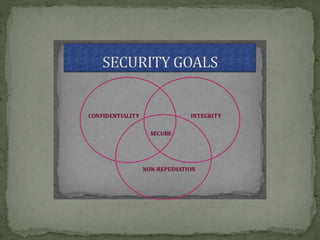
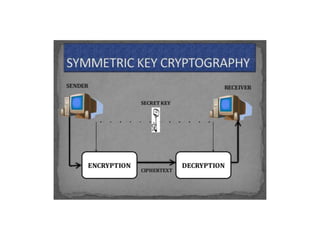
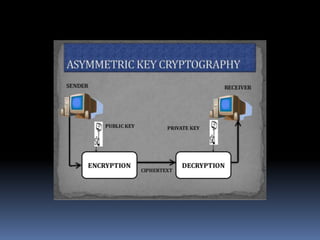
This document provides an overview of cryptography and security. It discusses symmetric and asymmetric cryptography, comparing their basic approaches. Symmetric cryptography uses the same key for encryption and decryption, while asymmetric cryptography uses different public and private keys. The document also defines basic cryptography terms like plain text, cipher text, and encryption/decryption. It describes traditional substitution and transposition ciphers as well as modern symmetric and asymmetric techniques. The goal is to maintain data security, confidentiality, authentication, and integrity through the appropriate use of encryption.