Embed presentation
Downloaded 19 times




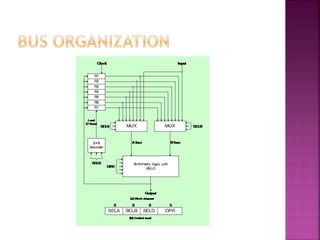
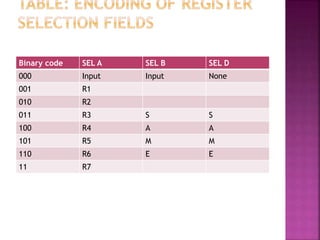
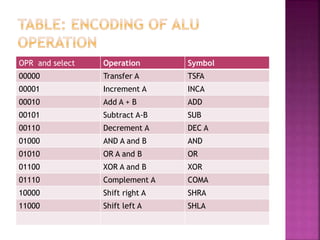
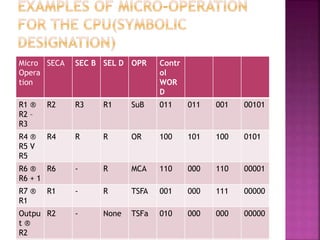

This document discusses the organization of a CPU and its registers. It includes tables that encode the register selection fields and ALU operations. It also provides examples of micro-operations for the CPU, showing the register selections, ALU operations, and control words. Key registers discussed include the accumulator, instruction register, address register, and program counter.








