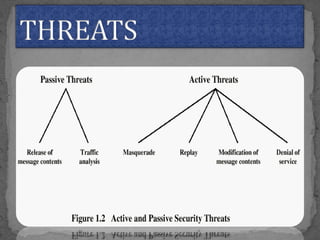
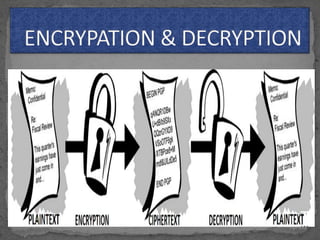
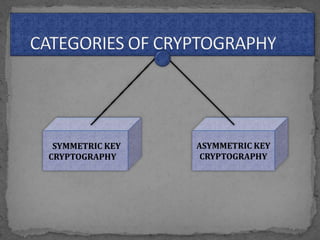
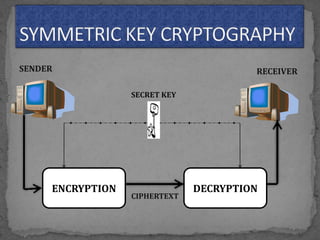
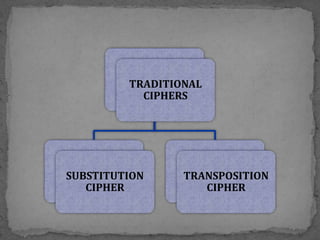
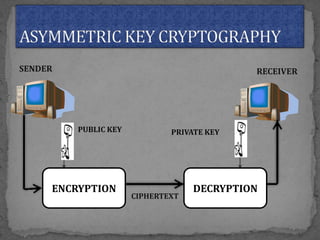
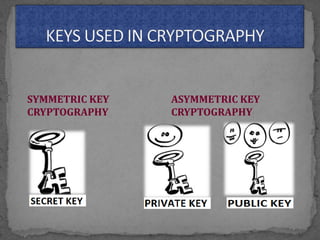
This document provides an overview of cryptography. It defines cryptography as the science of securing messages from attacks. It discusses basic cryptography terms like plain text, cipher text, encryption, decryption, and keys. It describes symmetric key cryptography, where the same key is used for encryption and decryption, and asymmetric key cryptography, which uses different public and private keys. It also covers traditional cipher techniques like substitution and transposition ciphers. The document concludes by listing some applications of cryptography like e-commerce, secure data, and access control.