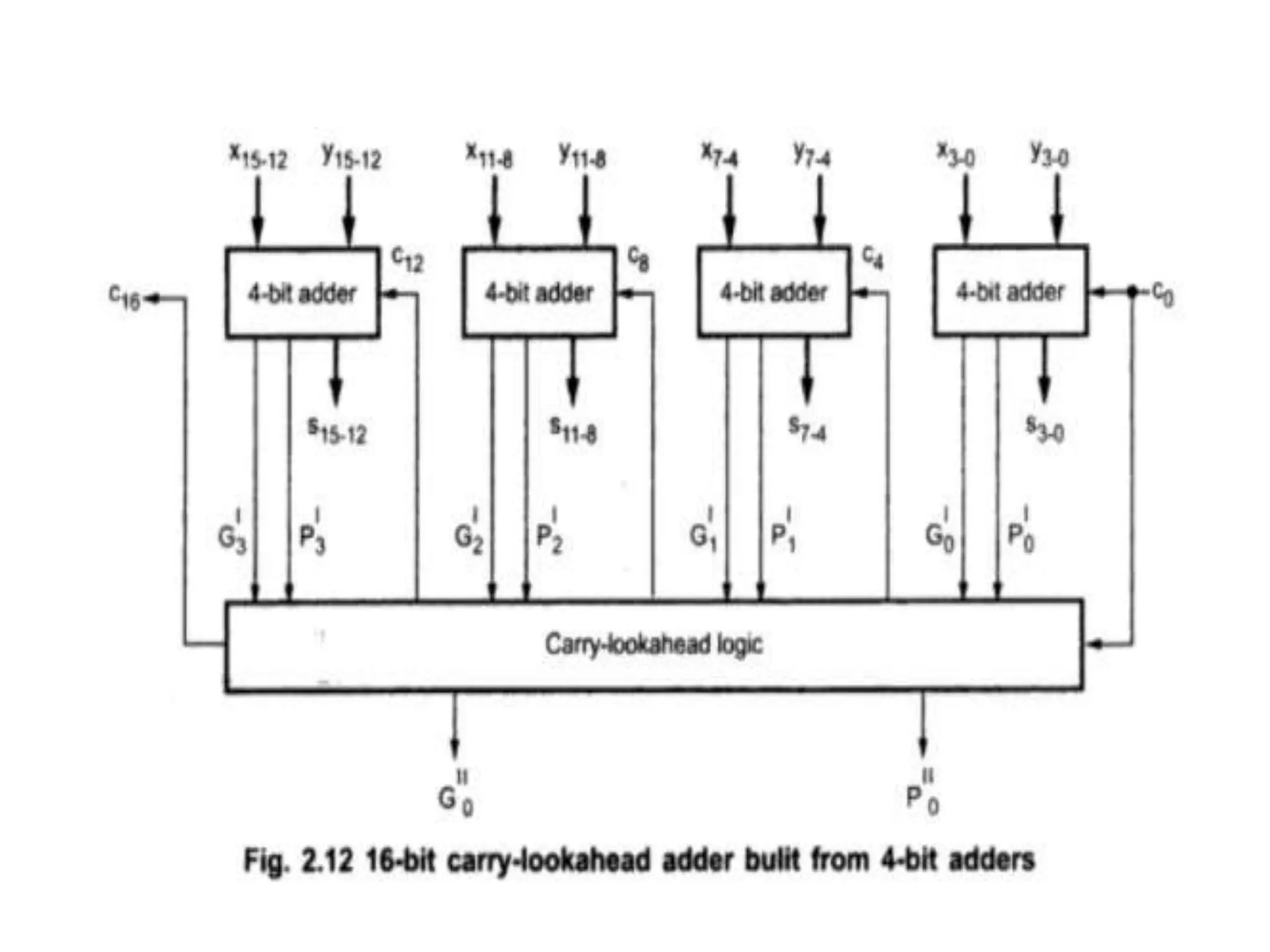
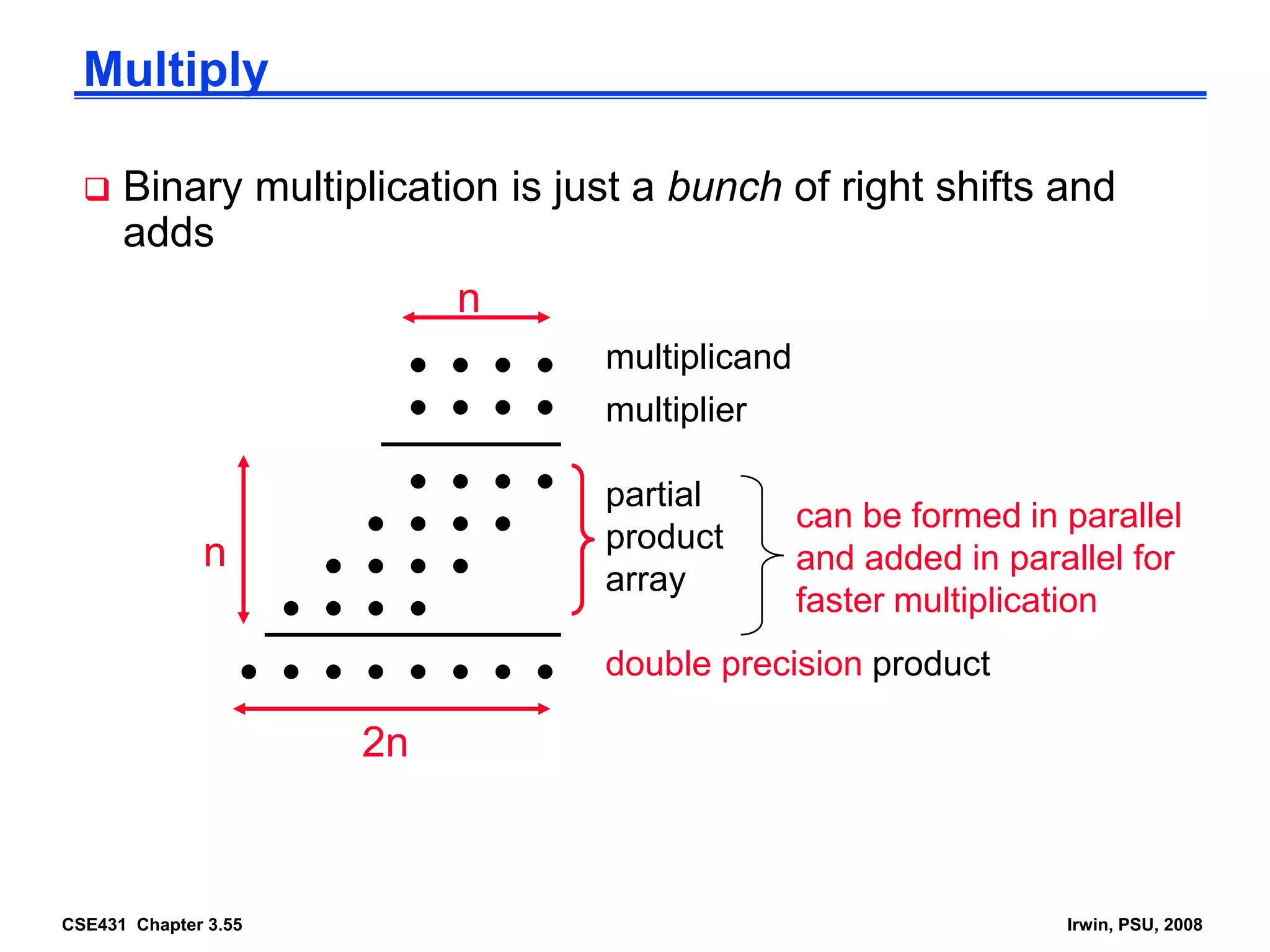
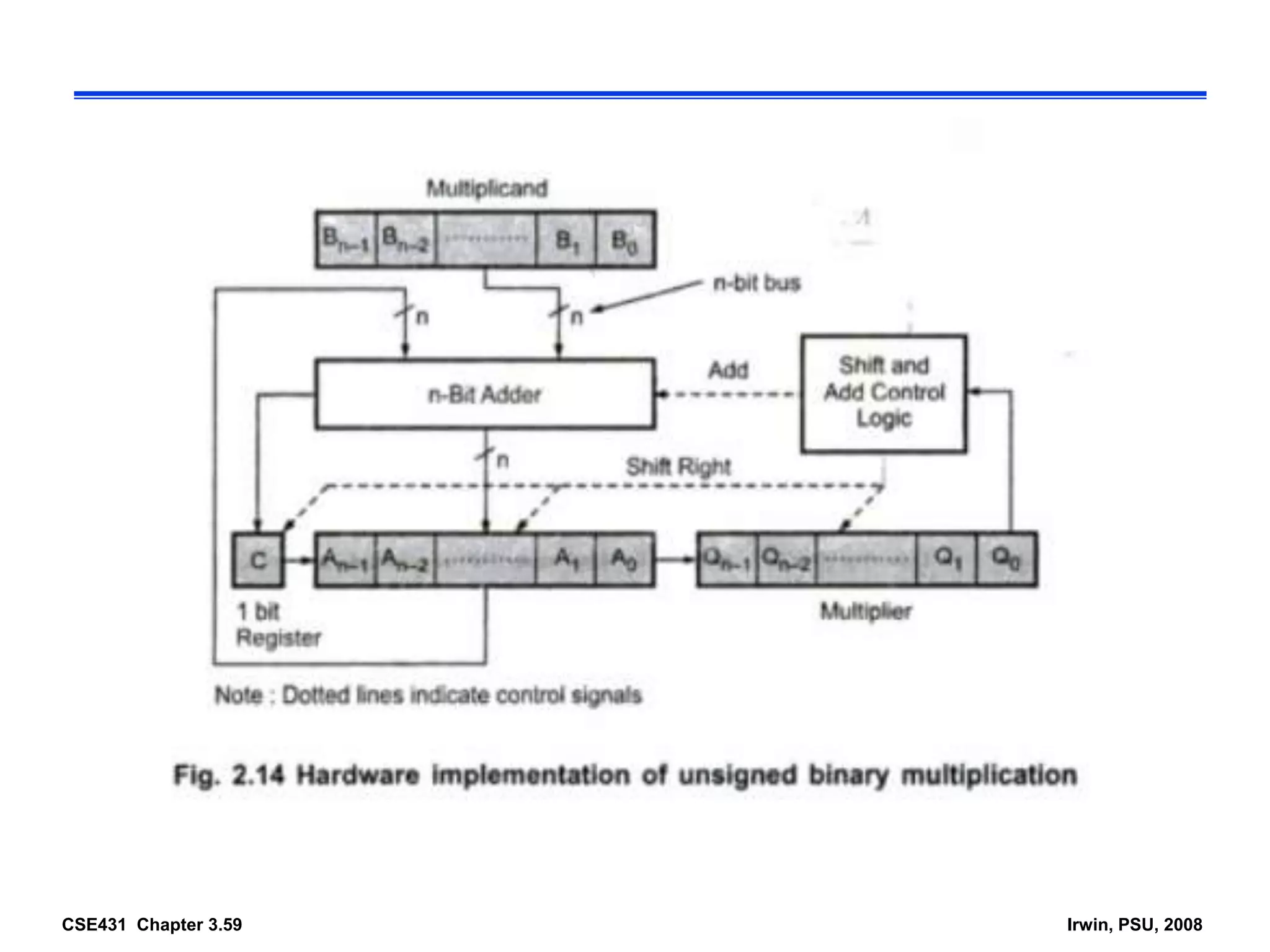
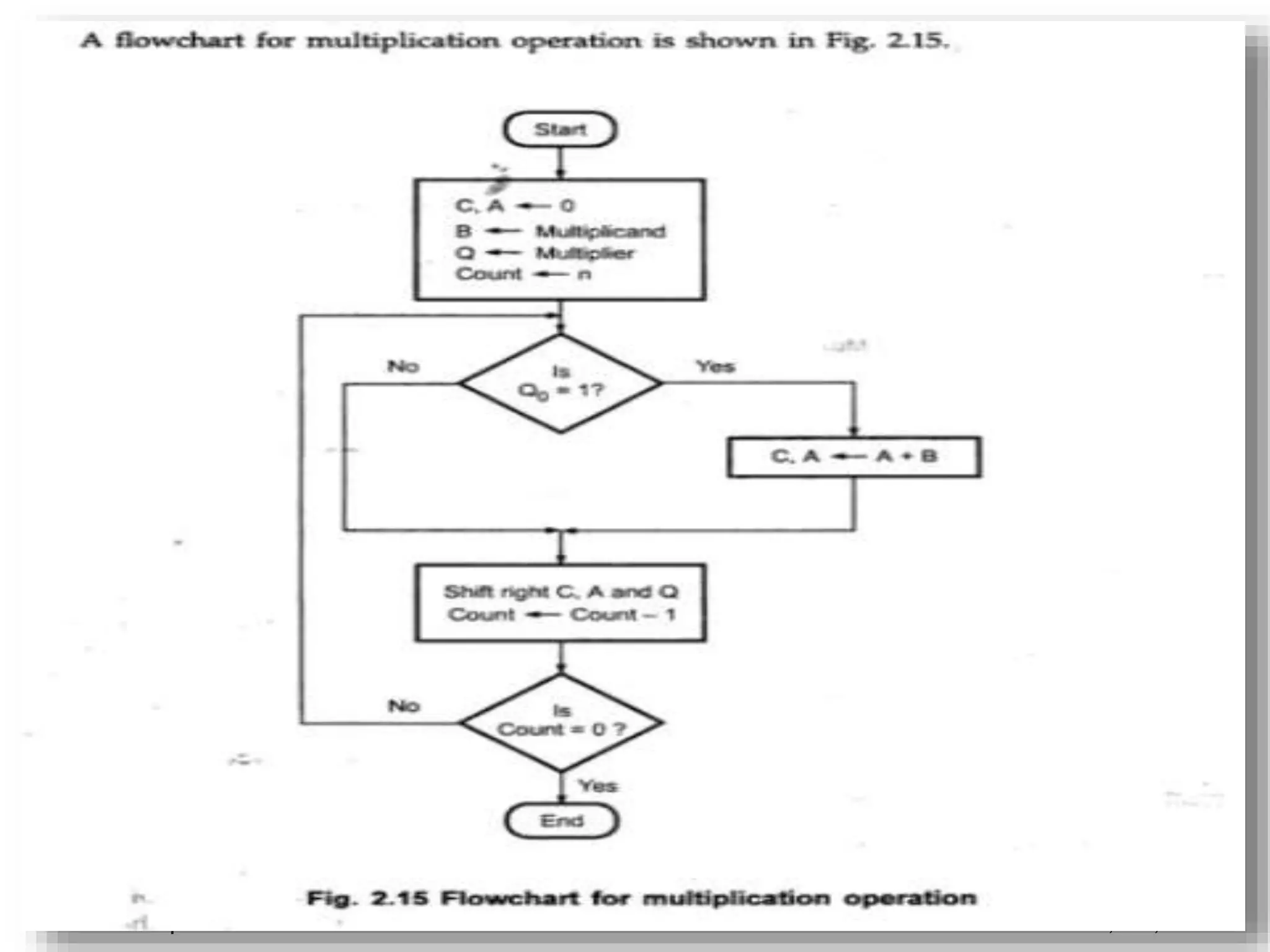
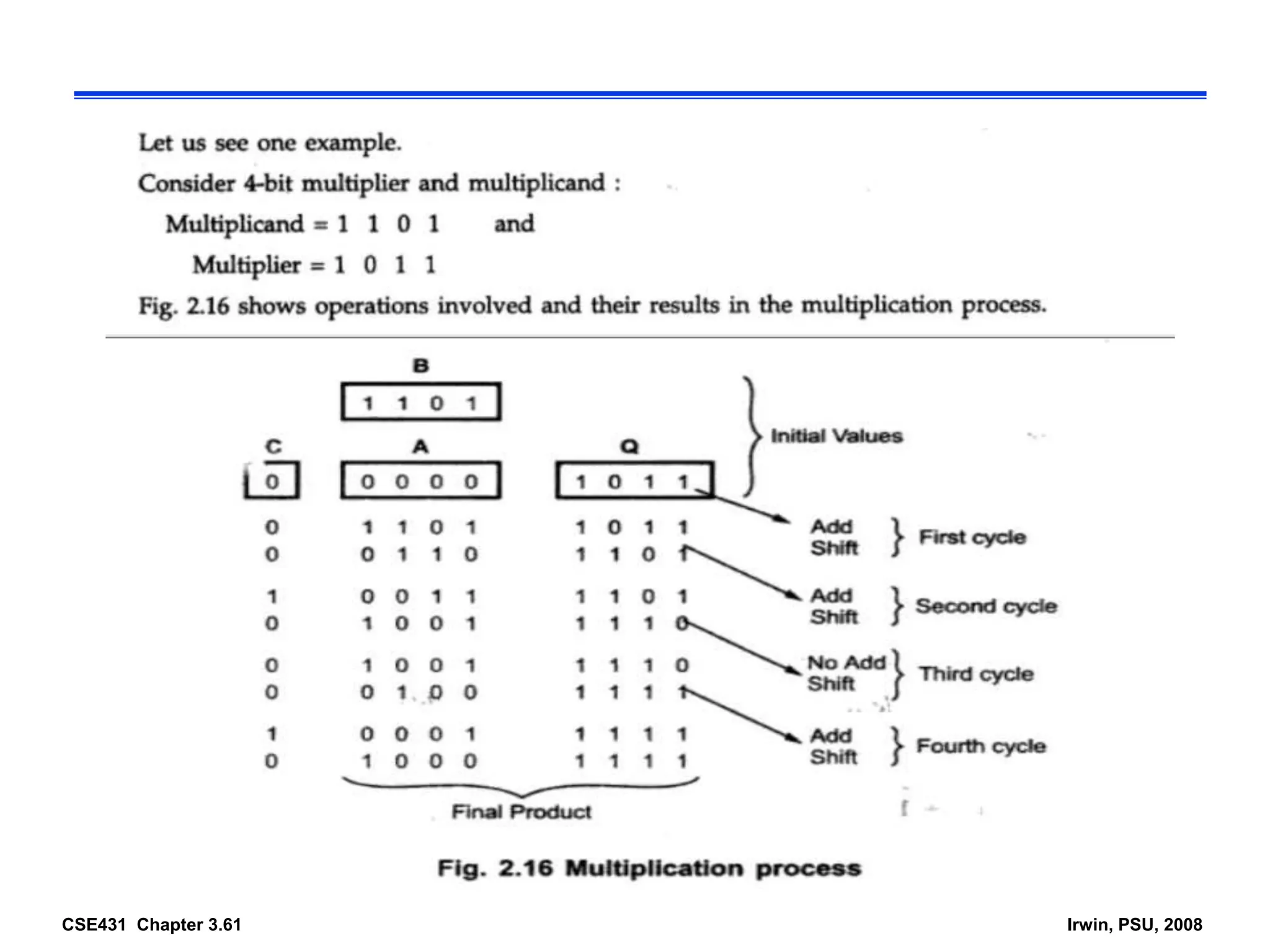
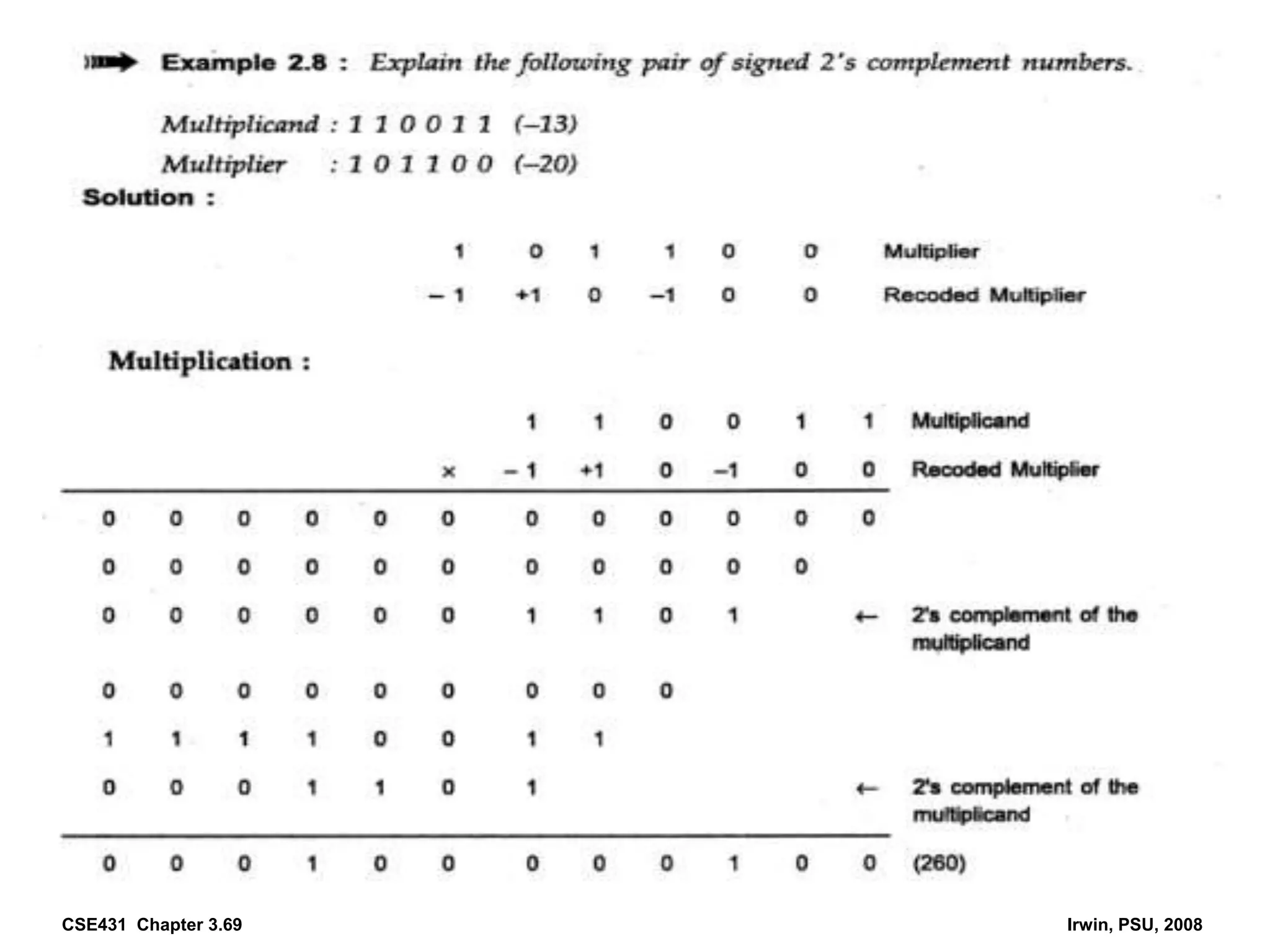
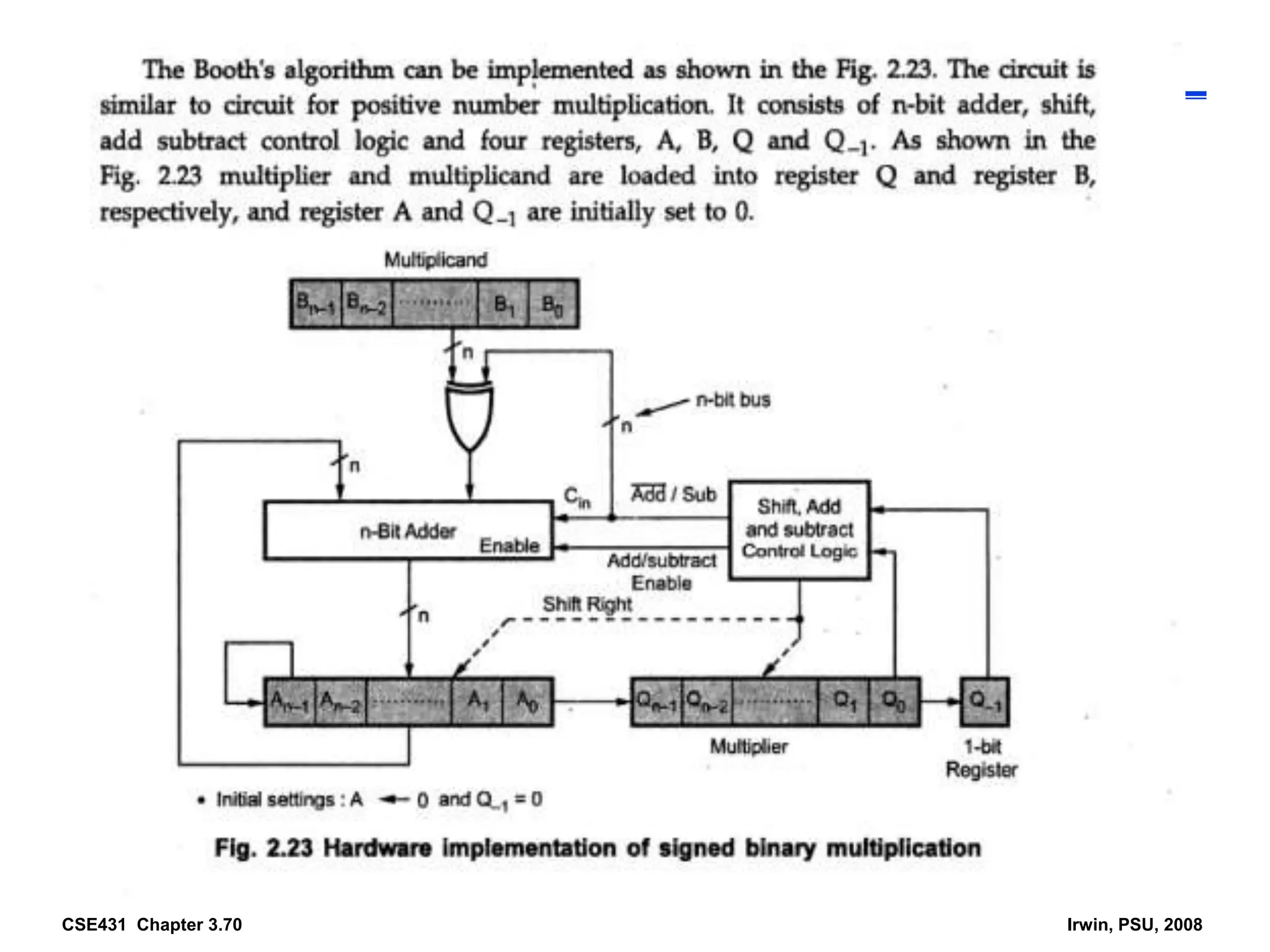
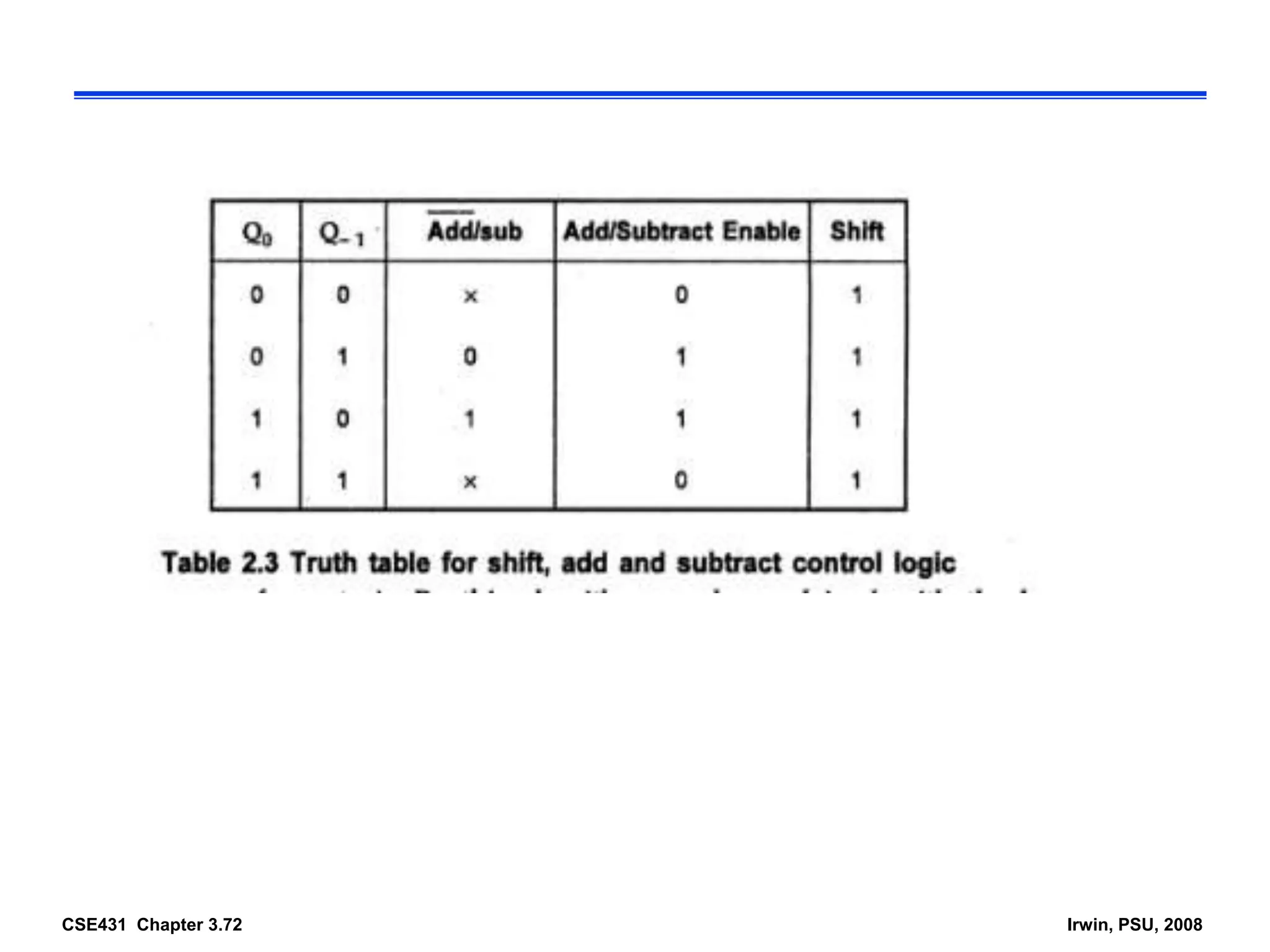
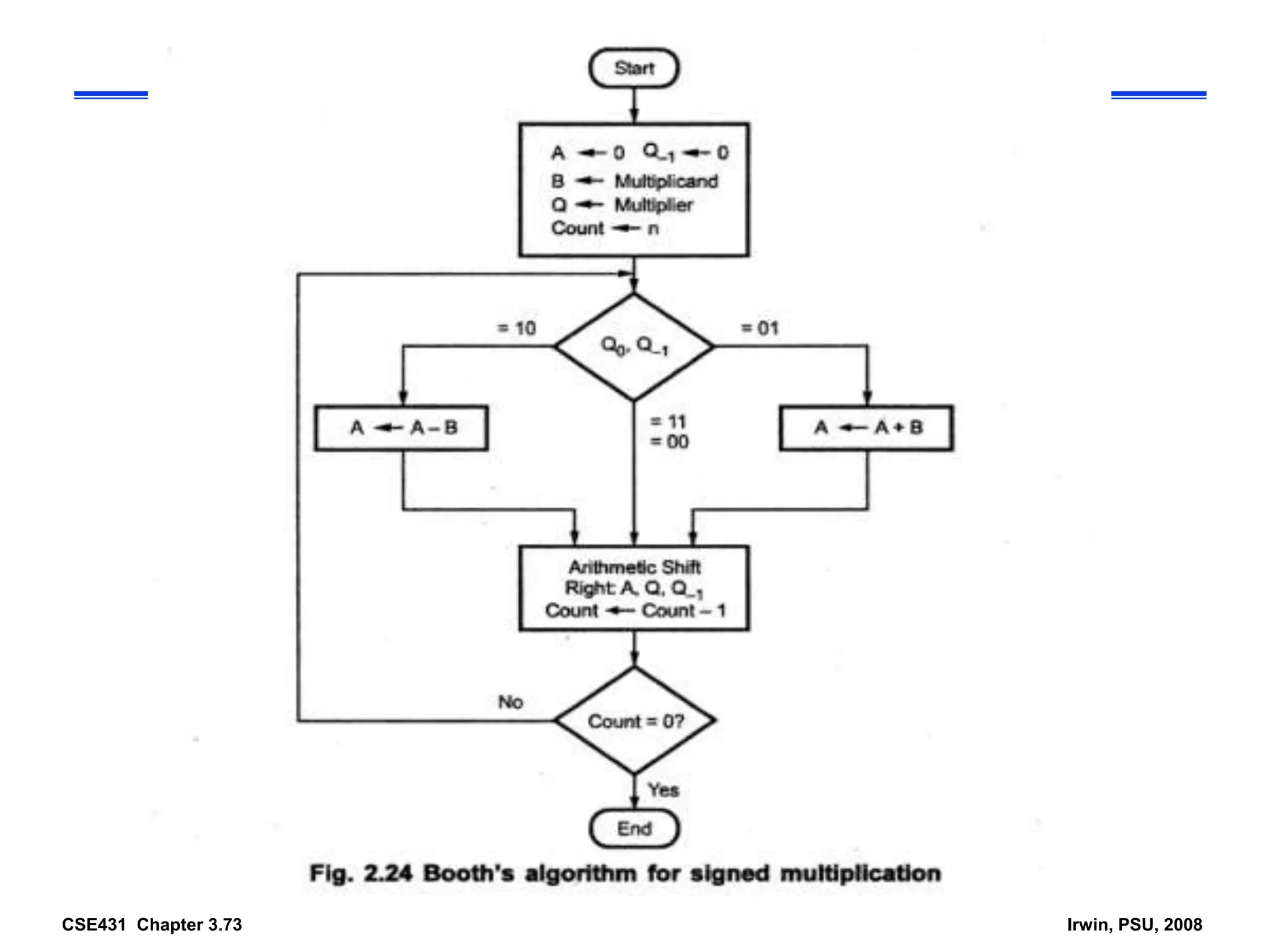
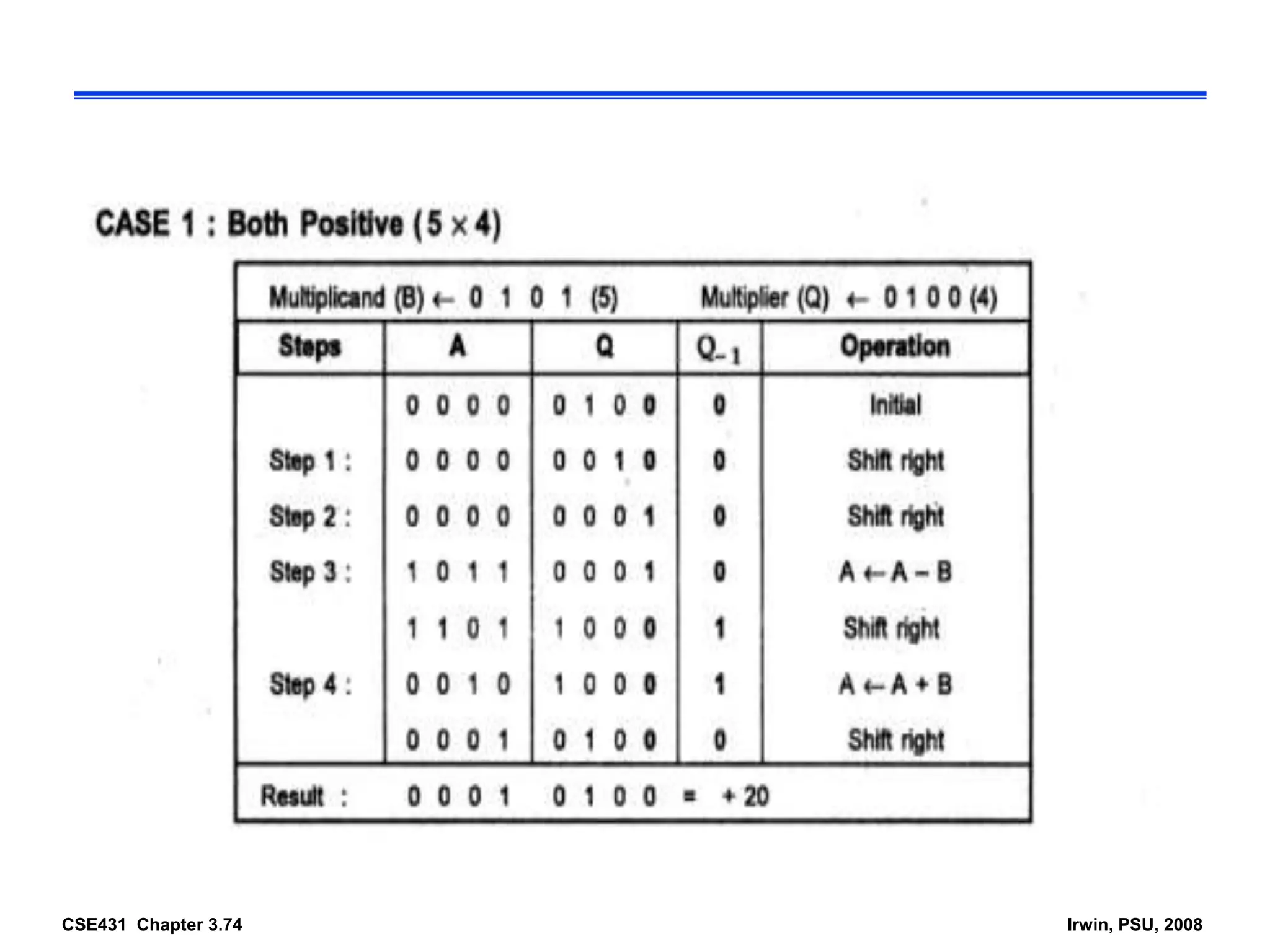
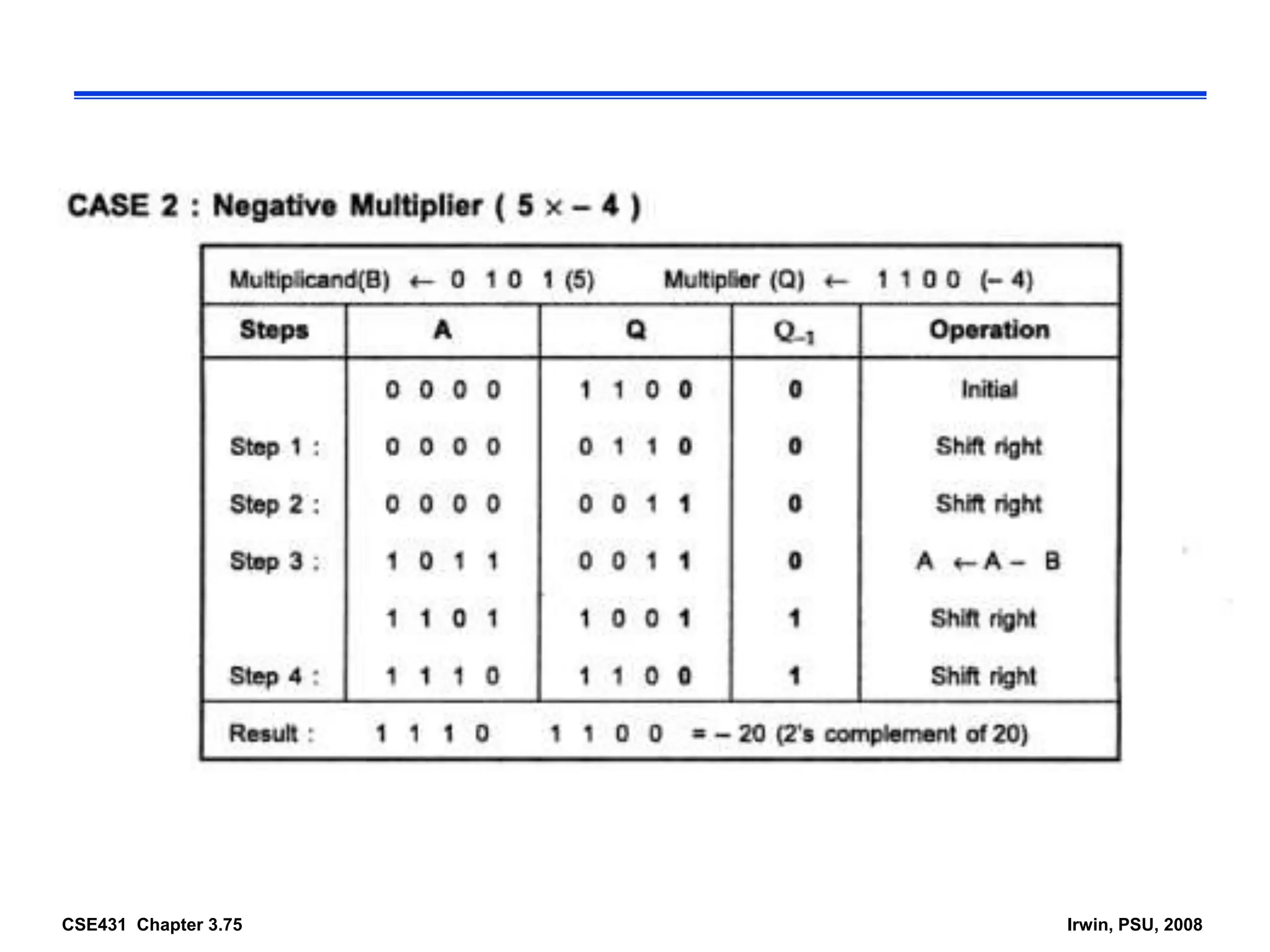
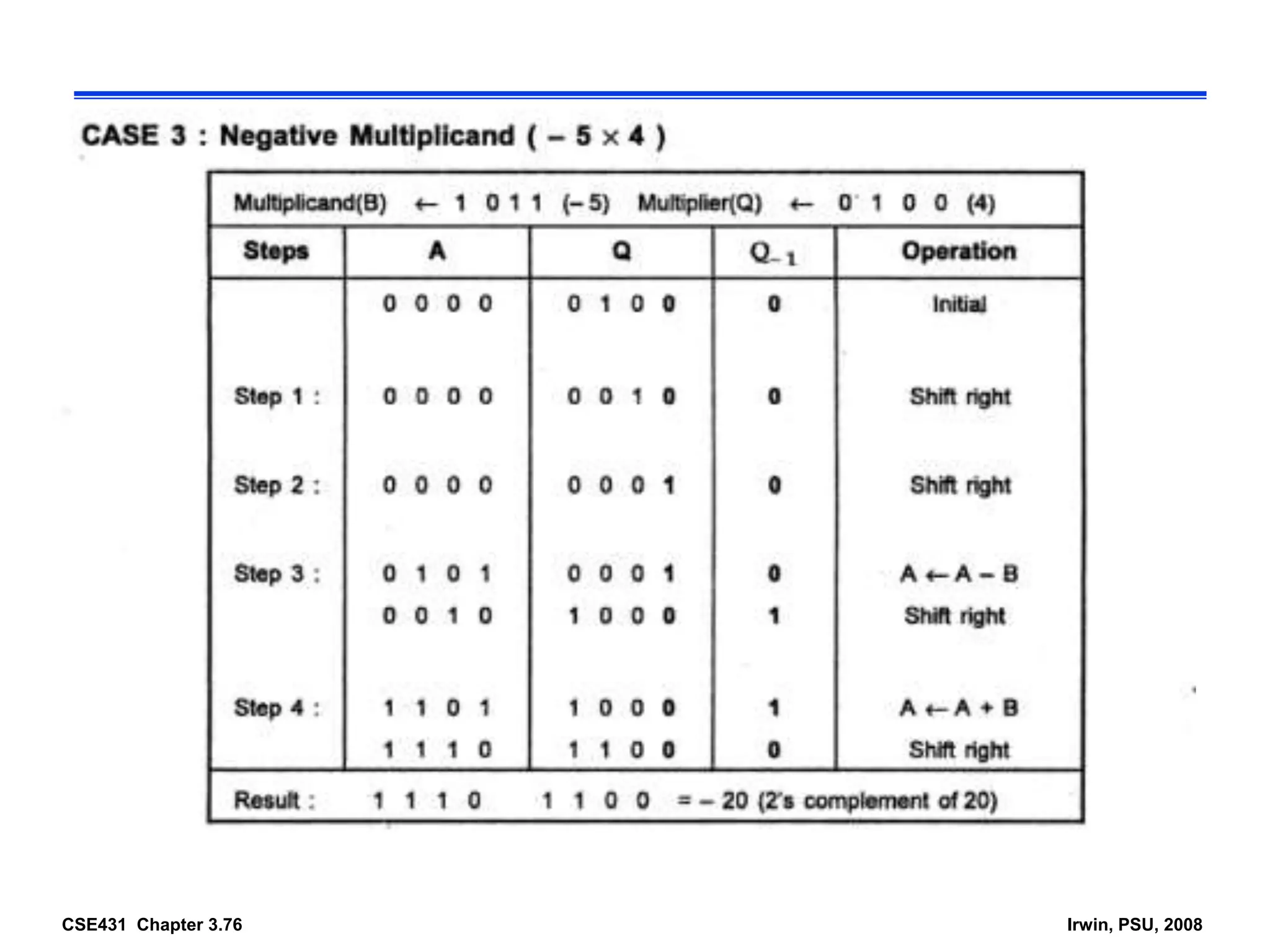
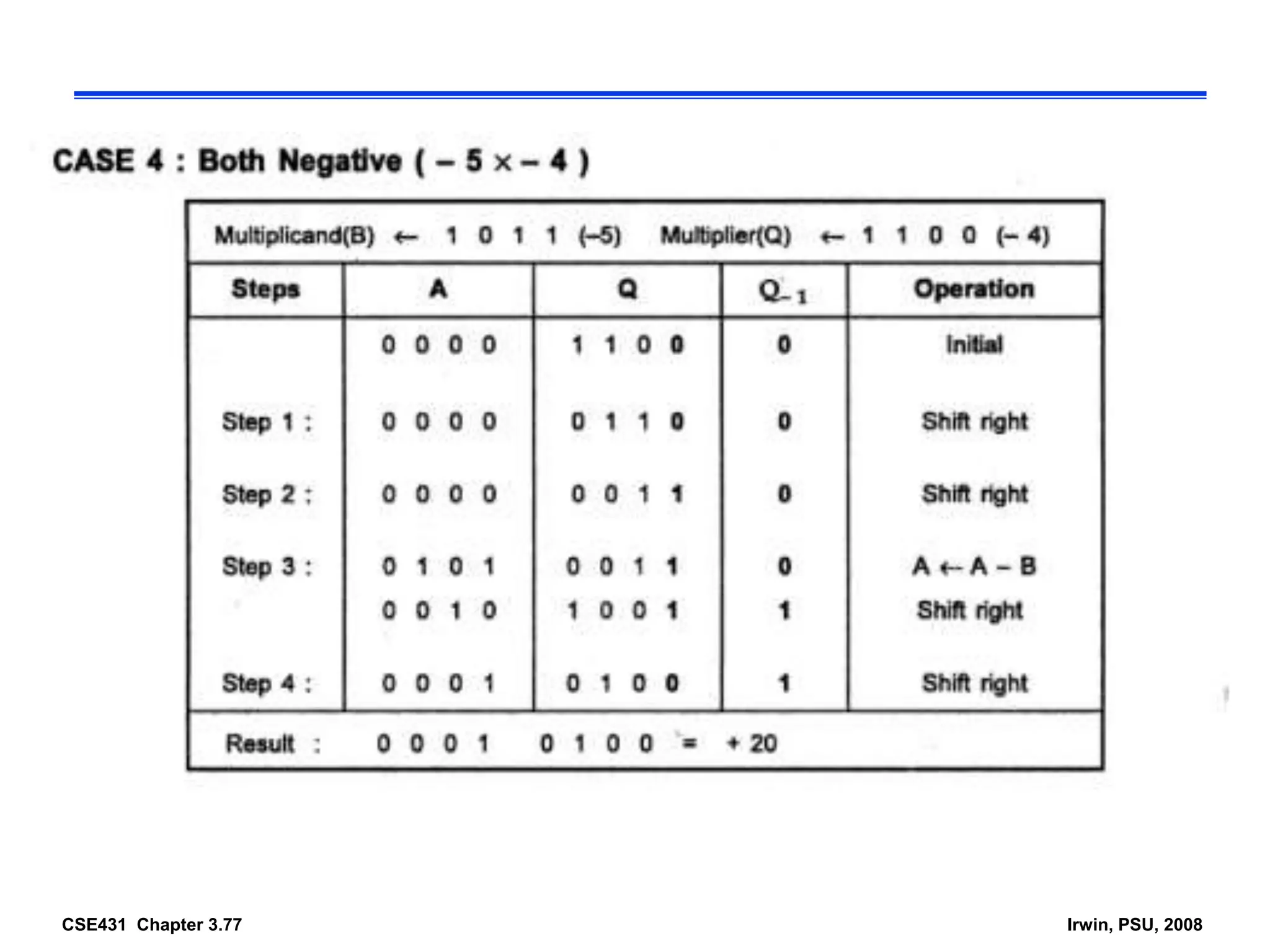
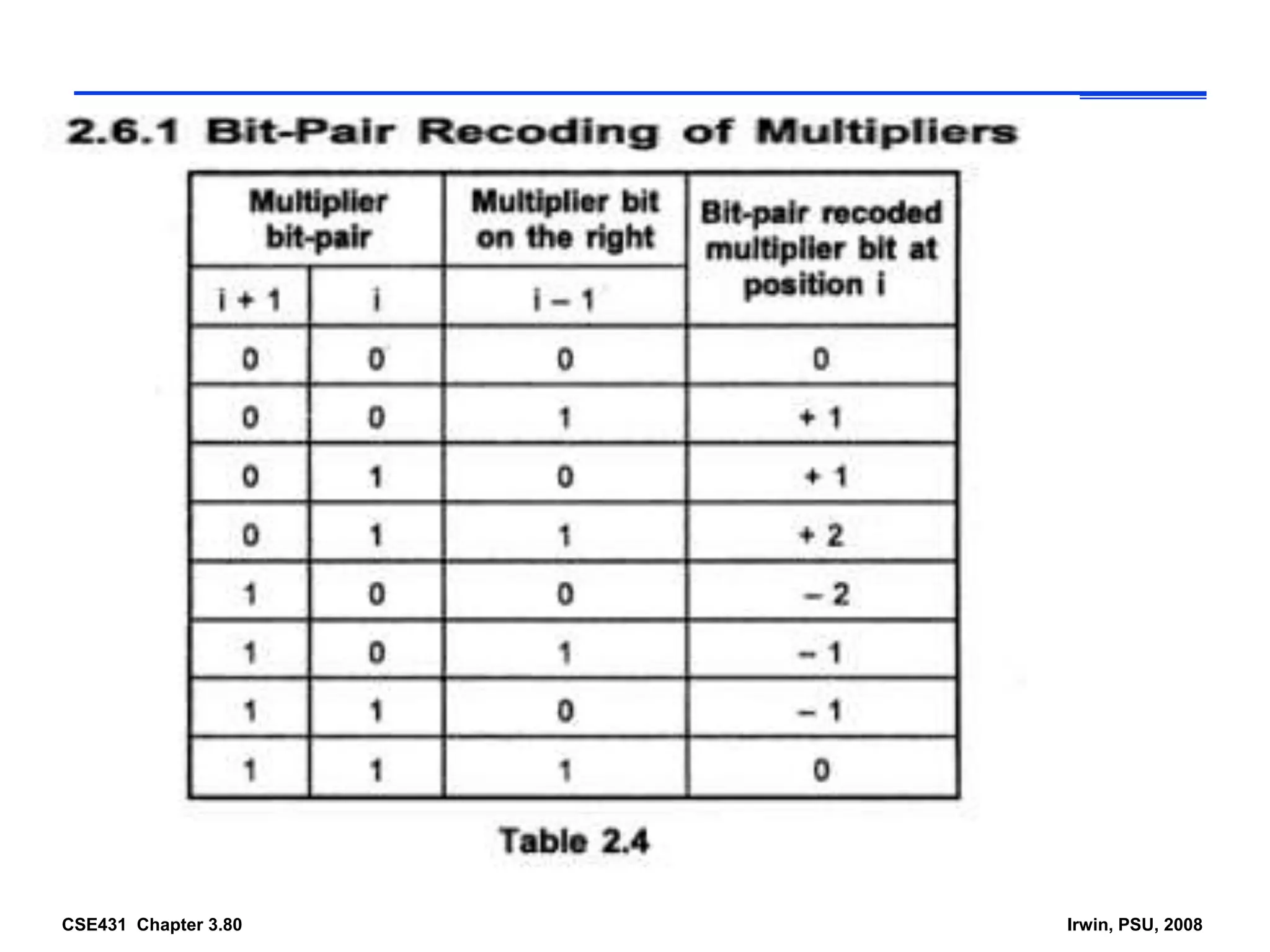
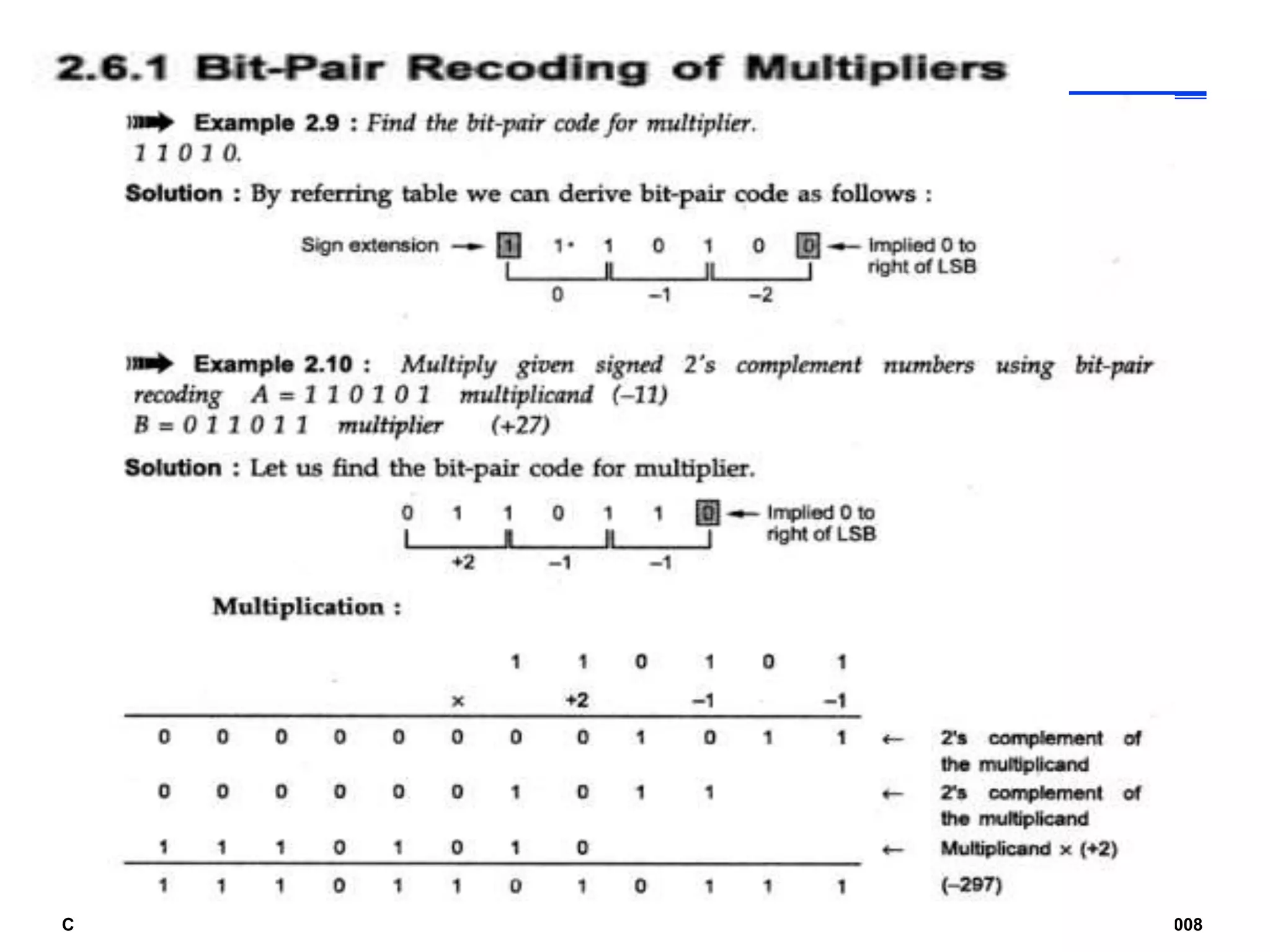
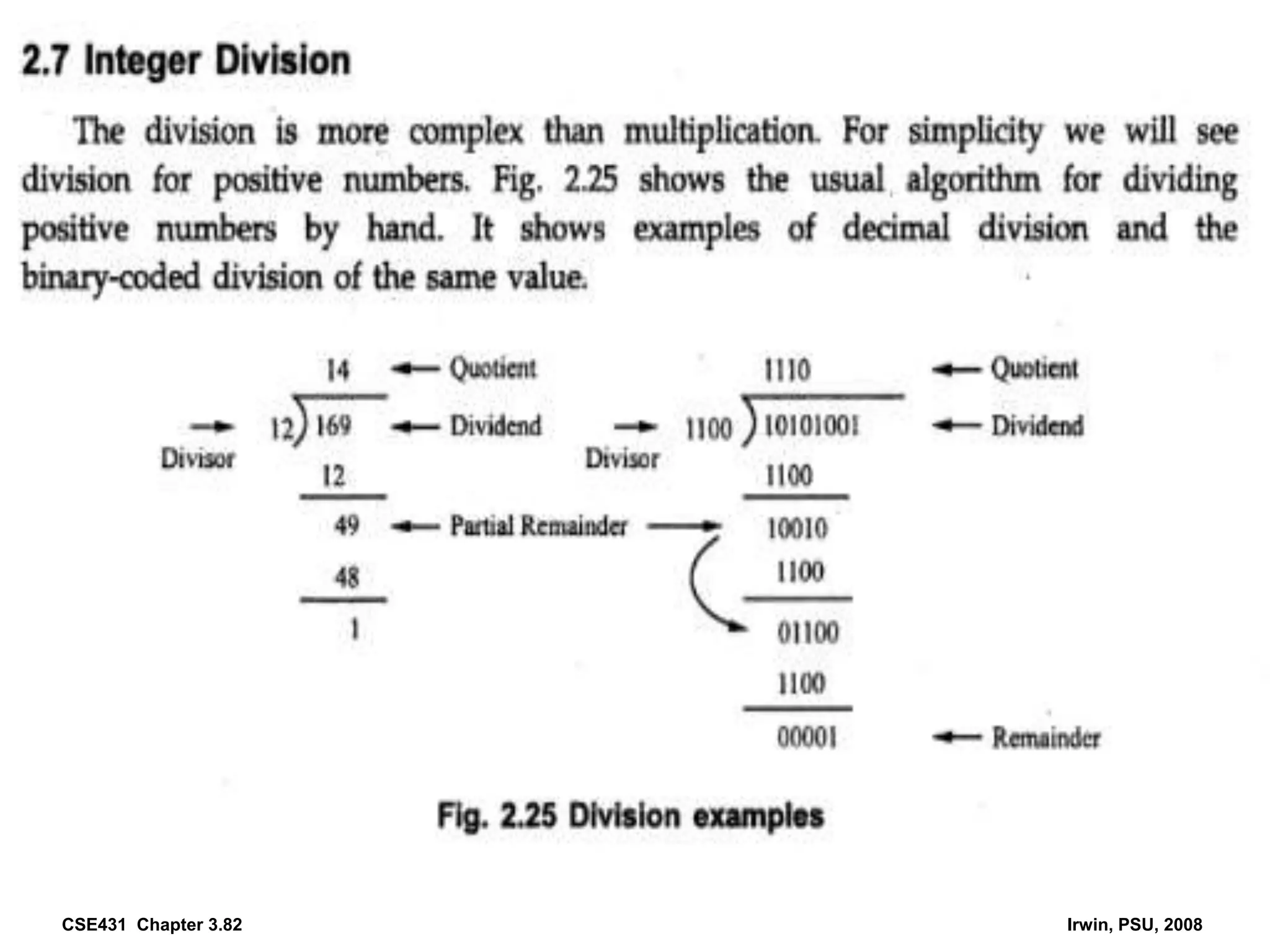
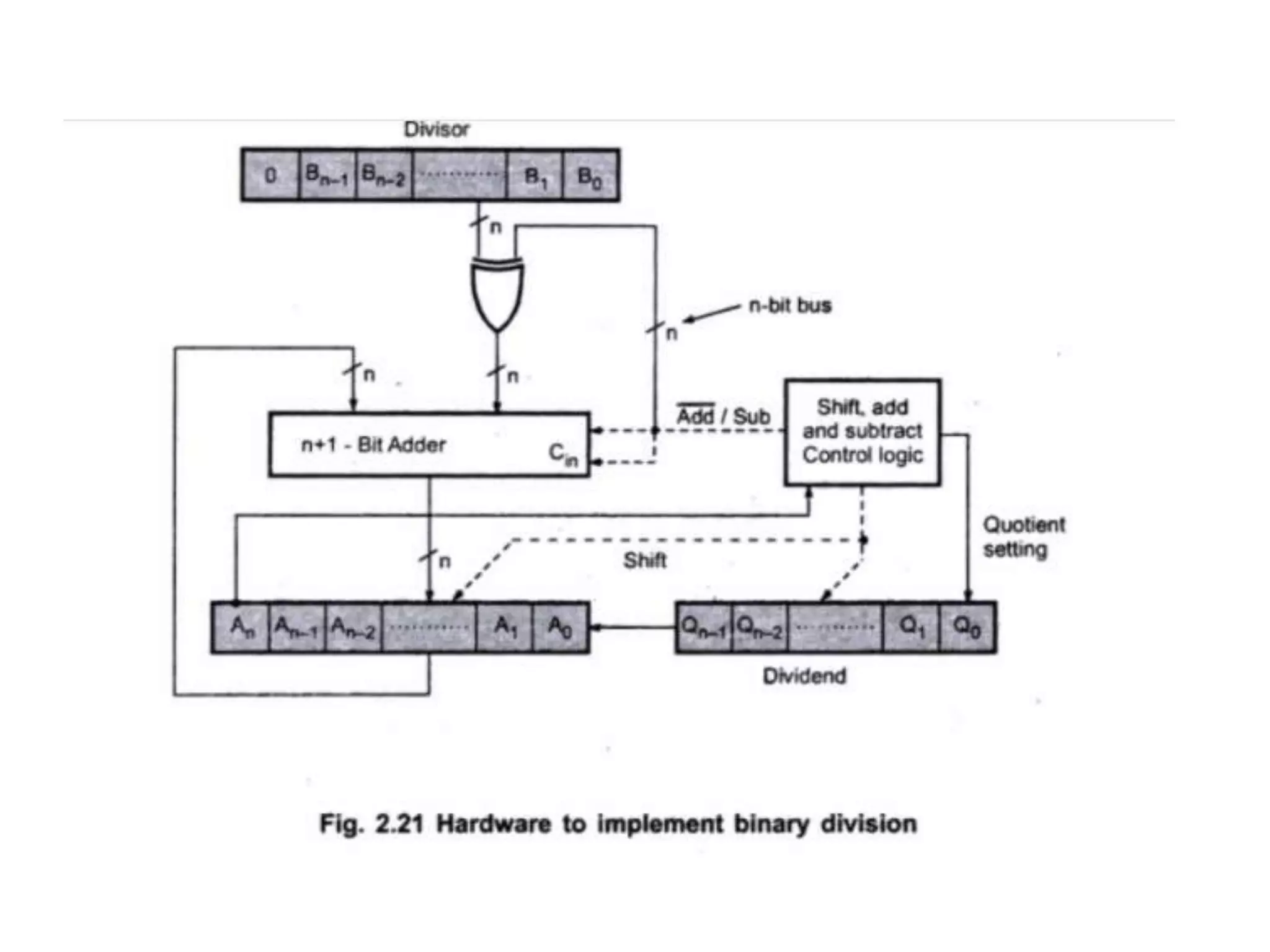
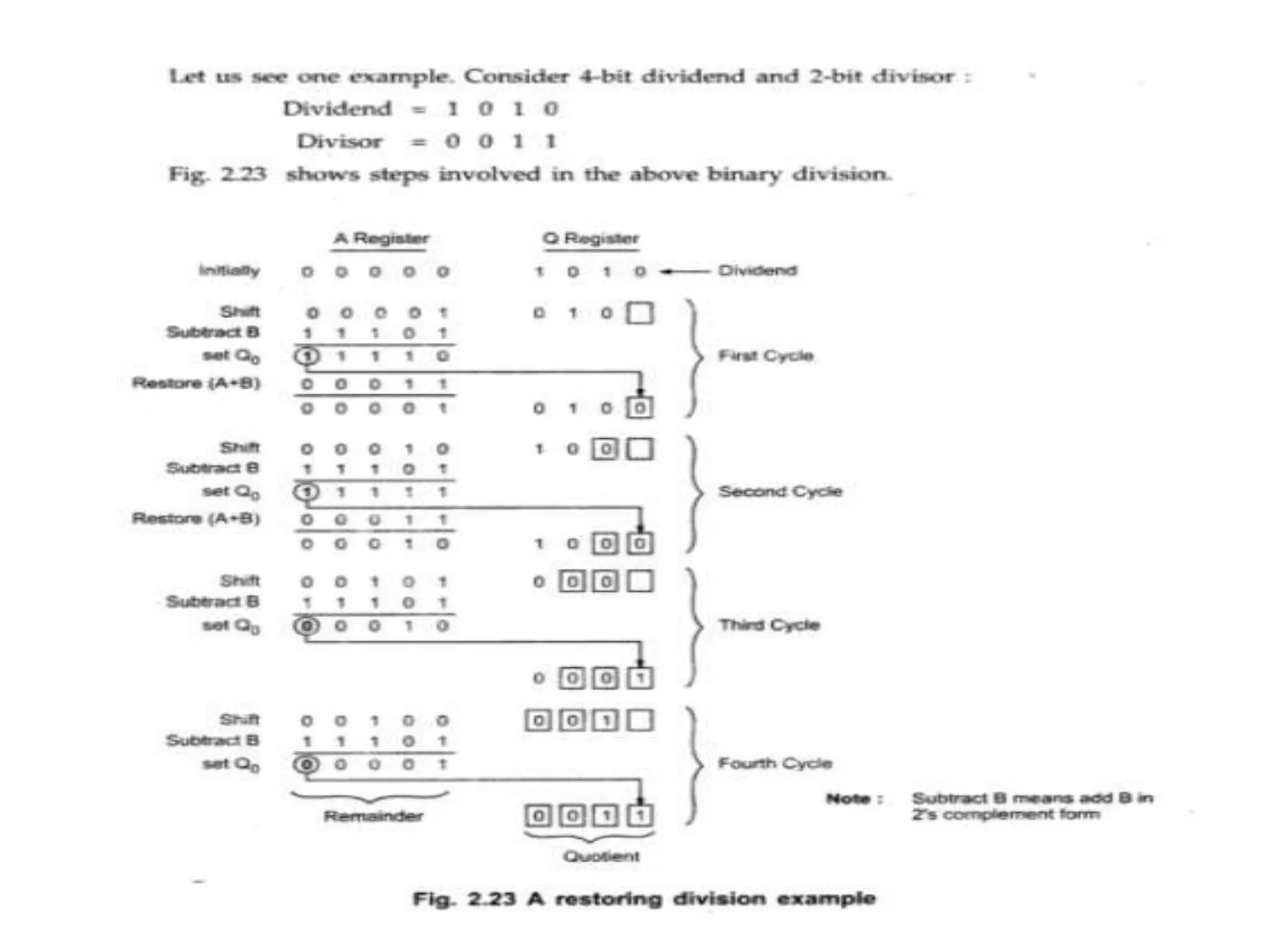
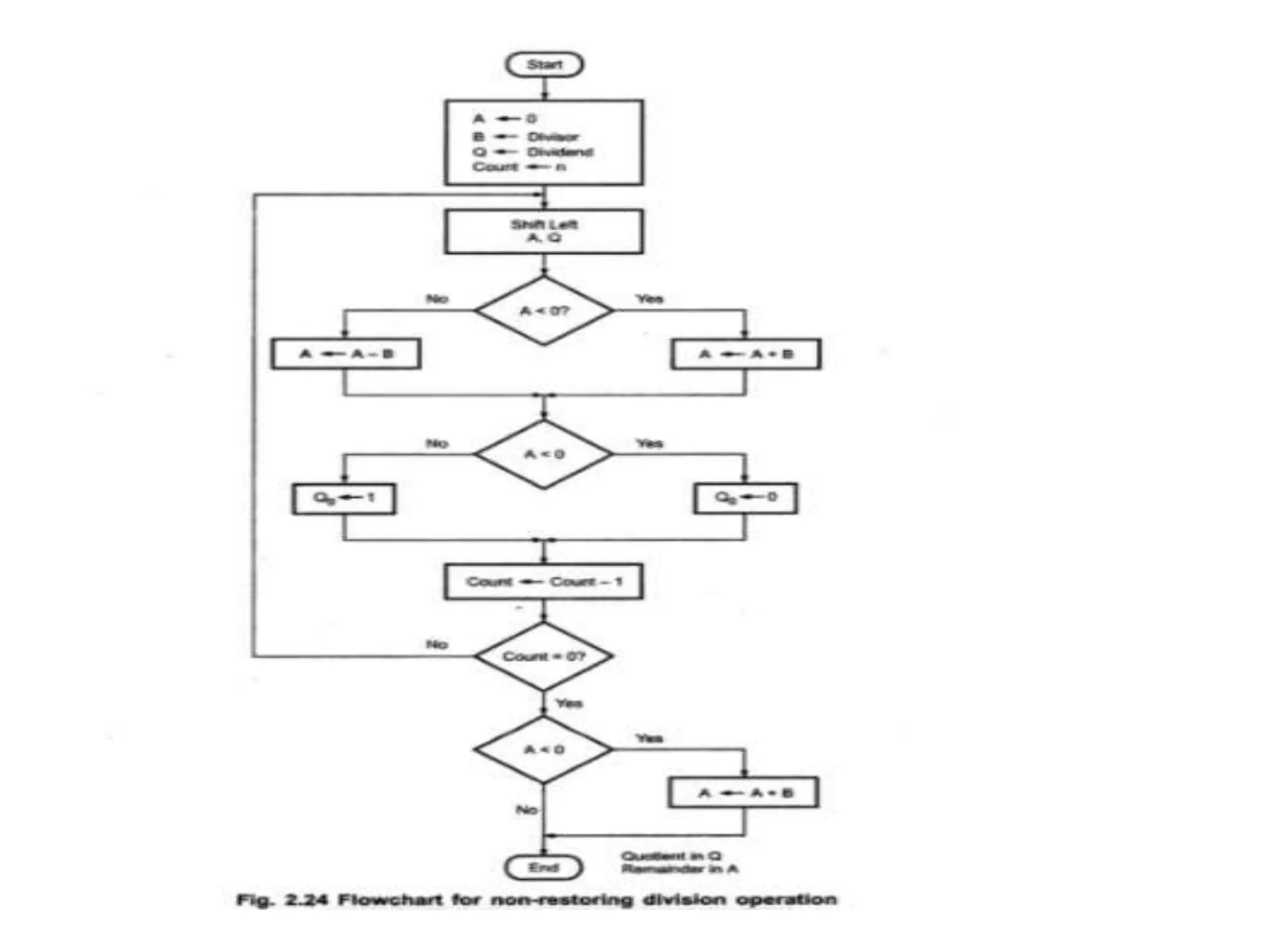
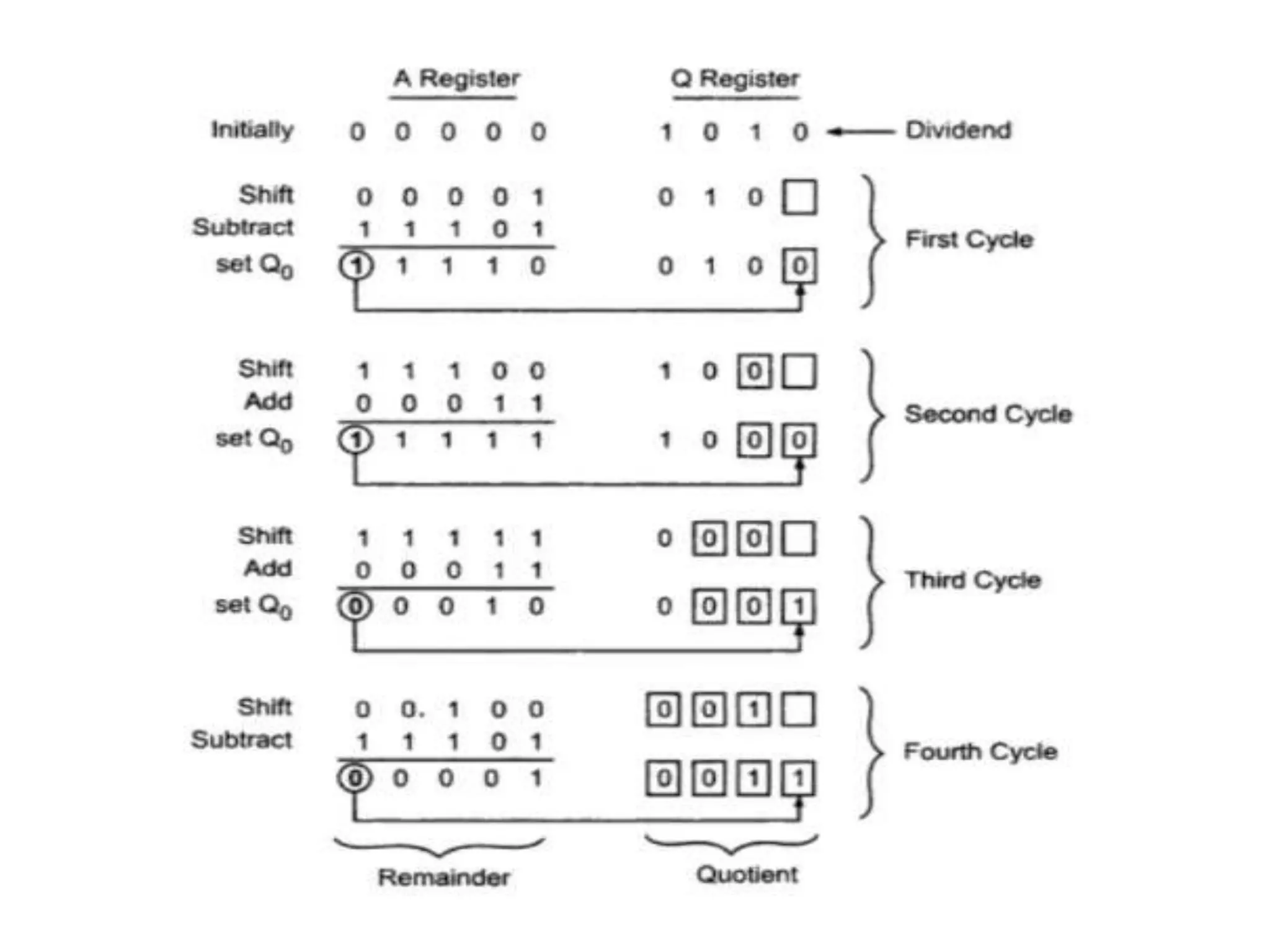
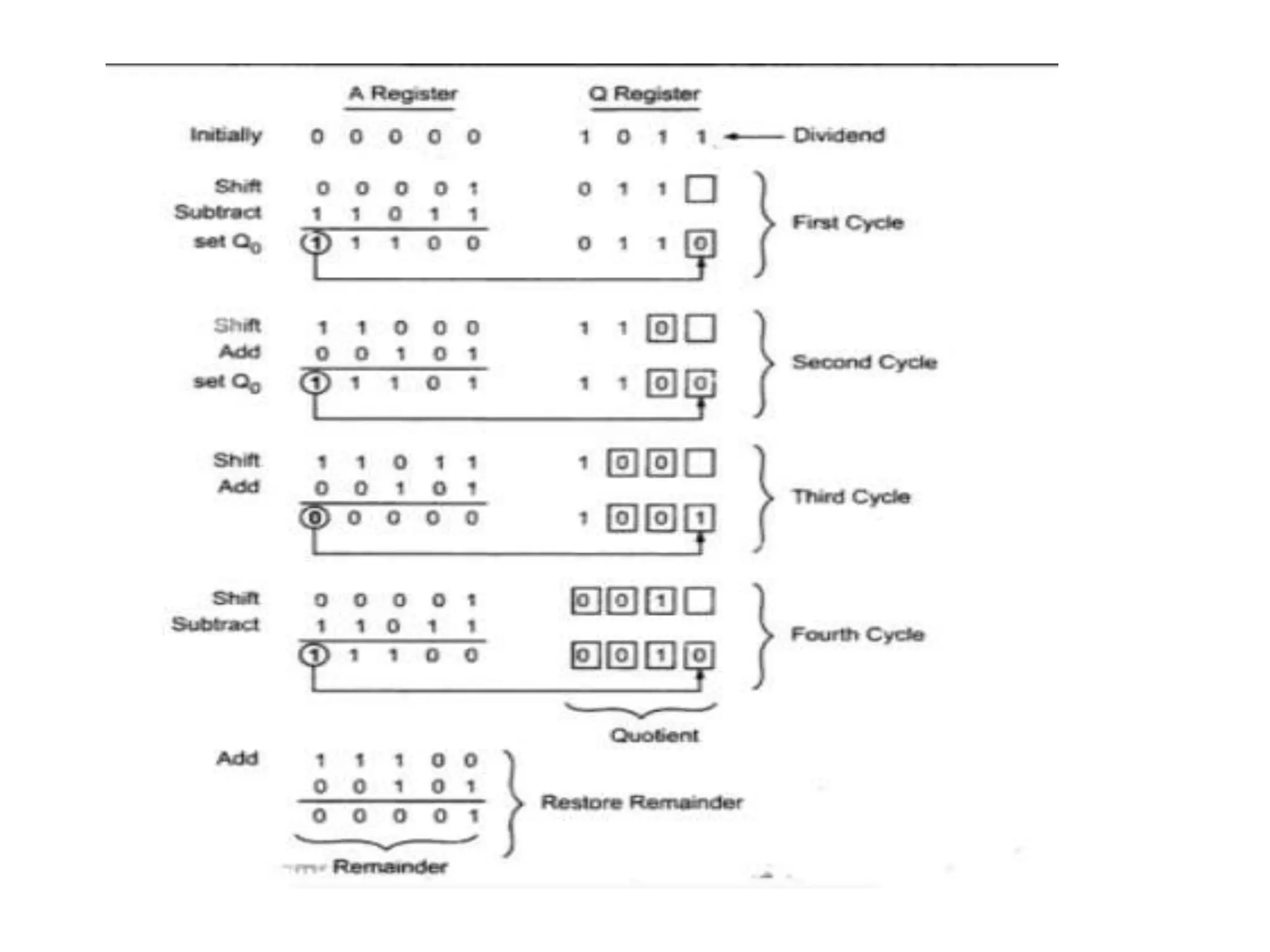
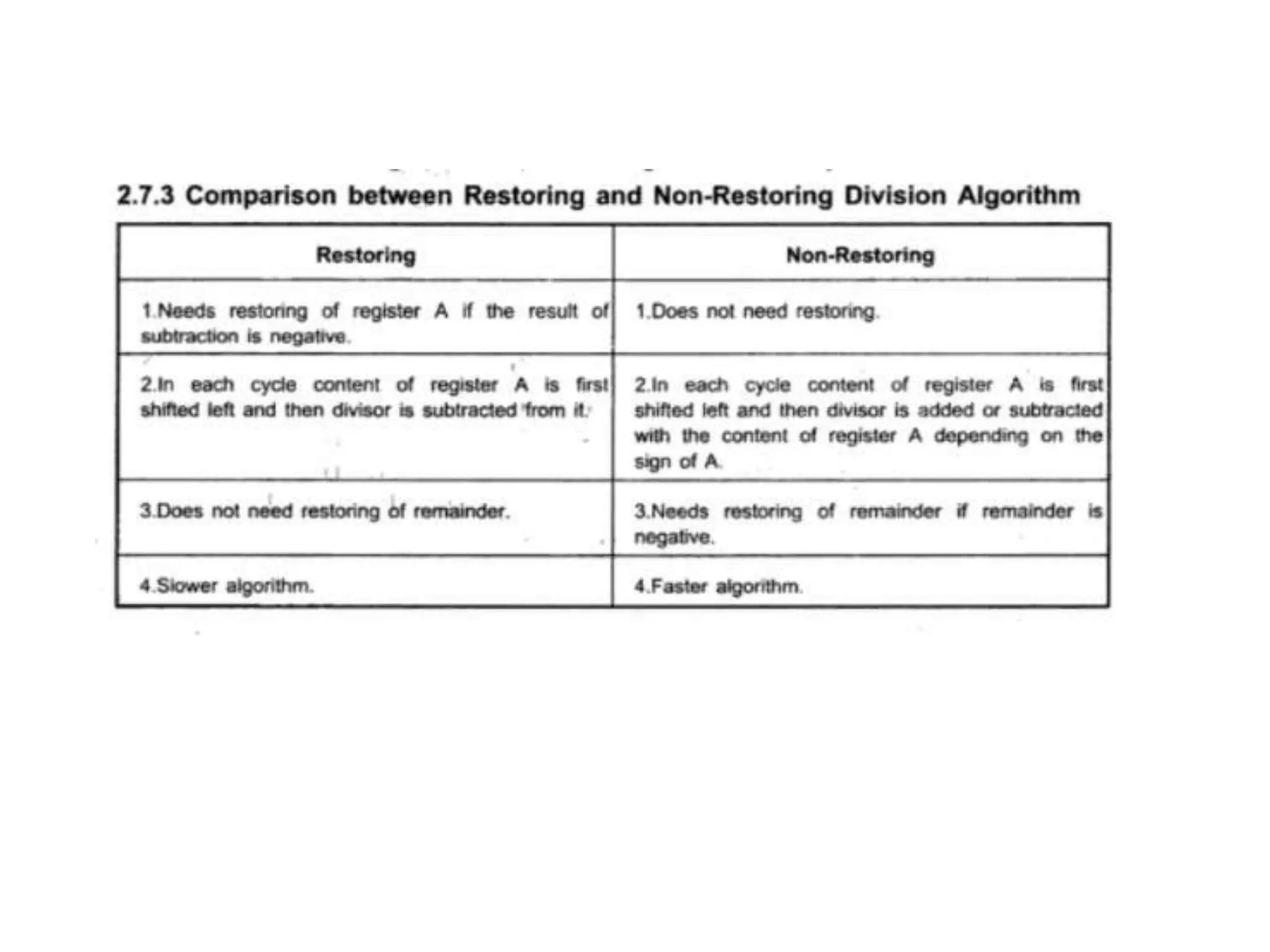
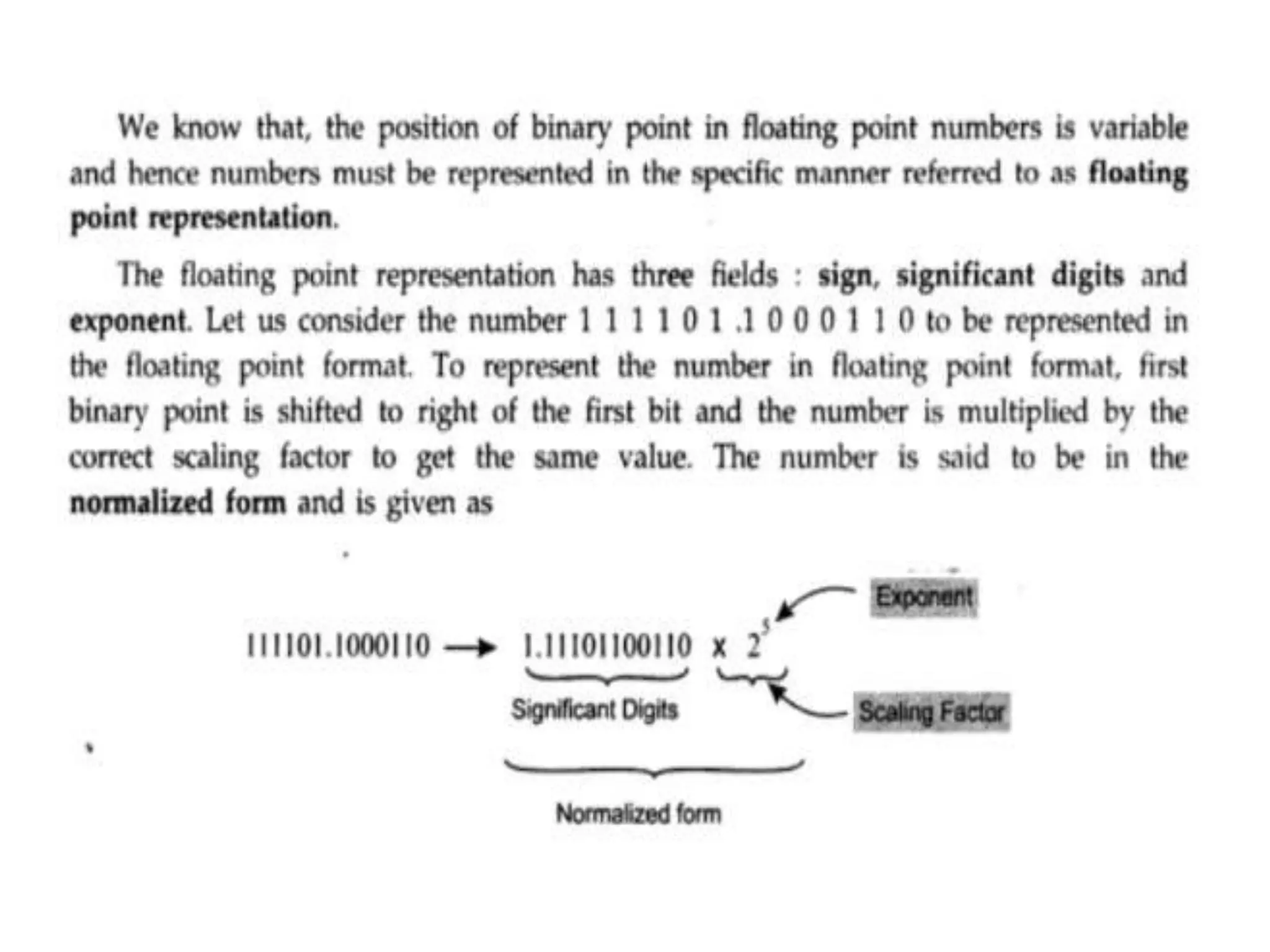
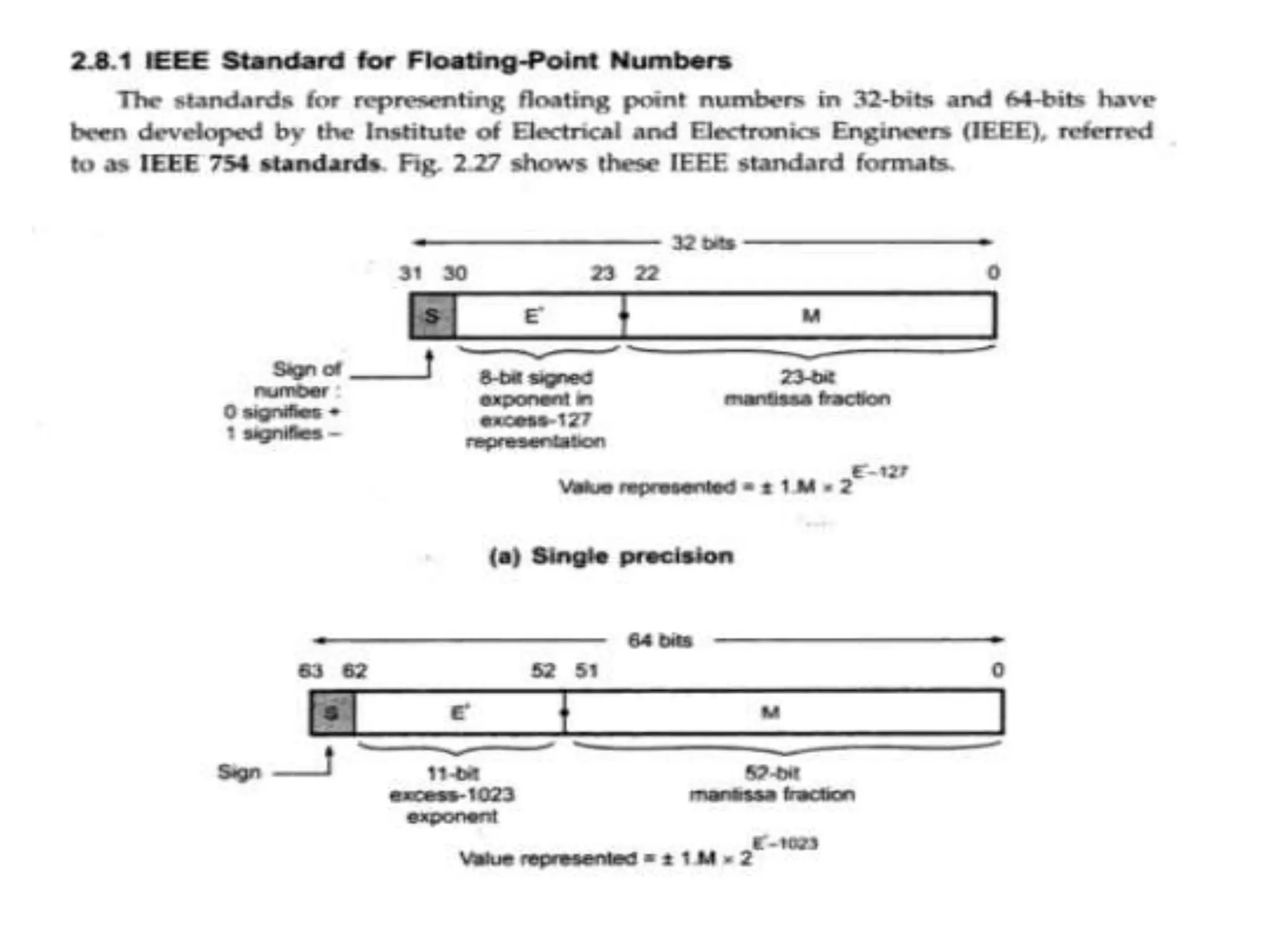
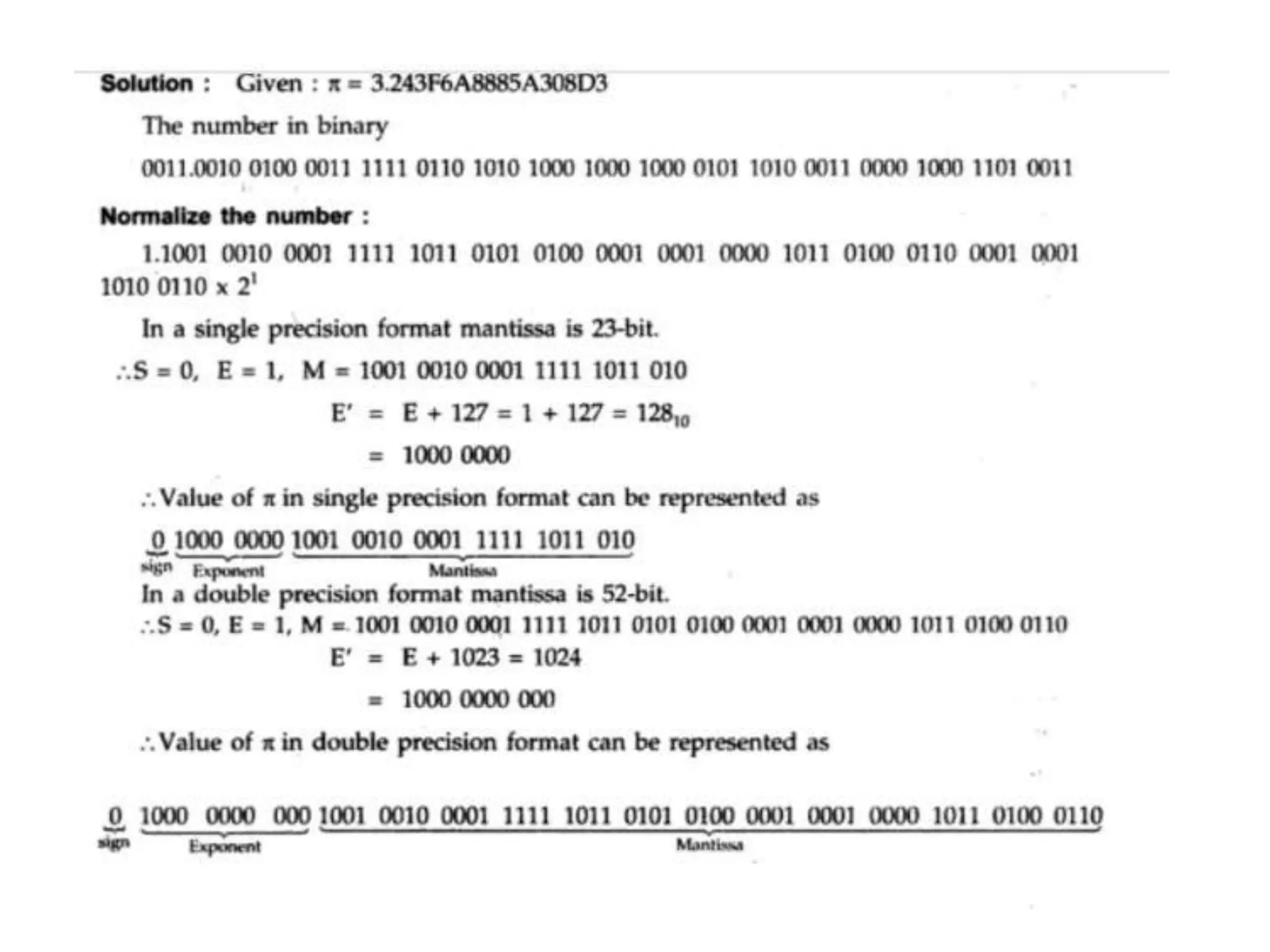
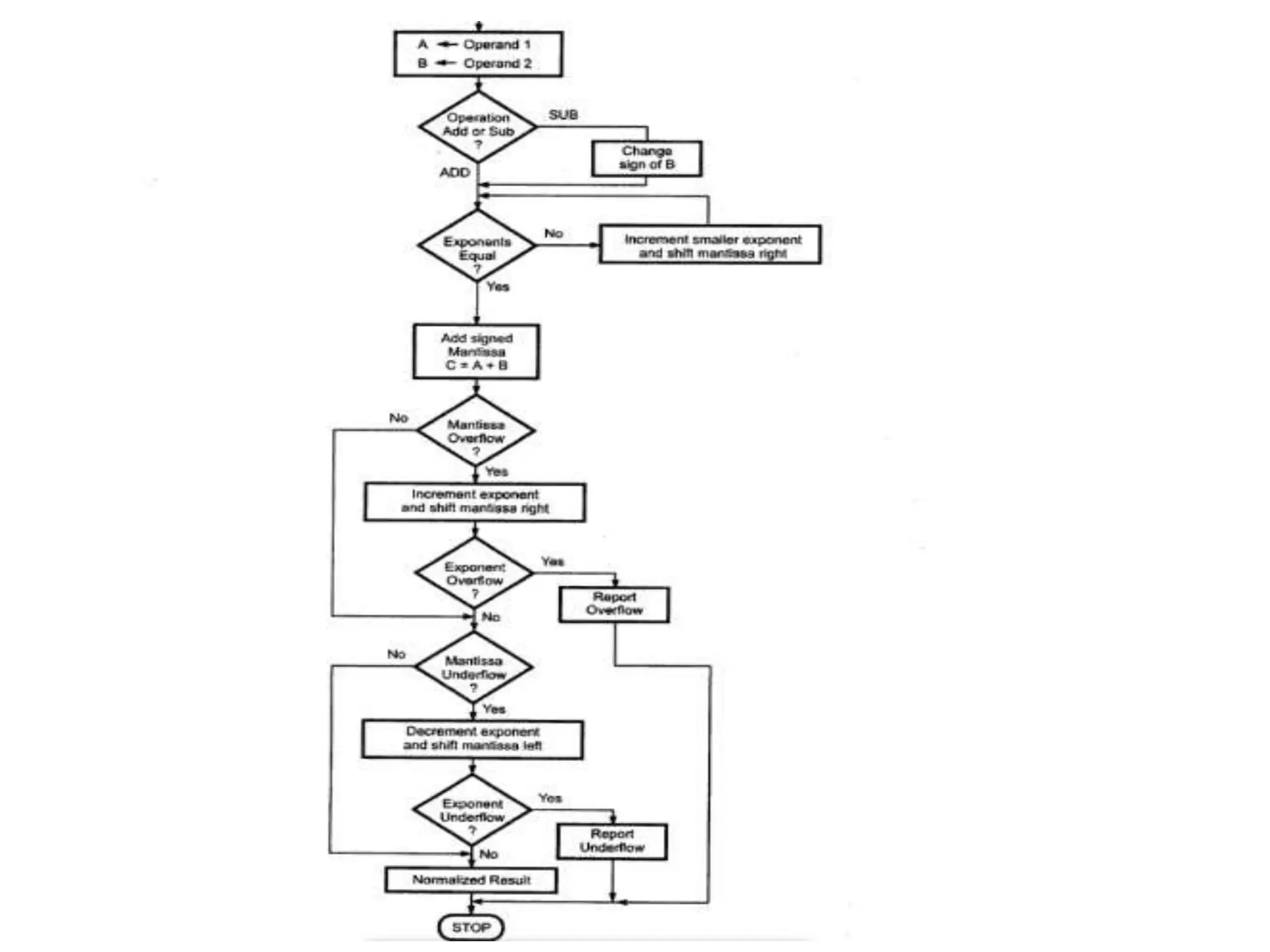
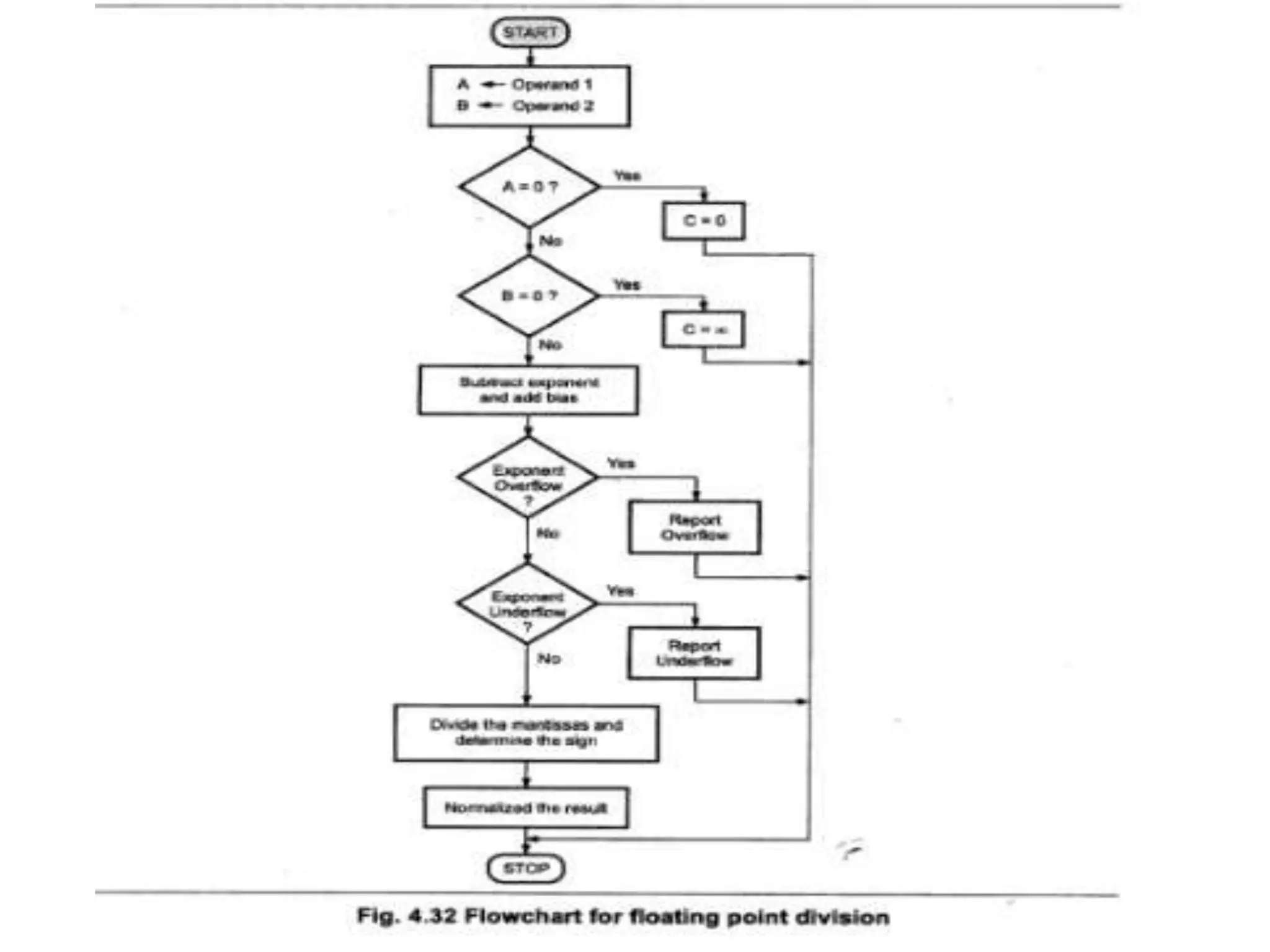
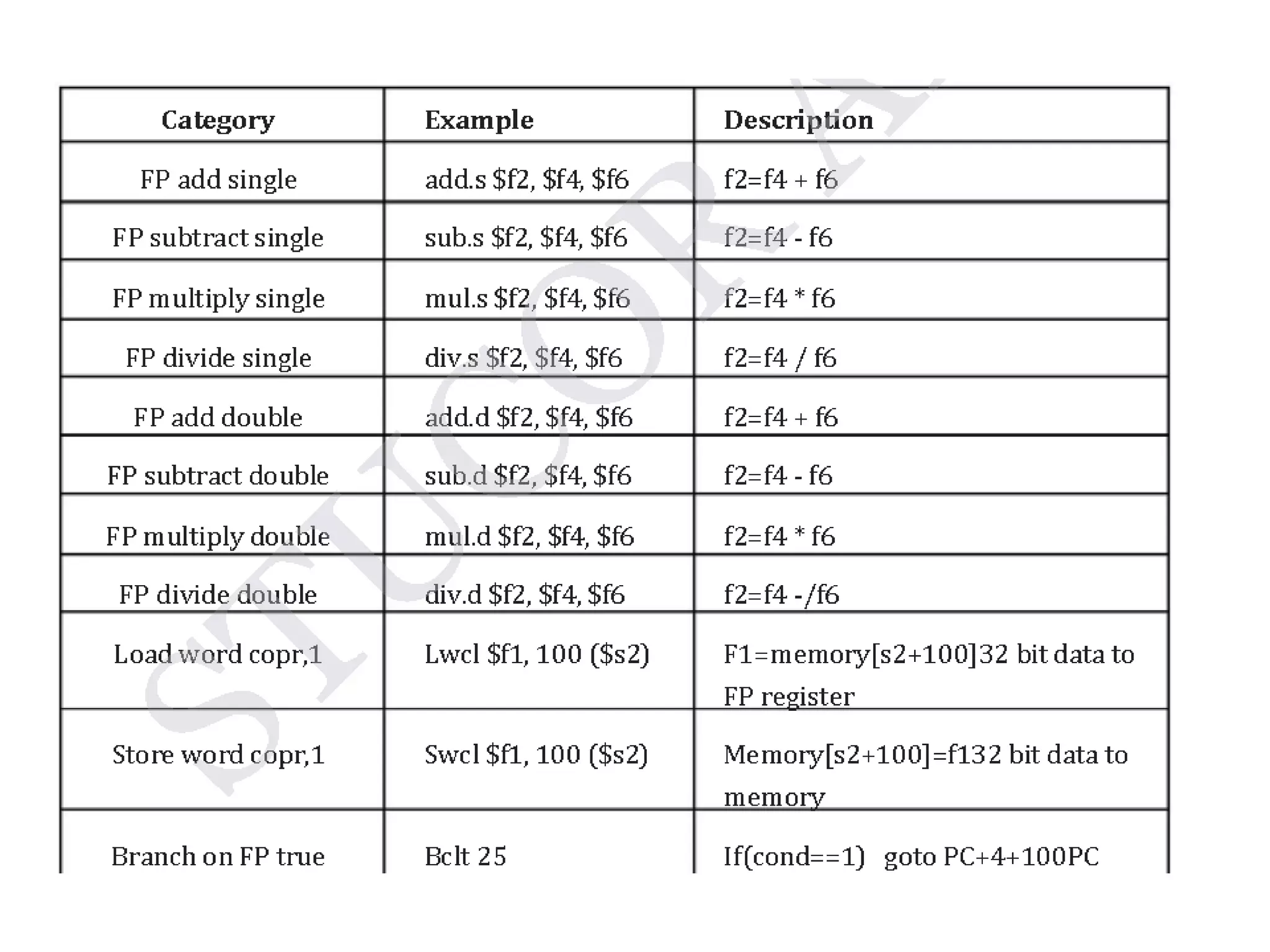
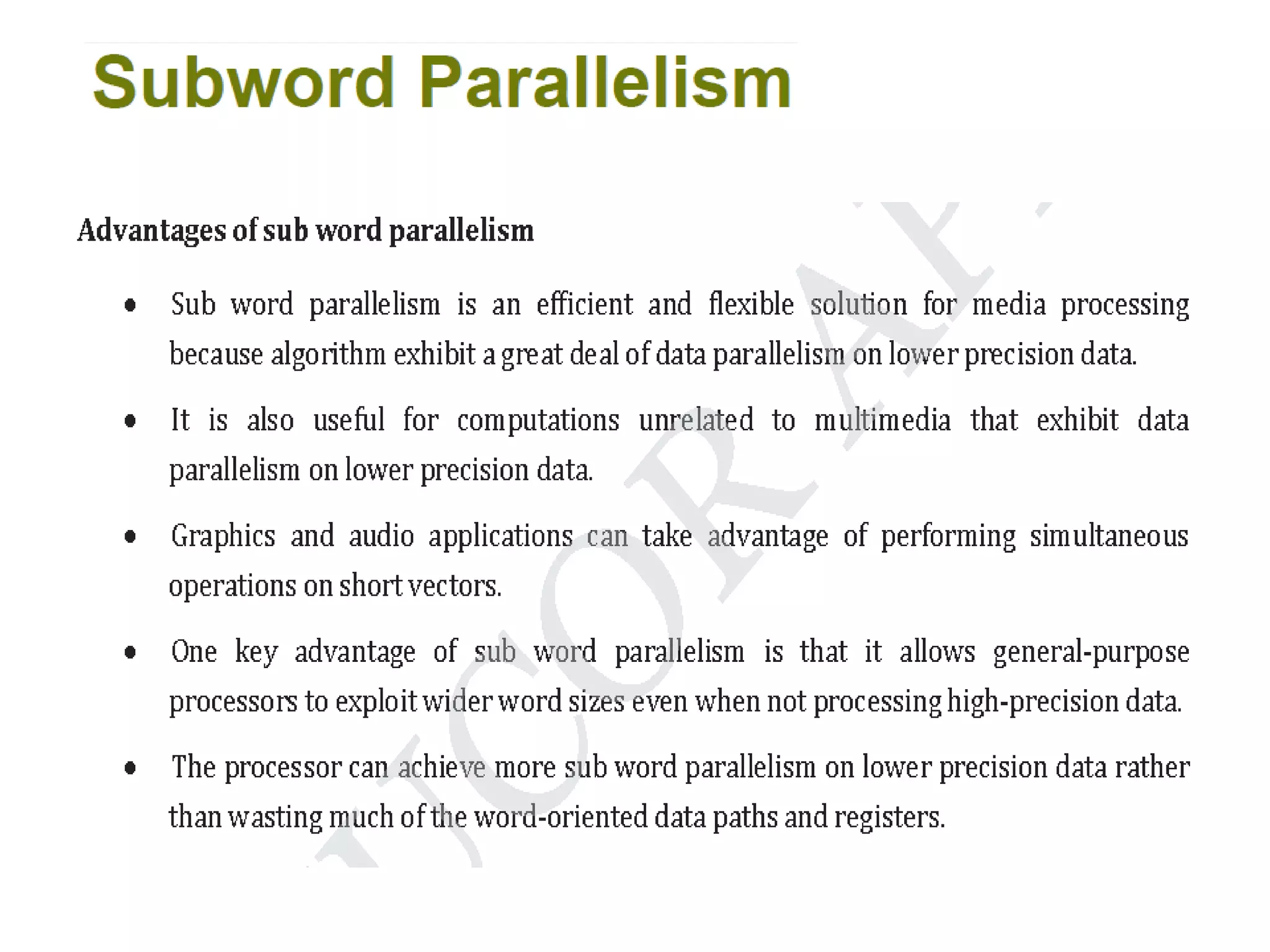
Digital computers represent all data, including numbers, using the binary number system. There are two main methods for representing real numbers: fixed-point notation reserves a fixed number of bits for the integer and fractional parts, while floating-point notation reserves bits for the significand and exponent to allow more flexibility in the number of fractional digits. Fixed-point has better performance but a more limited range, while floating-point can represent a wider range of values but requires more complex operations. Common number representations like two's complement are used to support arithmetic operations.