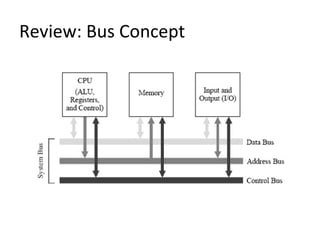
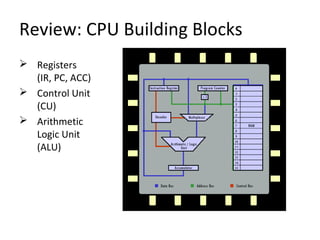
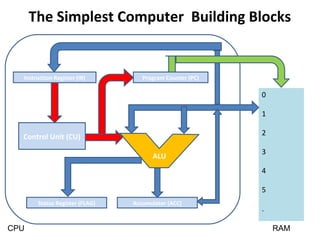
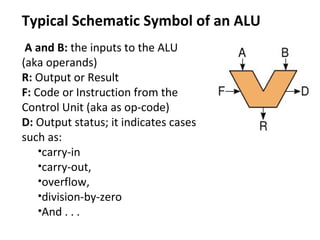
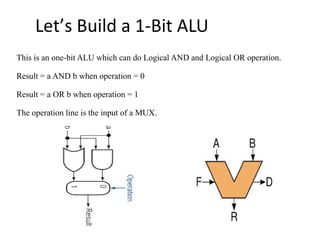
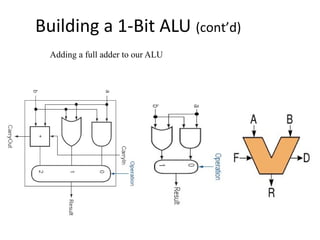
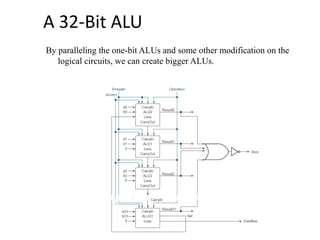
The document discusses the arithmetic logic unit (ALU), which is a digital circuit that performs arithmetic and logical operations in a central processing unit (CPU). It first reviews basic CPU concepts like registers and the control unit. It then defines the ALU and describes its typical components and symbol. The remainder of the document demonstrates how to build a simple 1-bit ALU and discusses how multiple 1-bit ALUs can be combined into a larger 32-bit ALU. Useful online resources on ALUs and CPU architecture are also provided.