There are several types of computer networks:
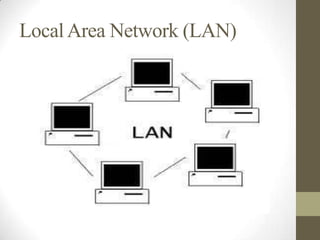
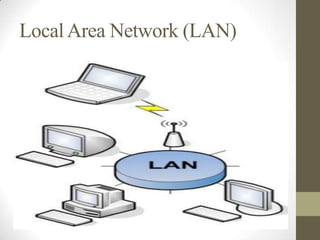
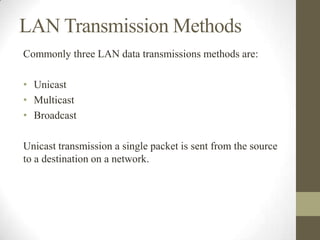
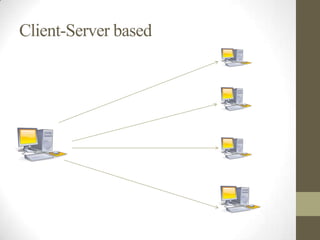
- Local area networks (LANs) connect devices within a small geographic area like a home or office using technologies like Ethernet or WiFi.
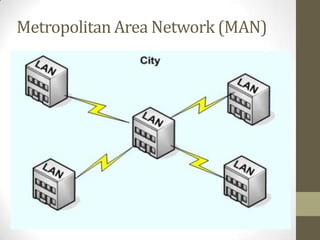
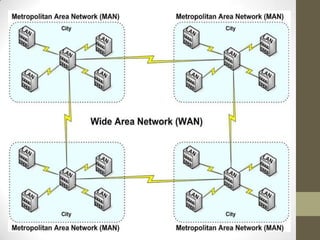
- Metropolitan area networks (MANs) connect devices within a city using technologies like DSL or cable.
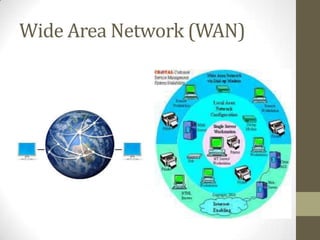
- Wide area networks (MANs) connect LANs over long distances using technologies like leased phone lines or satellites.