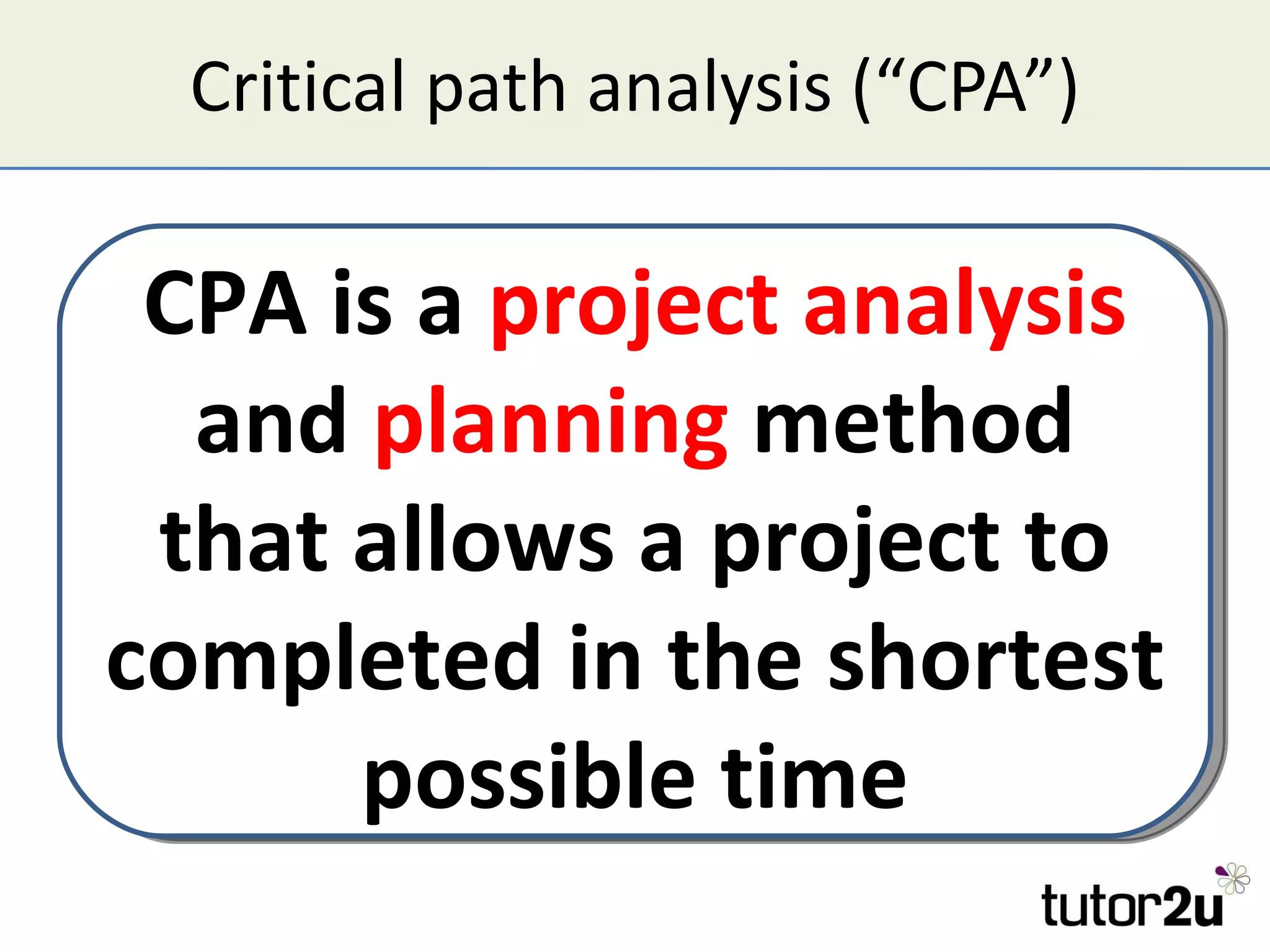
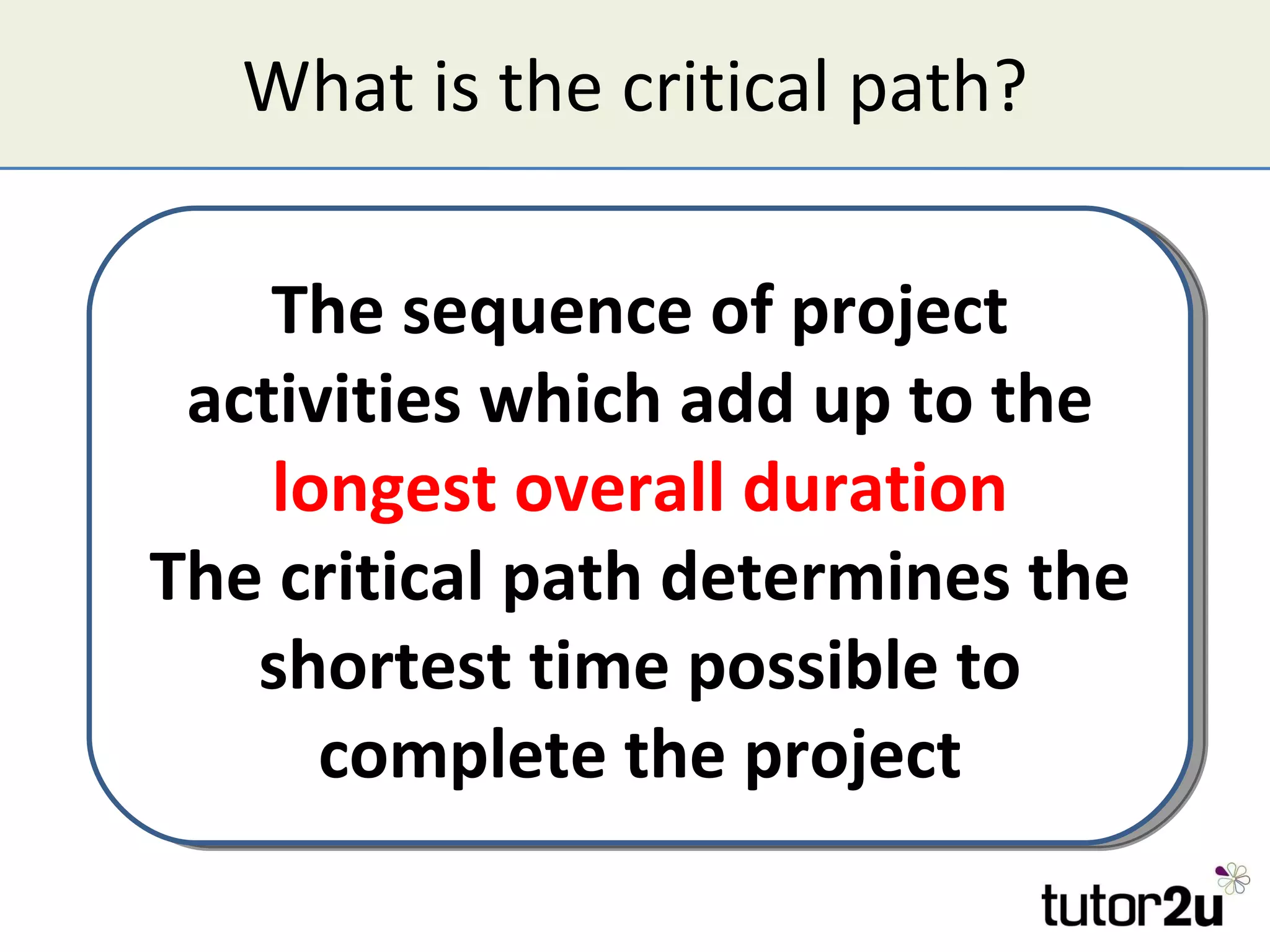
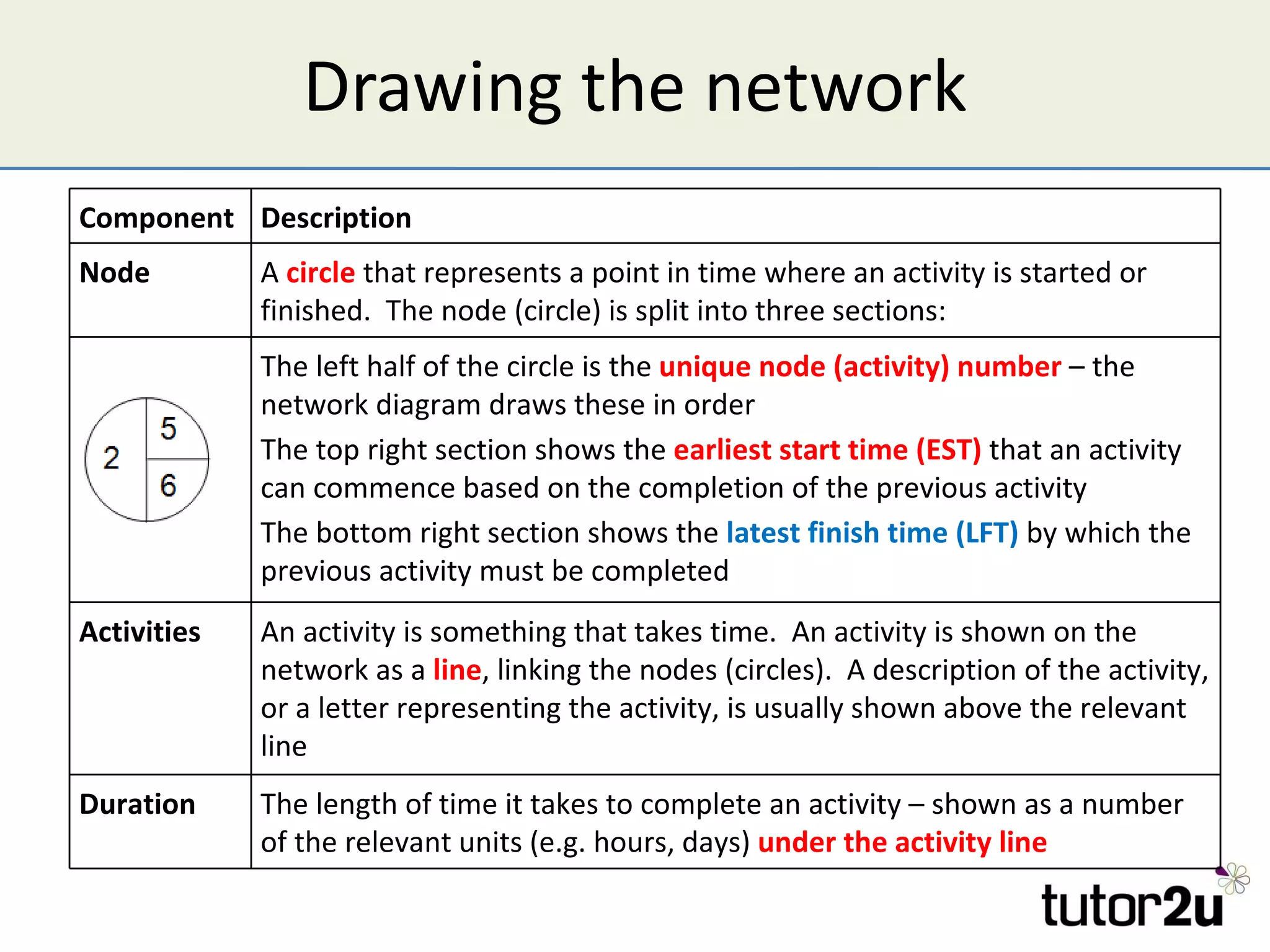
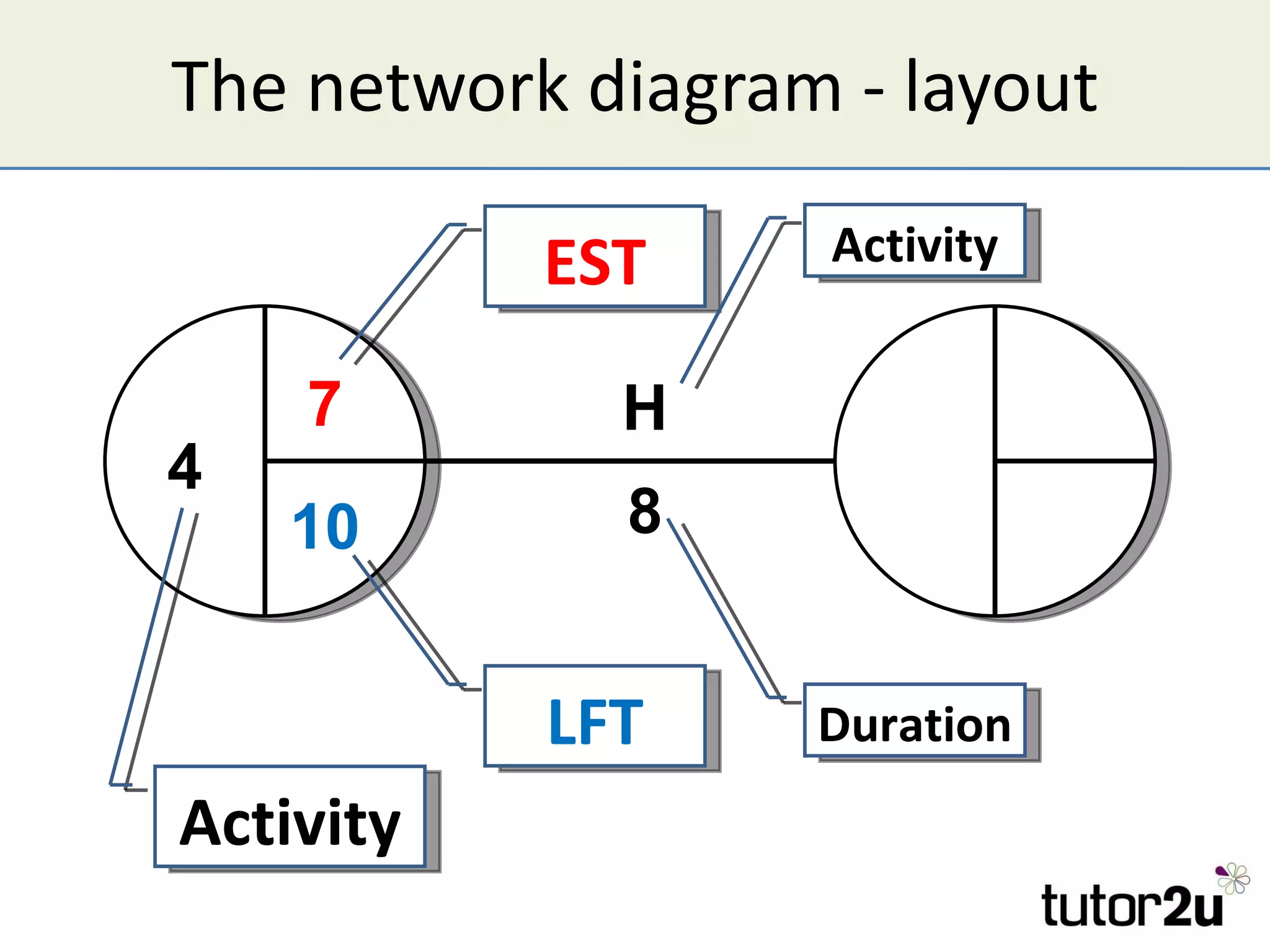
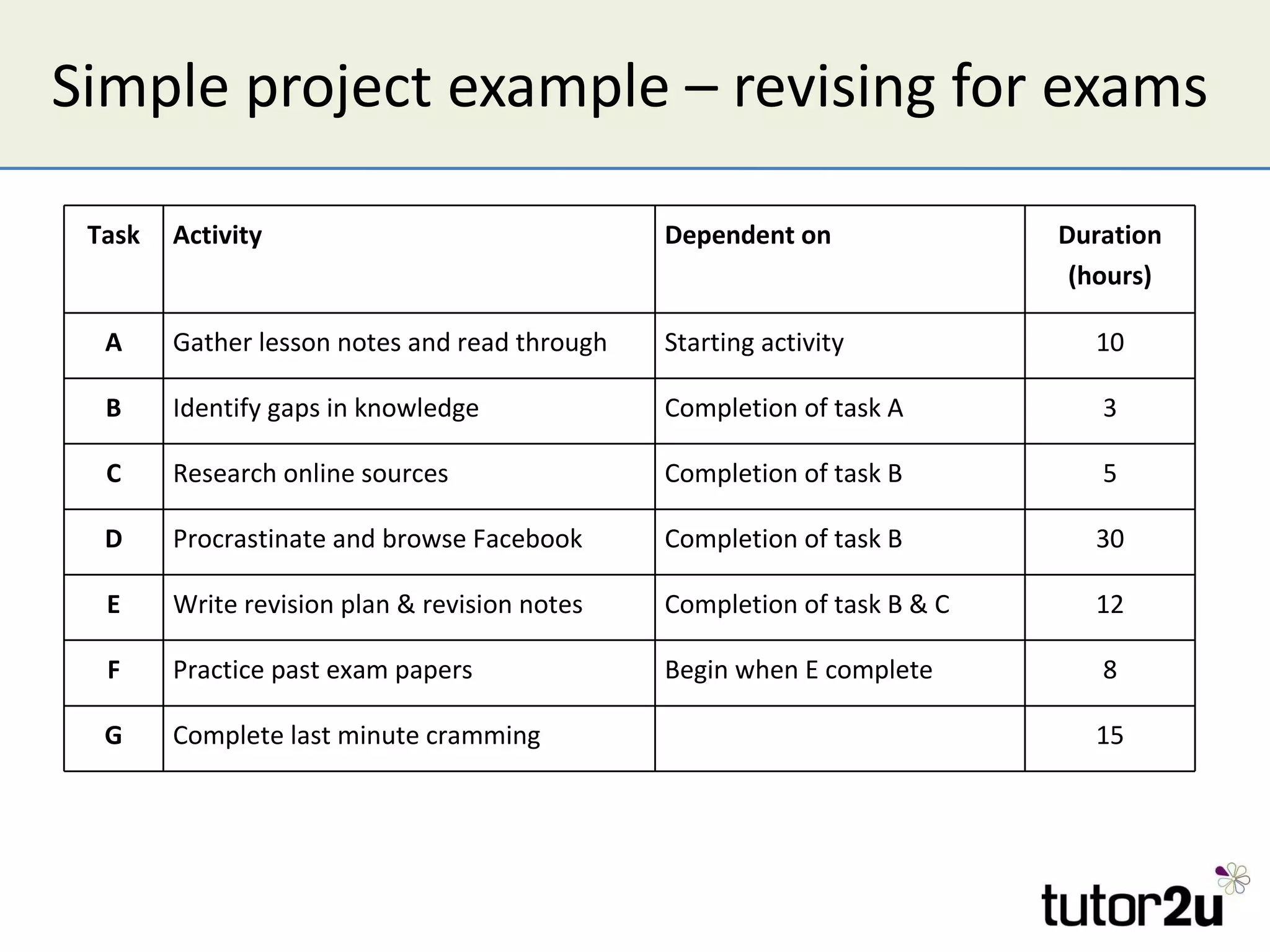
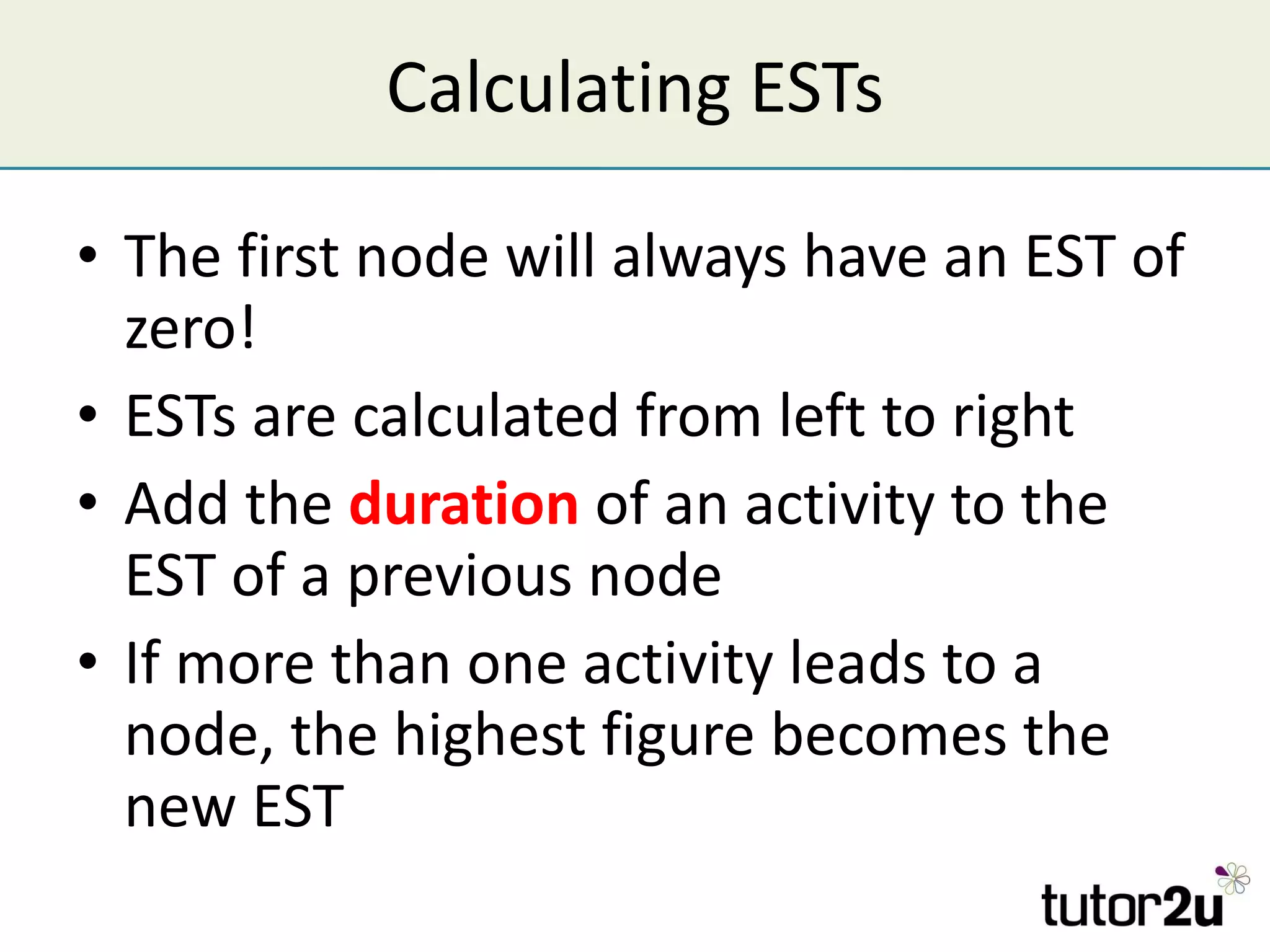
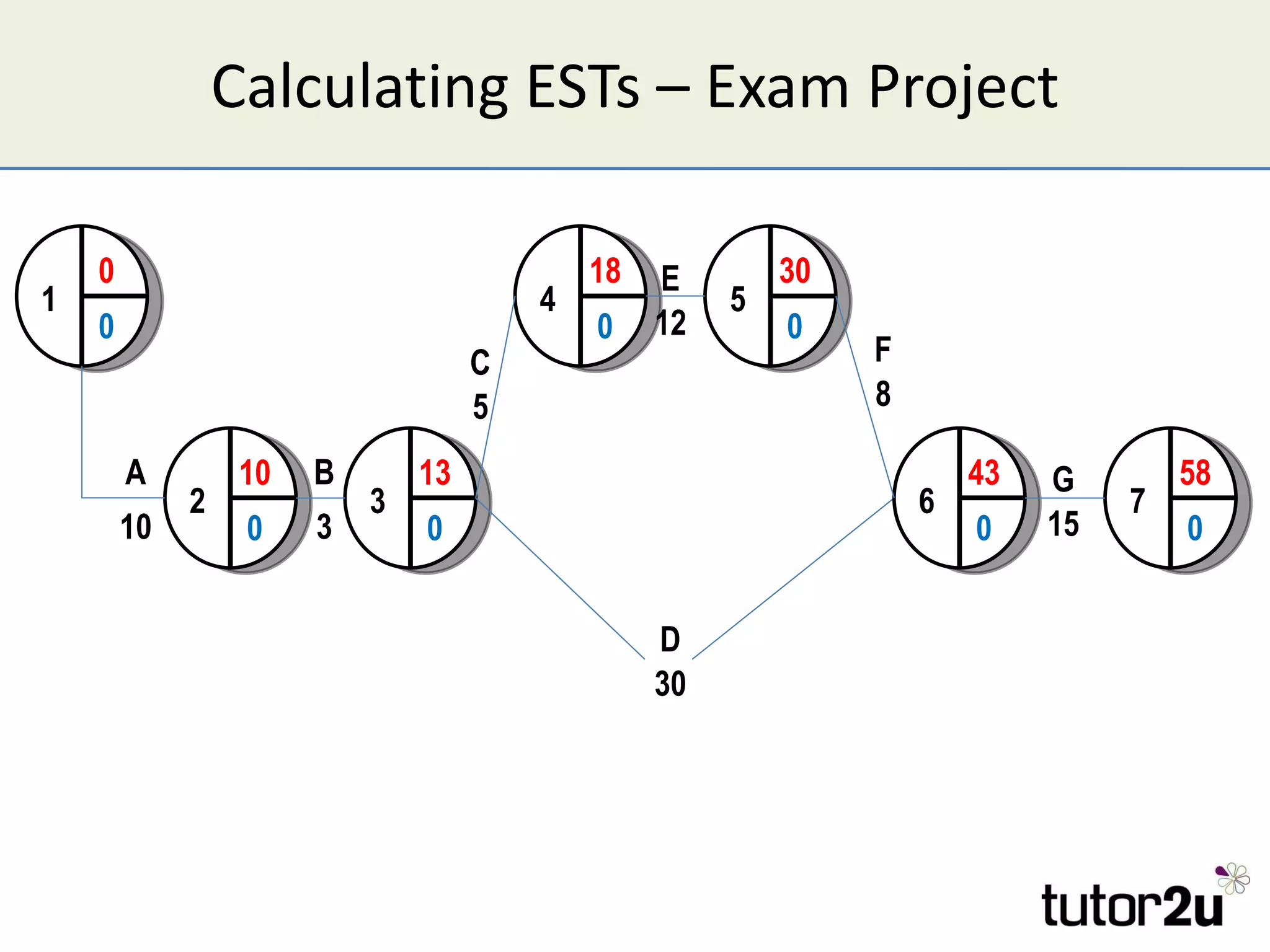
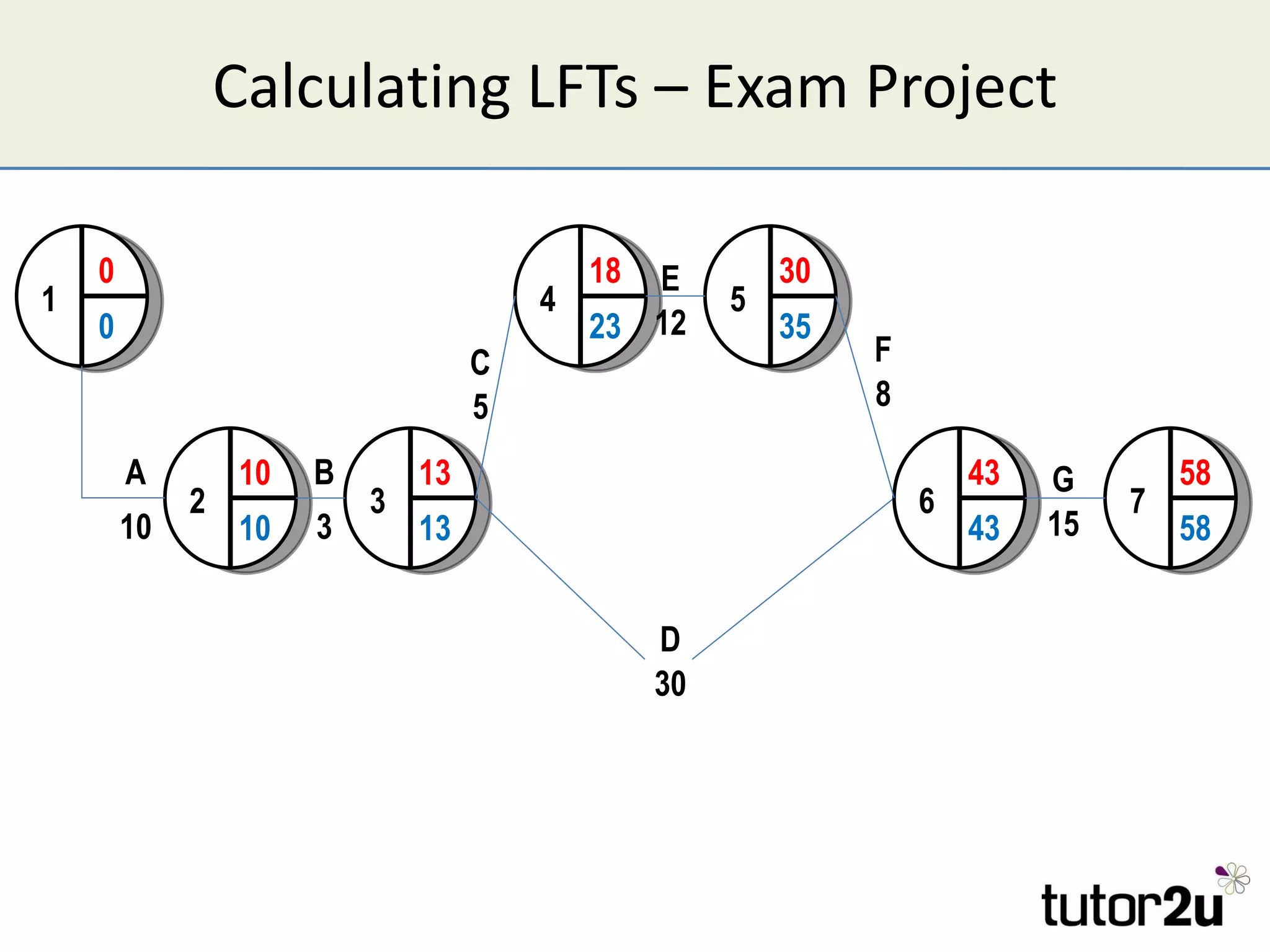
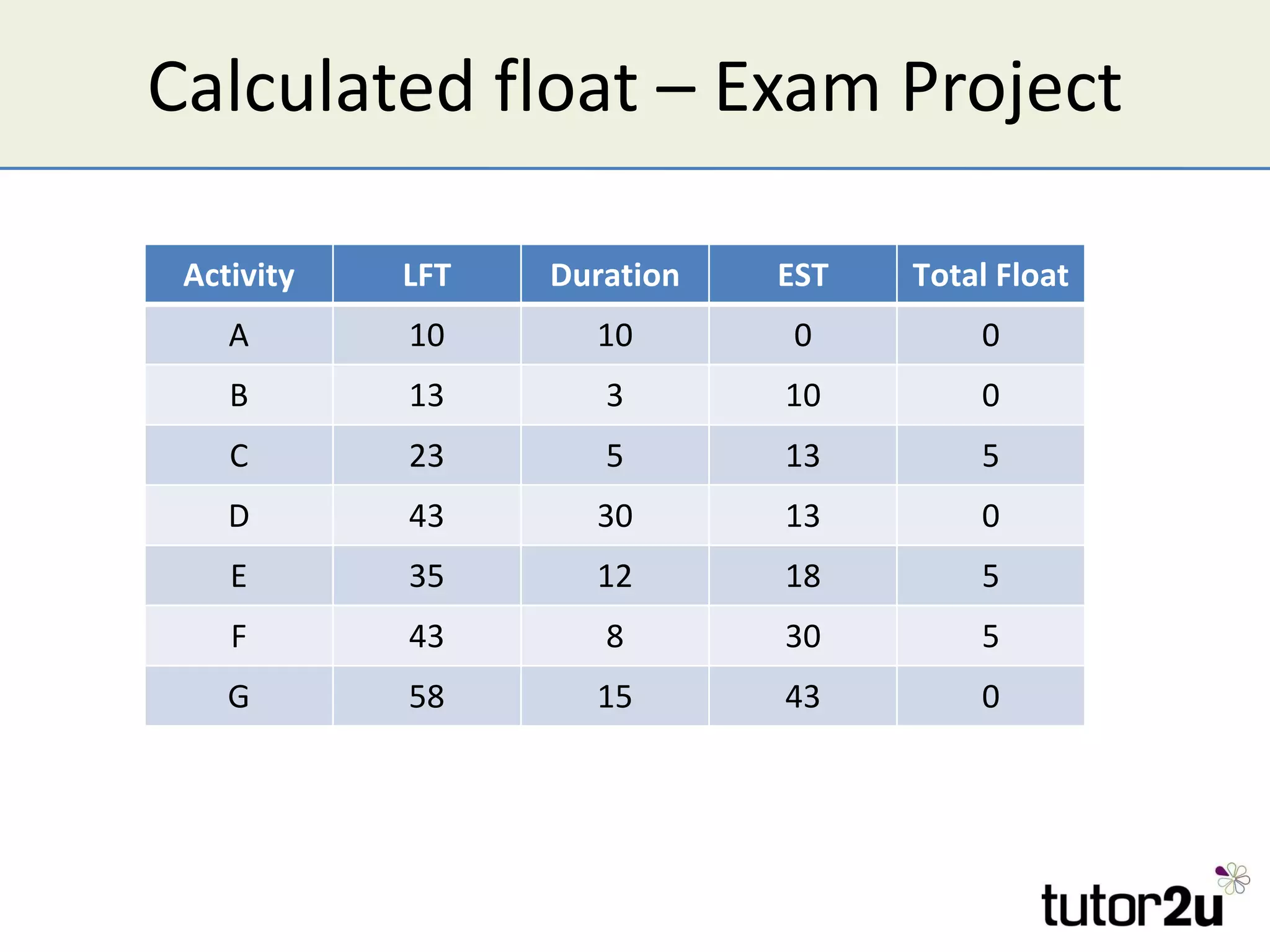
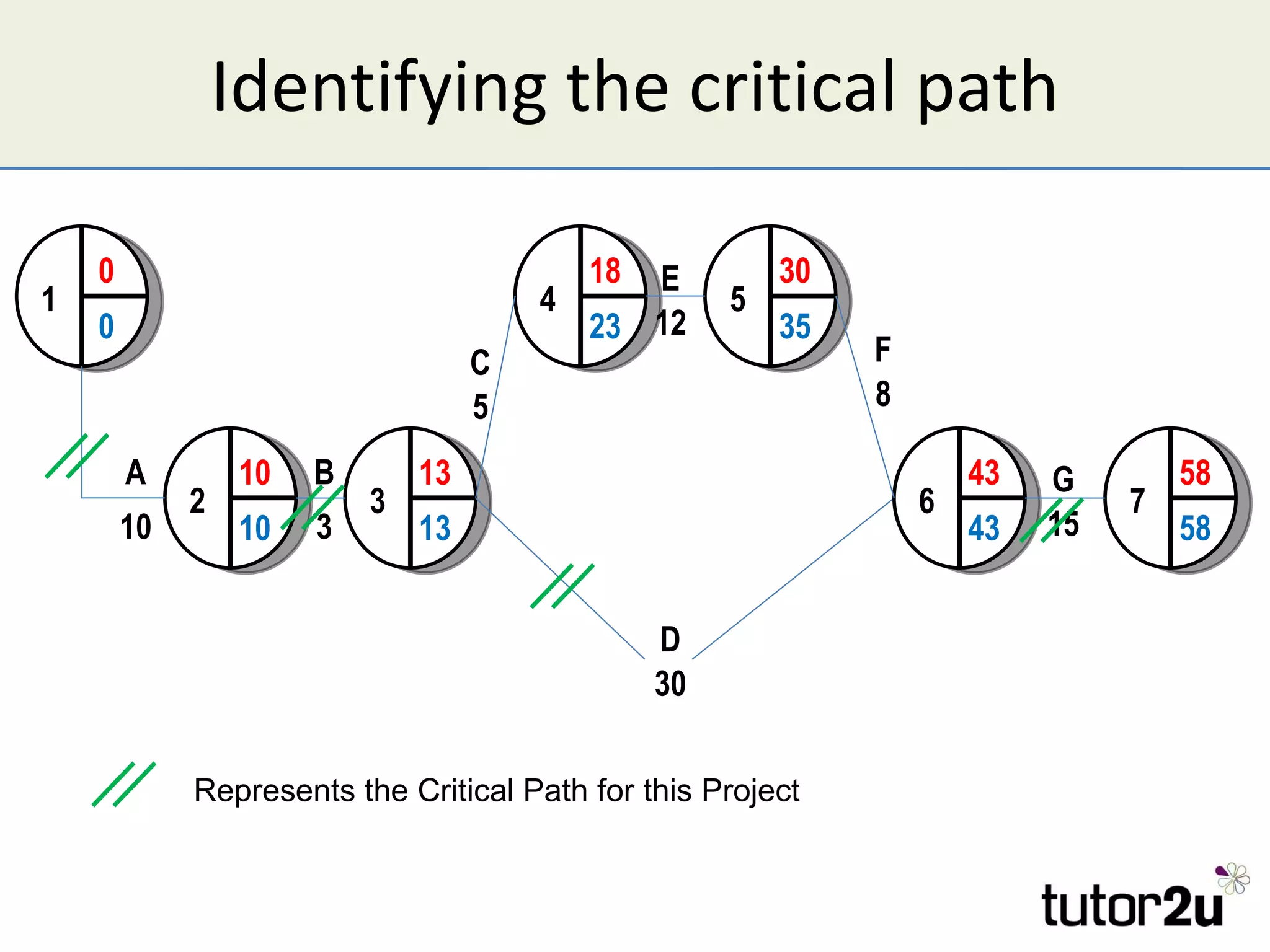
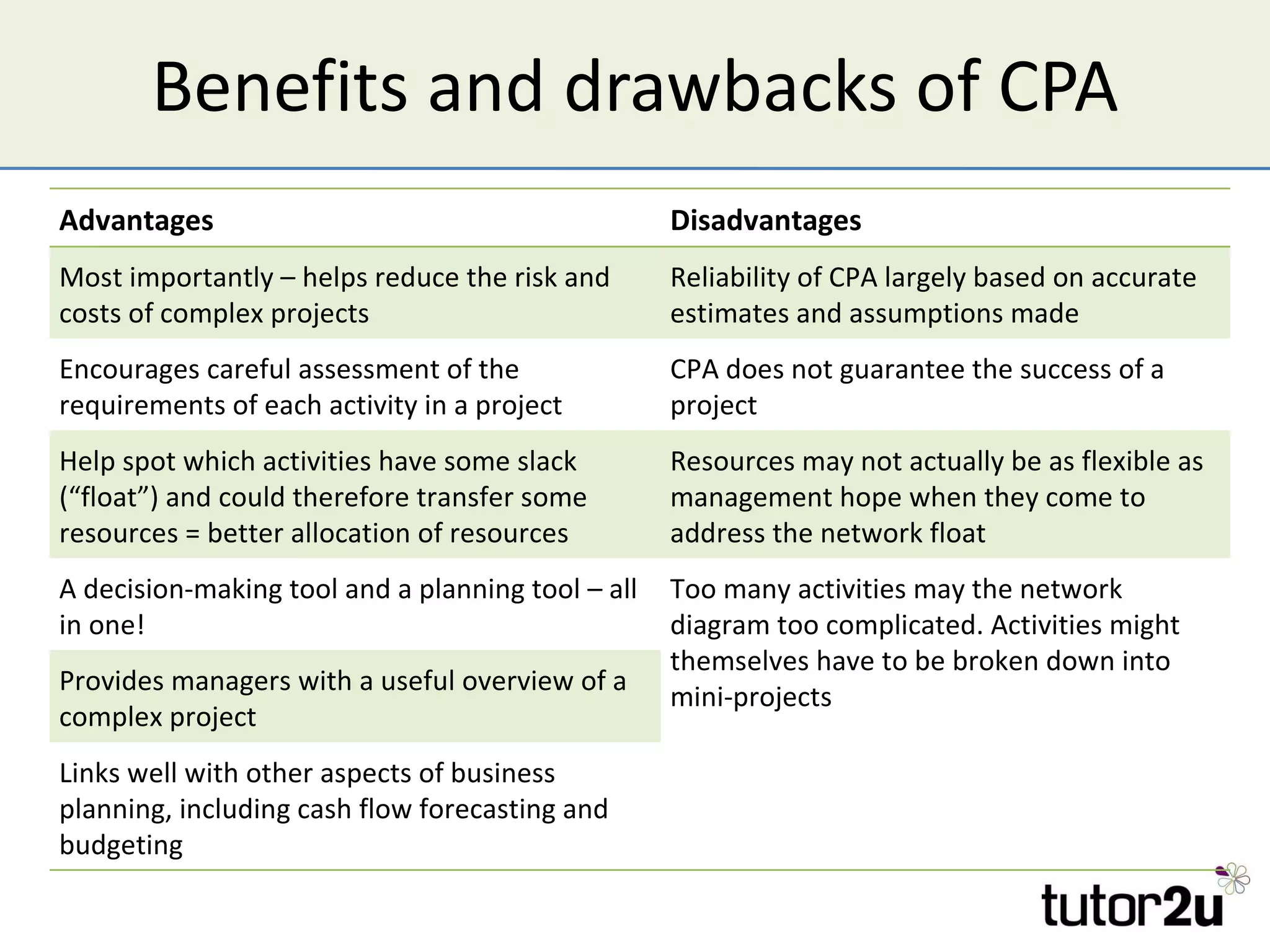
Critical path analysis (CPA) is a project planning method that allows a project to be completed in the shortest time possible. CPA requires identifying all project activities, their durations and dependencies. It then calculates the earliest and latest start and finish times to determine the critical path - the longest sequence of activities that determines the shortest project duration. Activities on the critical path cannot be delayed without impacting the planned end date. CPA helps optimize resource allocation and reduce project risks and costs.