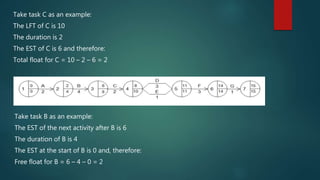
Critical path analysis (CPA) is a project management tool that uses network analysis to help managers handle complex projects. CPA involves identifying all project activities, their duration and dependencies to determine the longest path of activities (critical path) that dictates the shortest project timeline. It allows calculation of earliest and latest start/finish times for activities to identify float and sequence activities optimally. While CPA helps reduce risks and costs, its reliability depends on accurate estimates and flexibility may be limited by resource constraints.