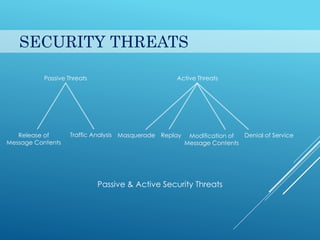
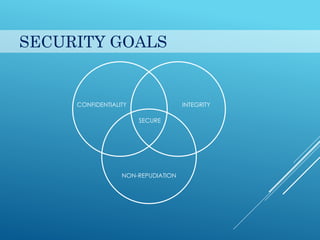
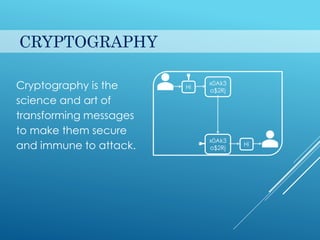
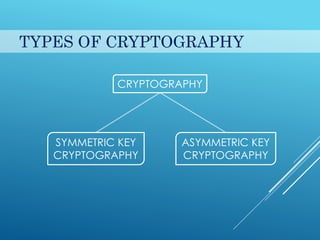
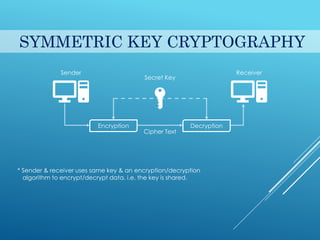
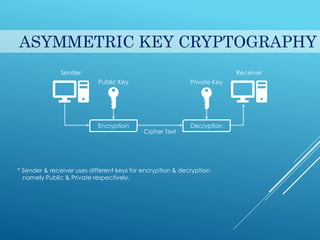
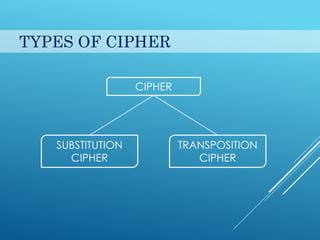
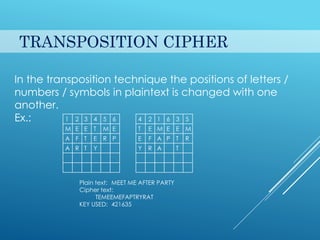
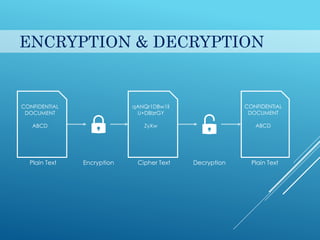
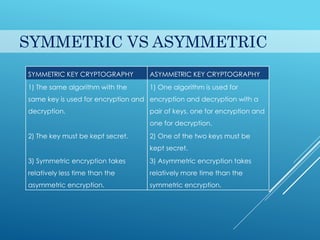
This document provides an introduction to cryptography. It discusses security goals like confidentiality and integrity. Cryptography is defined as transforming messages to make them secure. There are two main types: symmetric key cryptography where the same key is used to encrypt and decrypt, and asymmetric key cryptography where different public and private keys are used. Basic cryptography terms like cipher, ciphertext, encryption and decryption are also explained. Examples of cipher types like substitution and transposition ciphers are given. Applications of cryptography include defense, e-commerce, and data security.