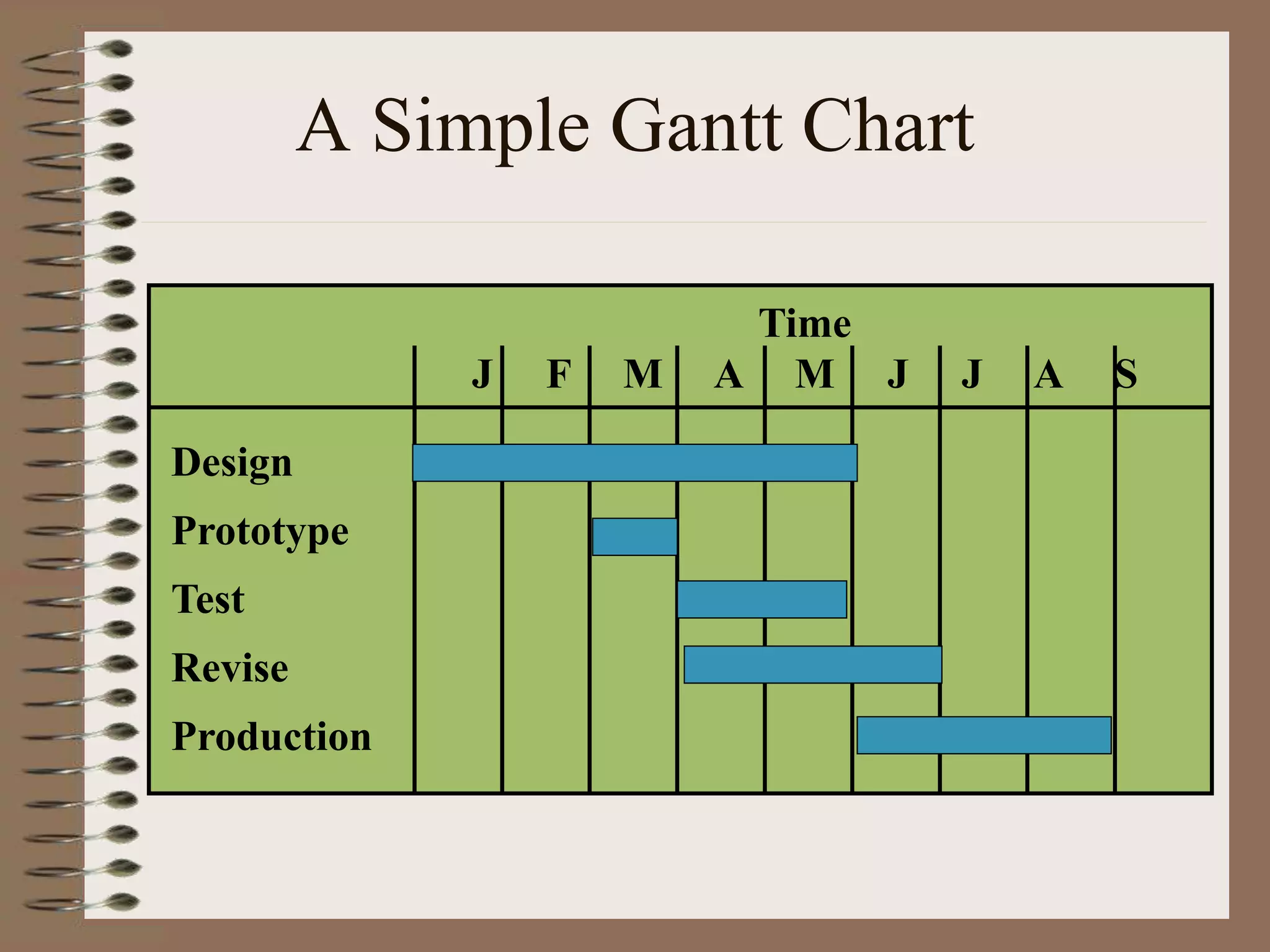
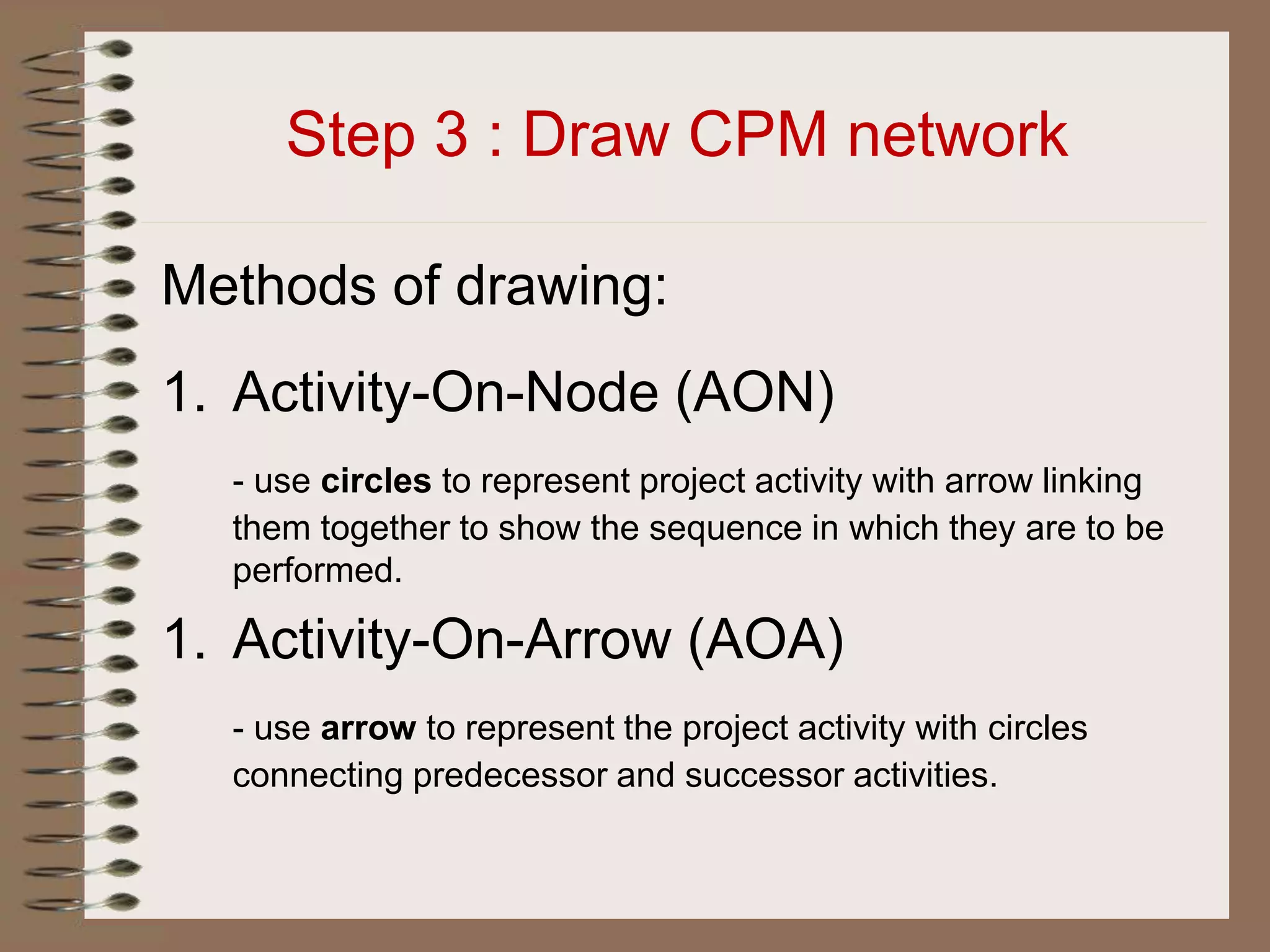
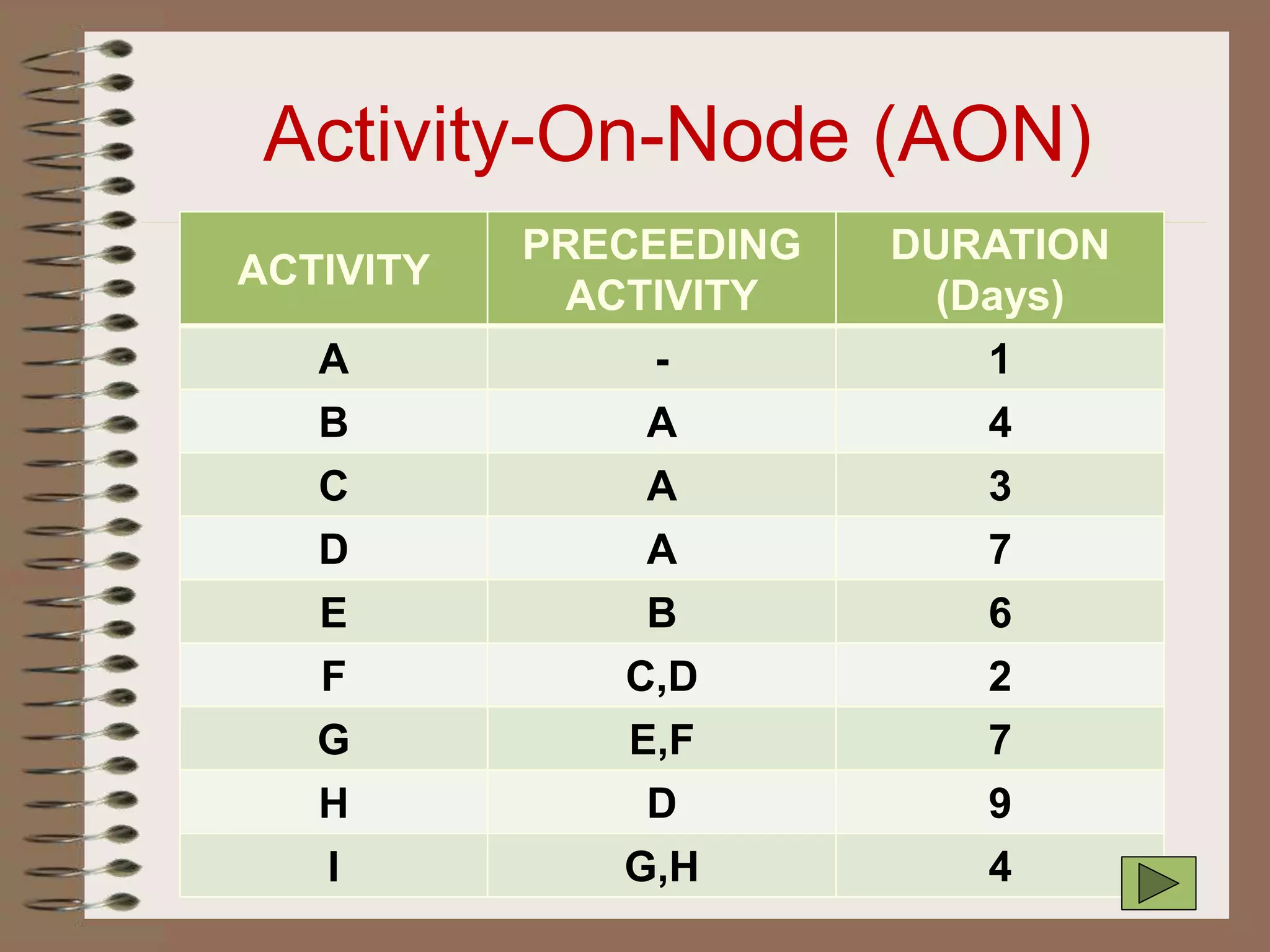
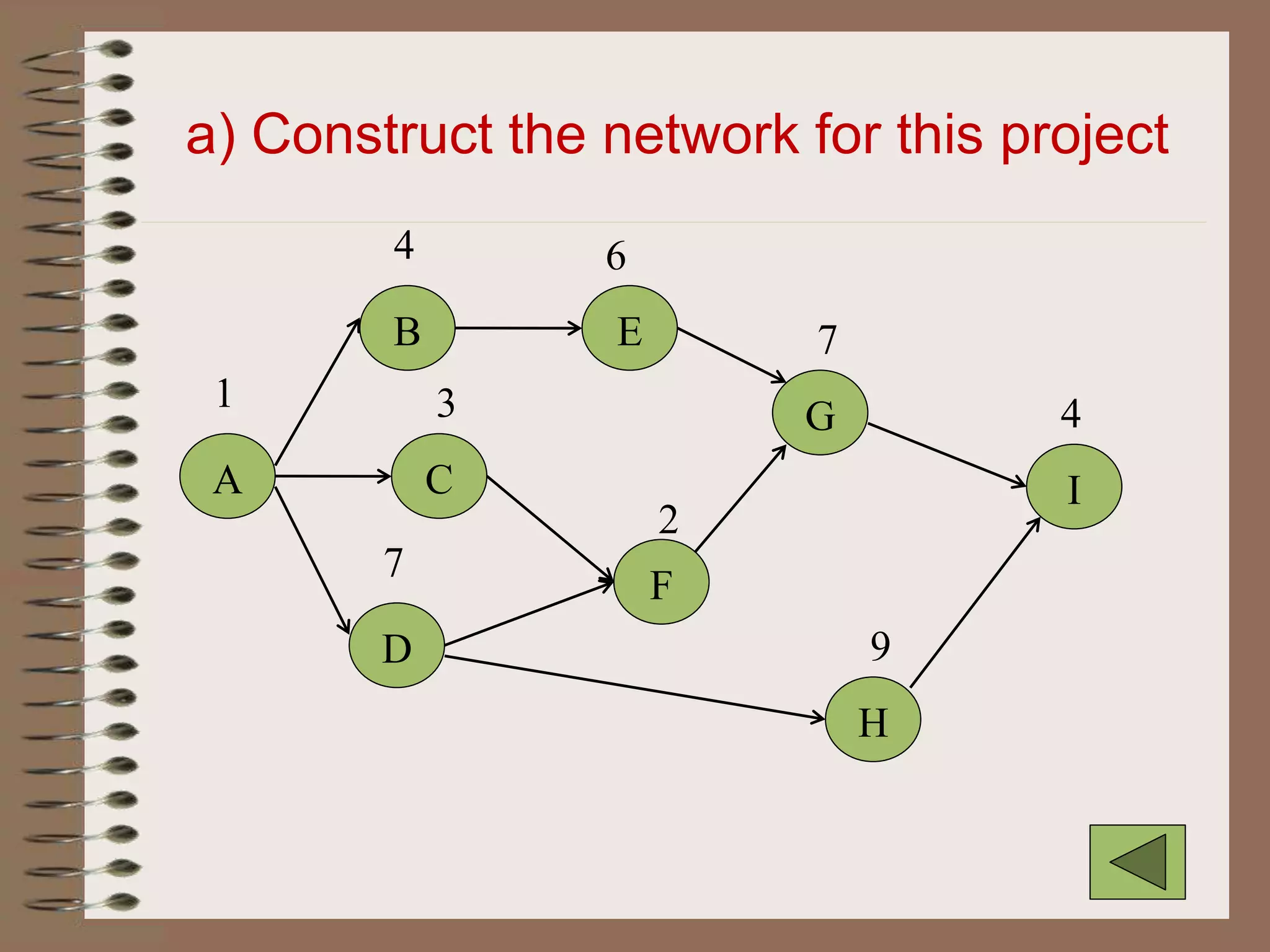
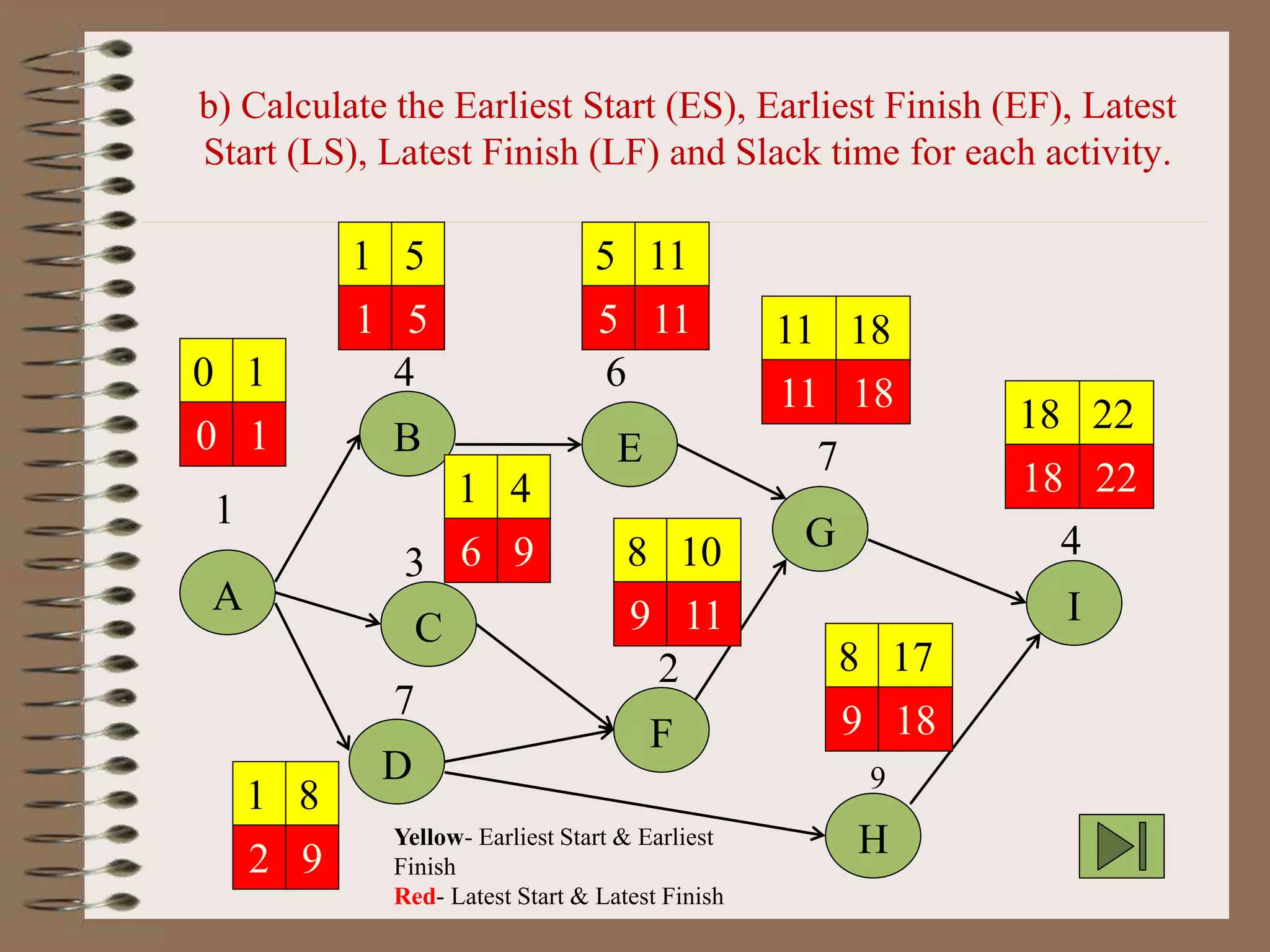
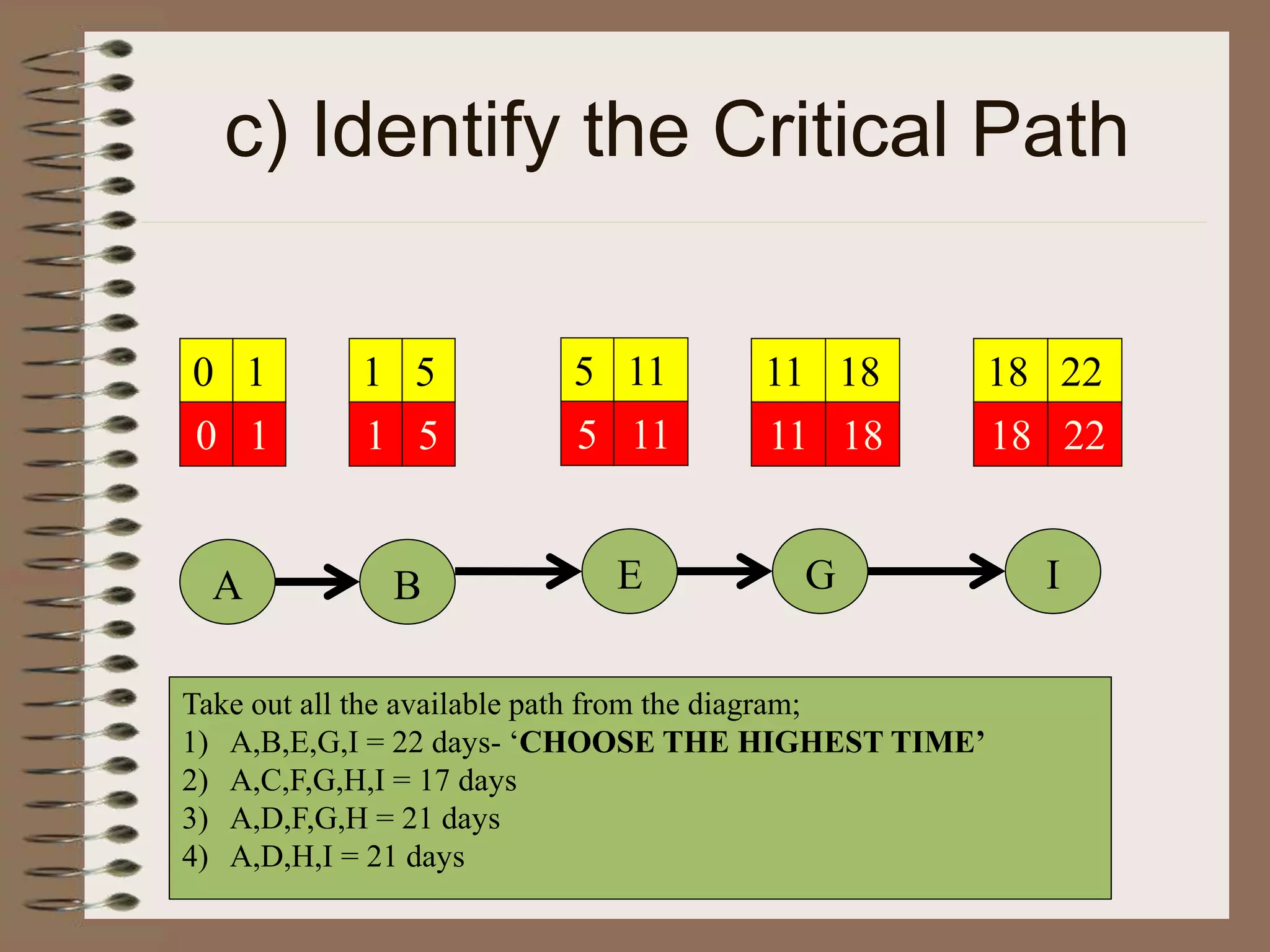
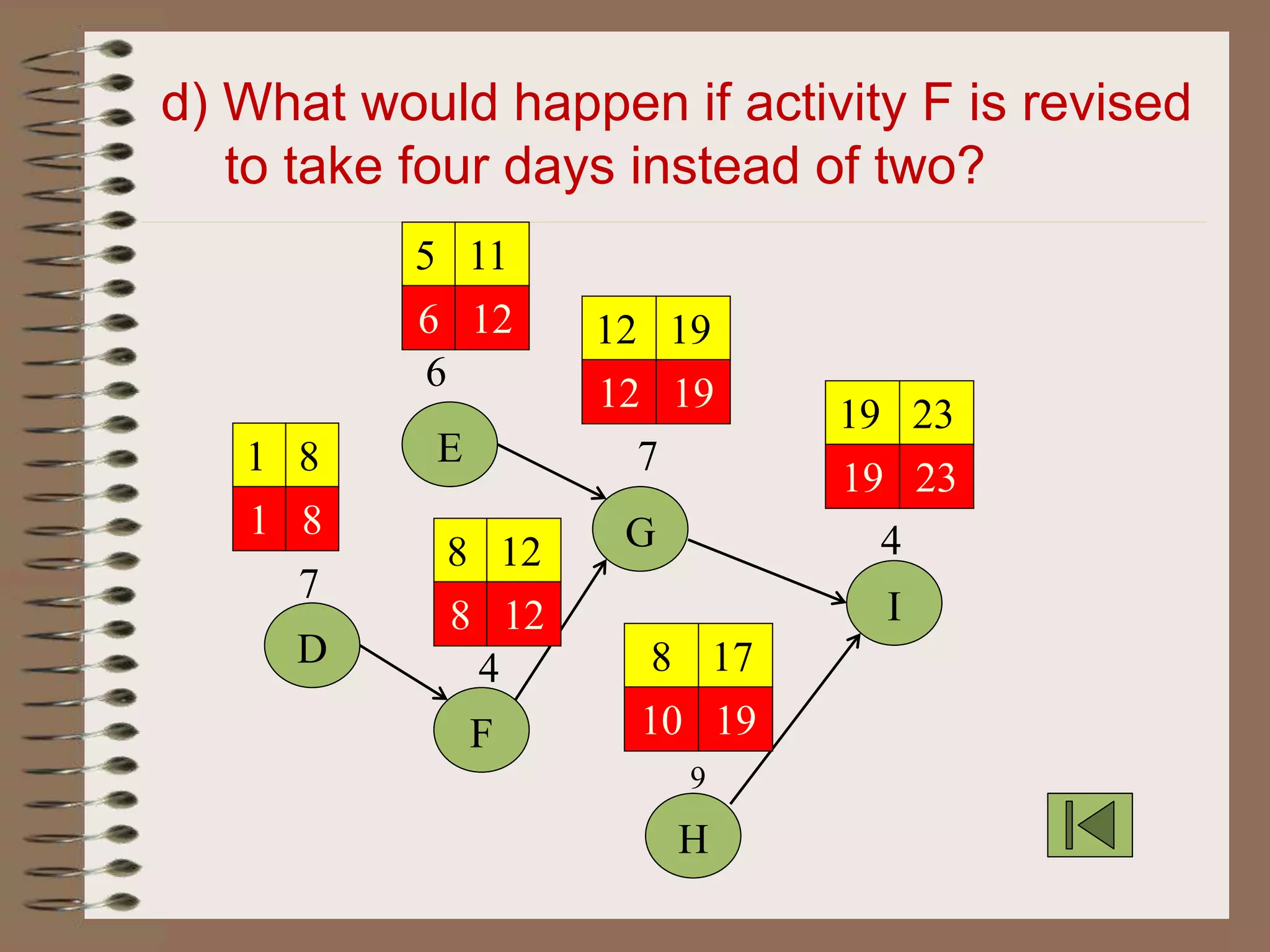
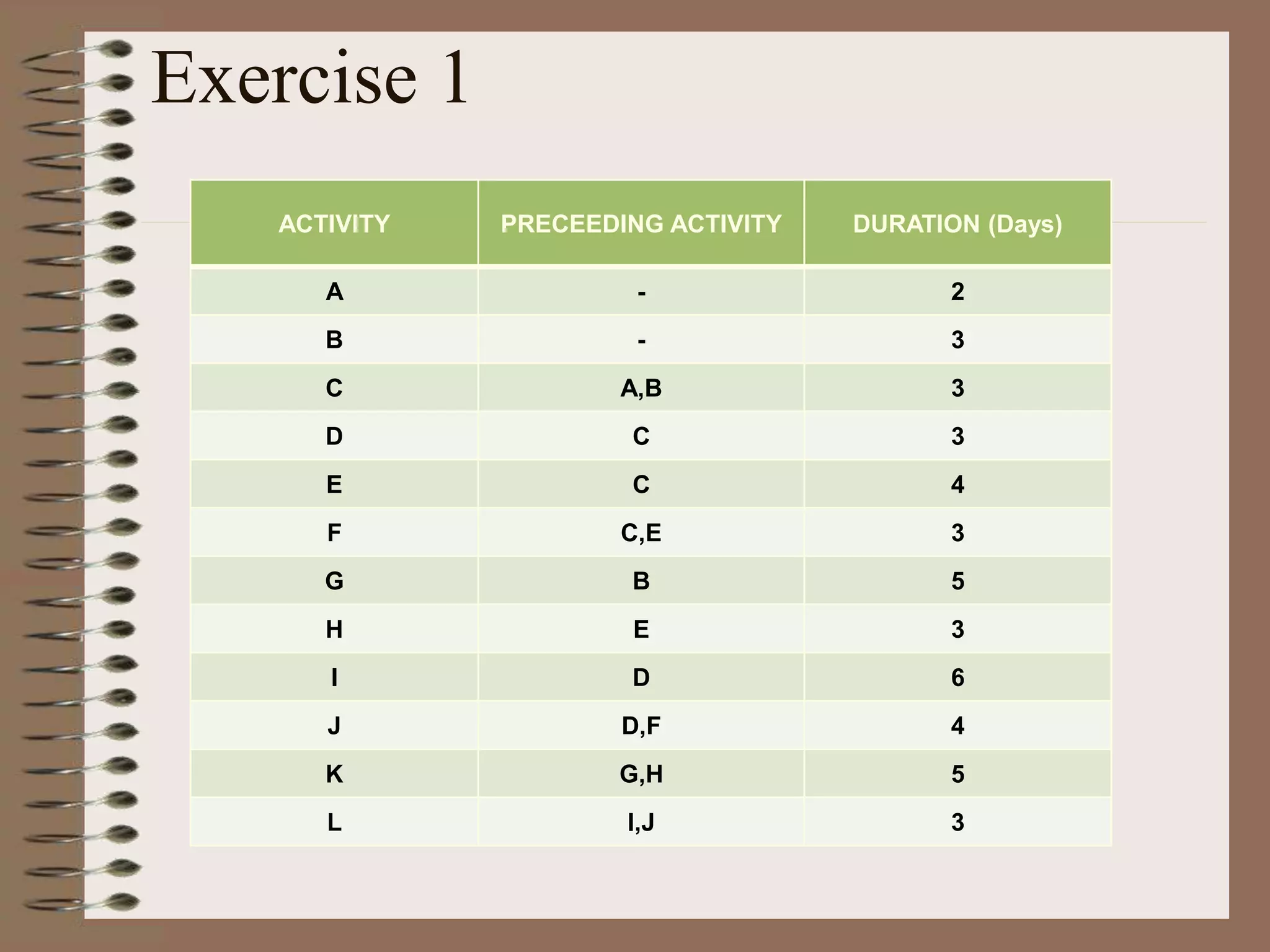
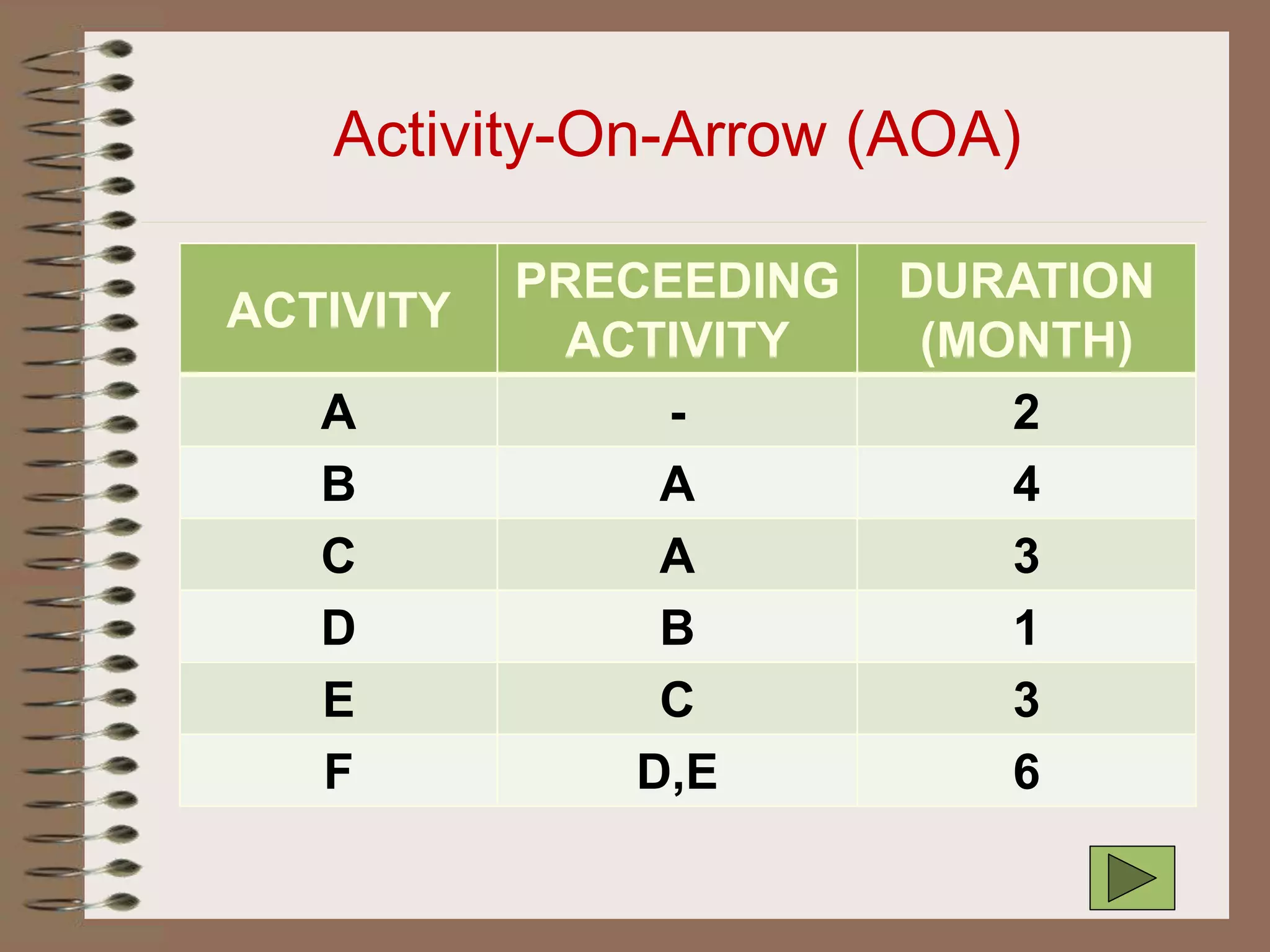
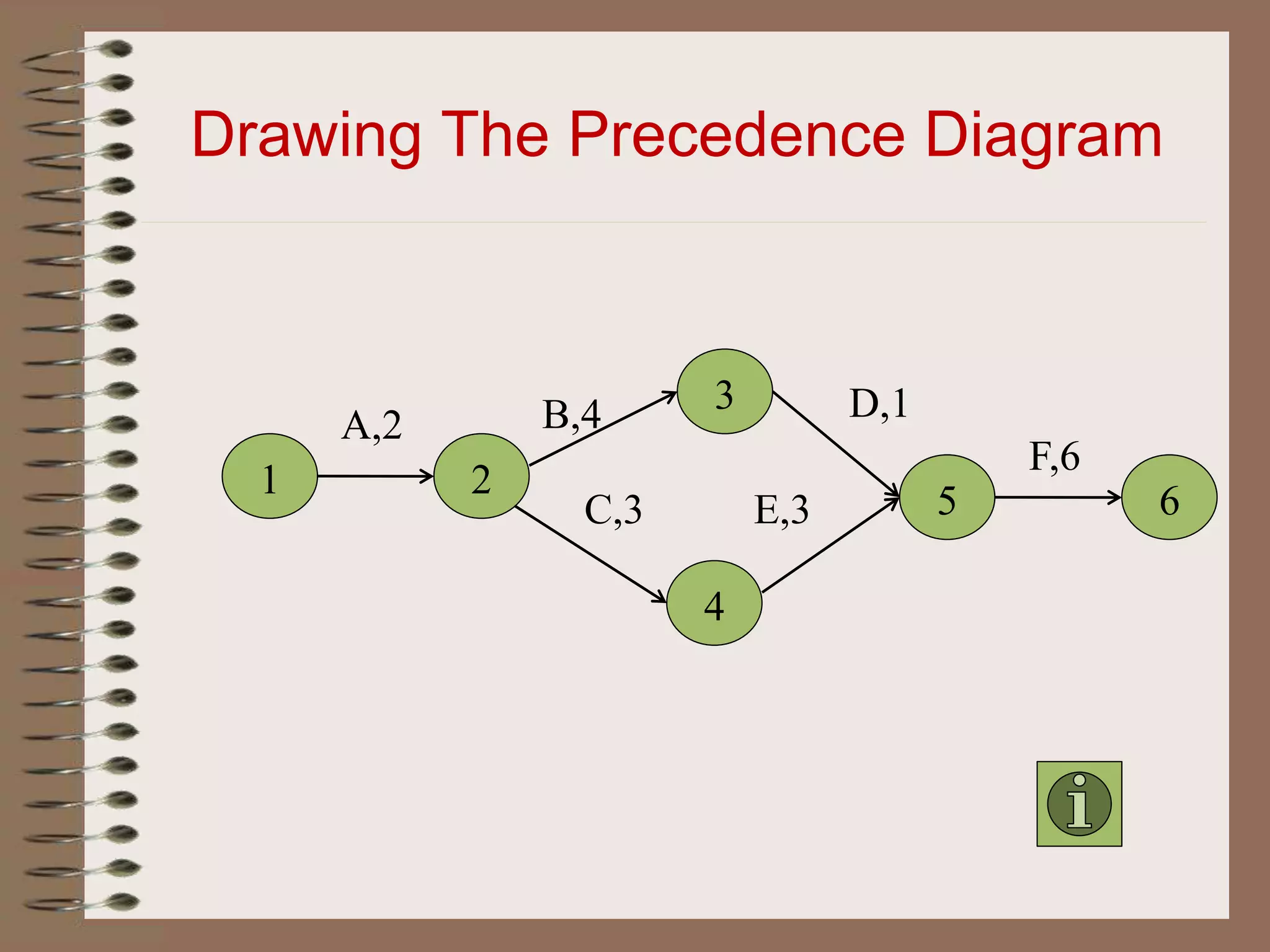
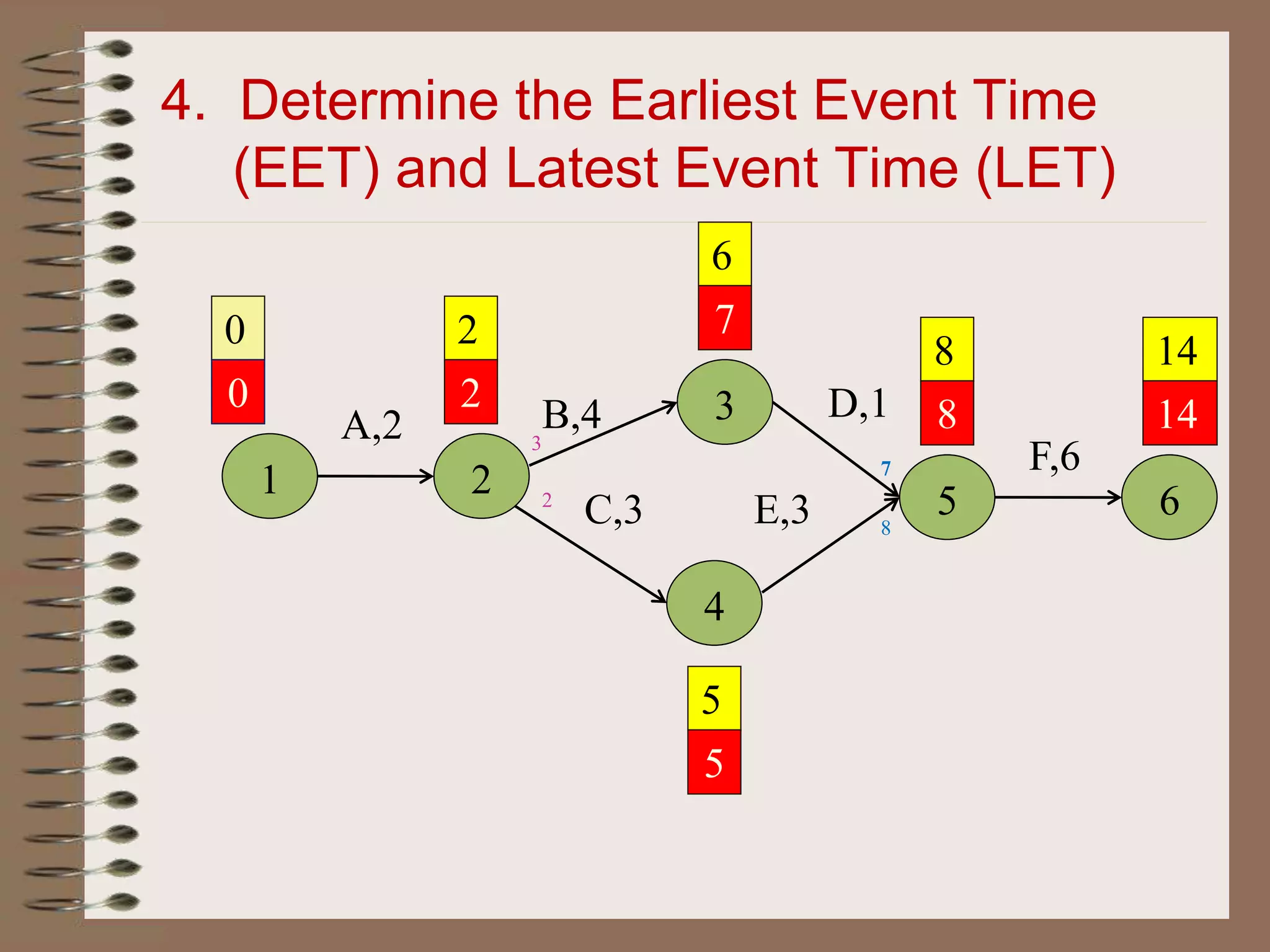
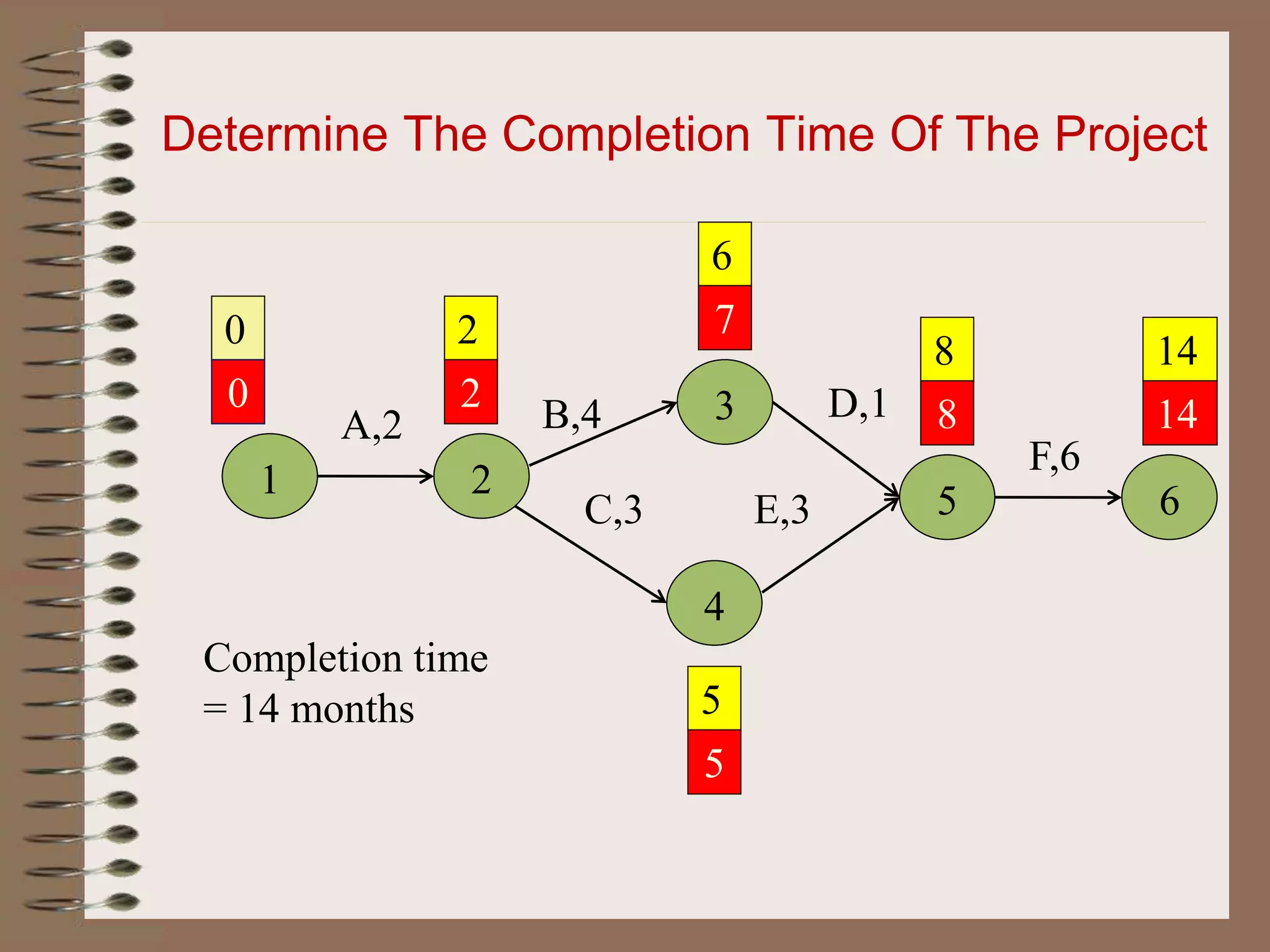
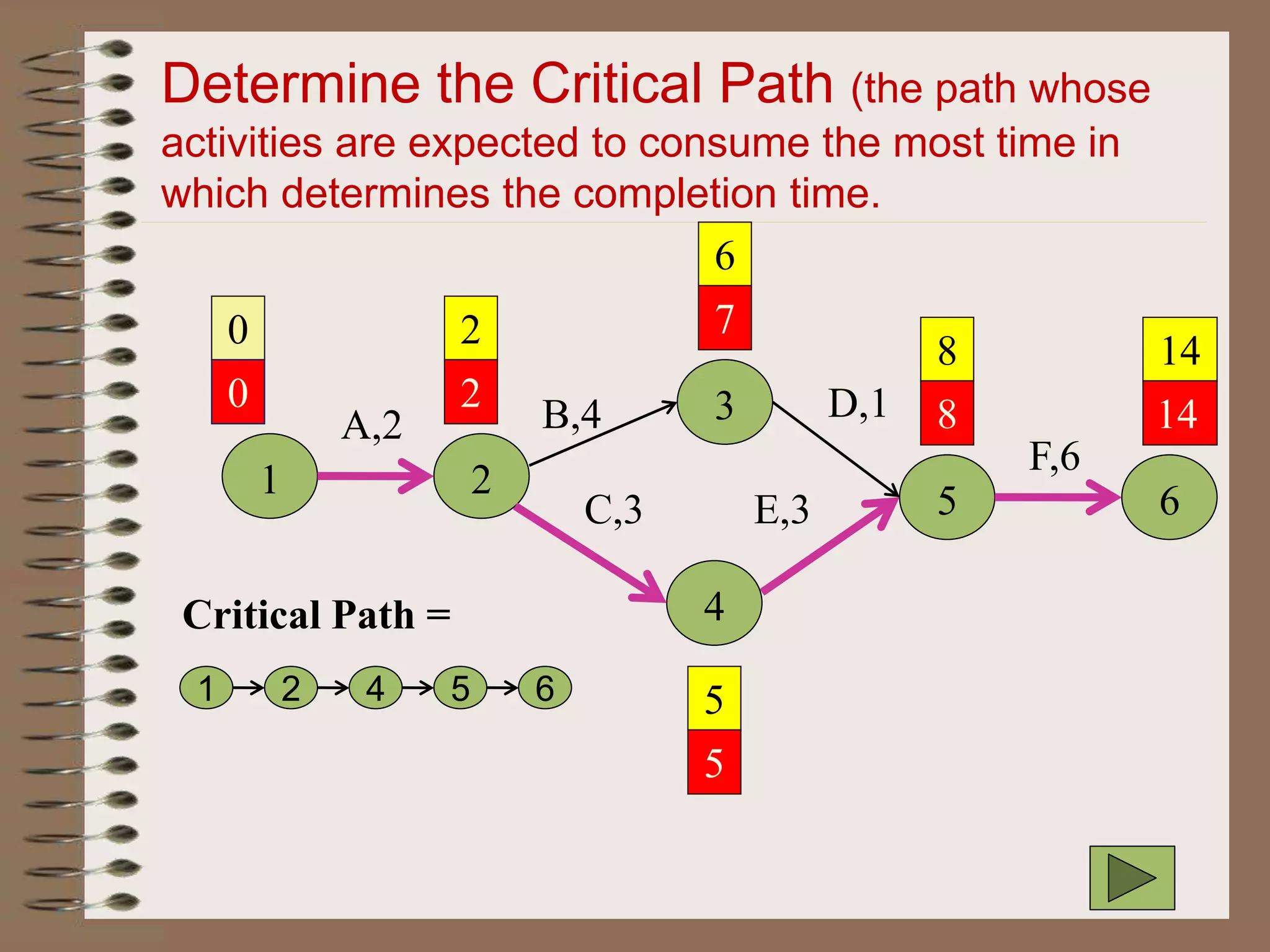
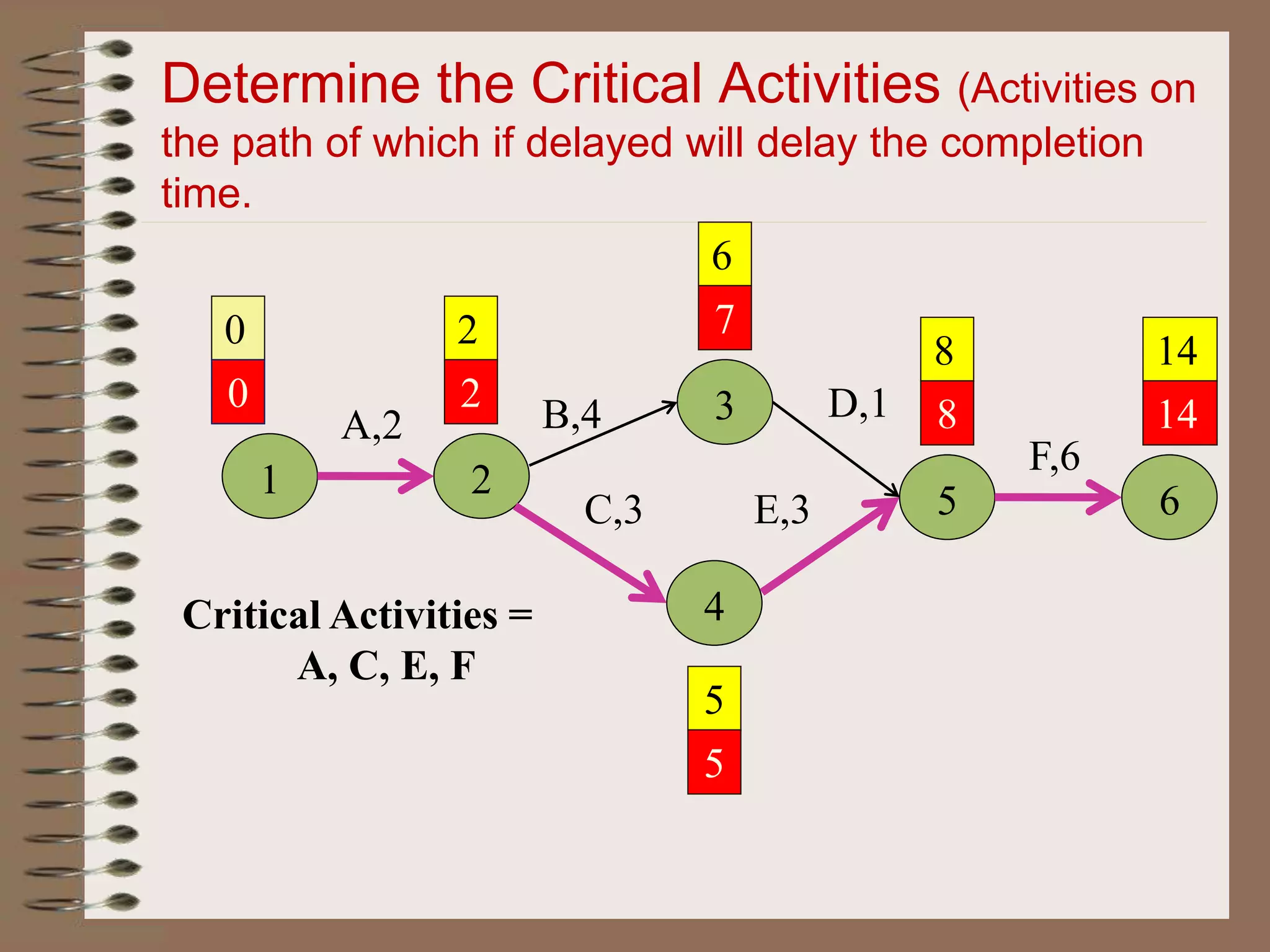
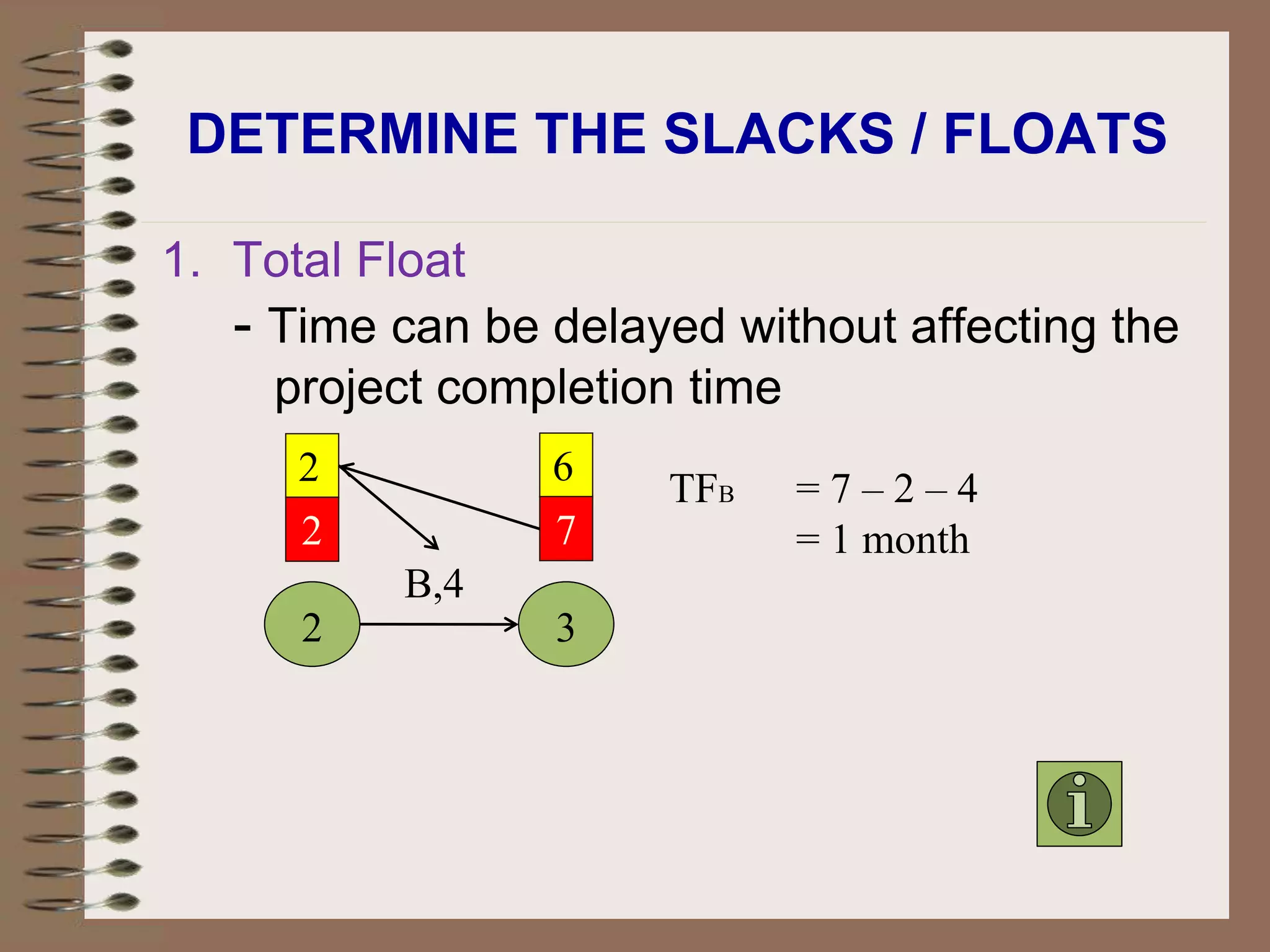
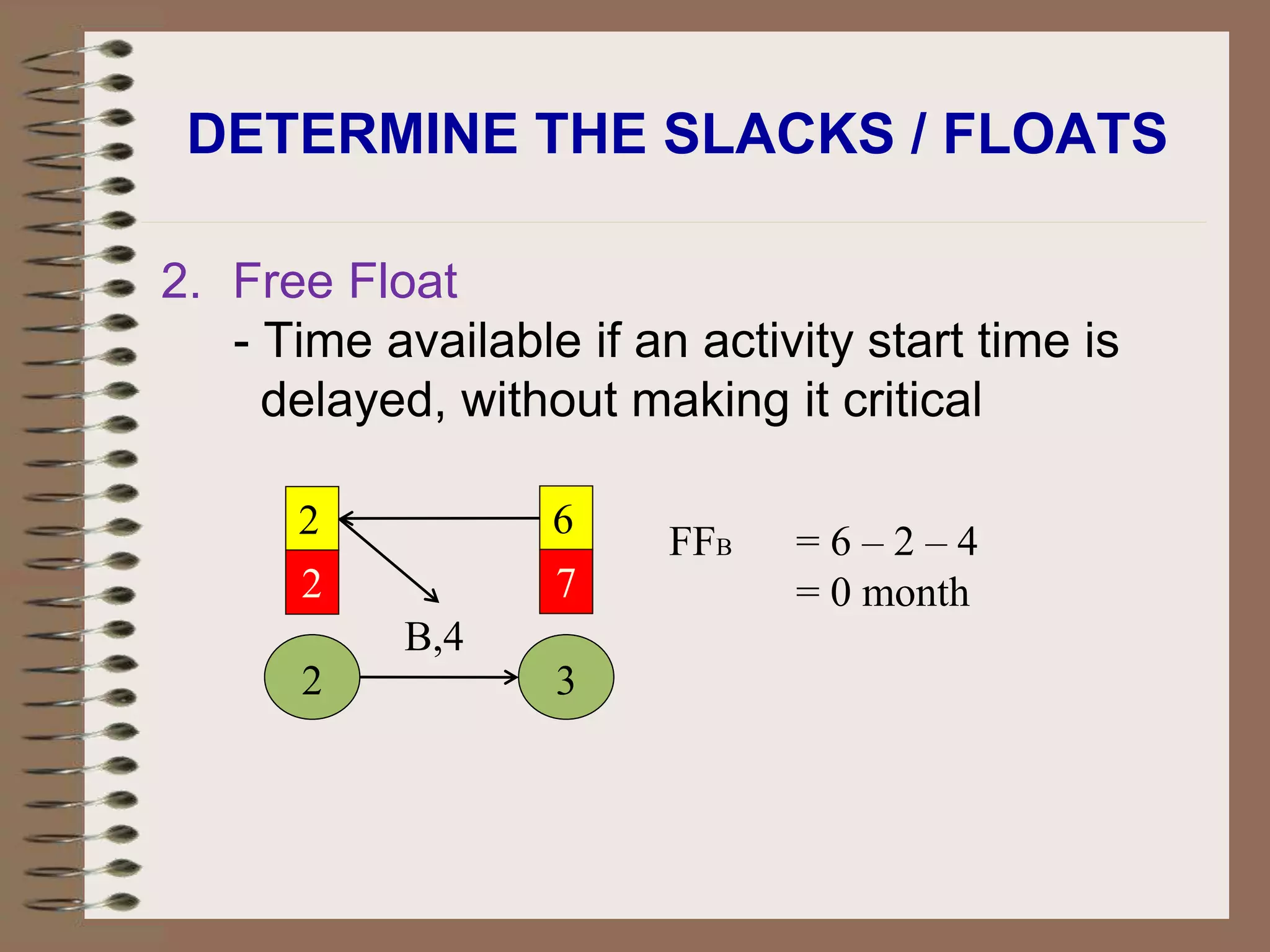
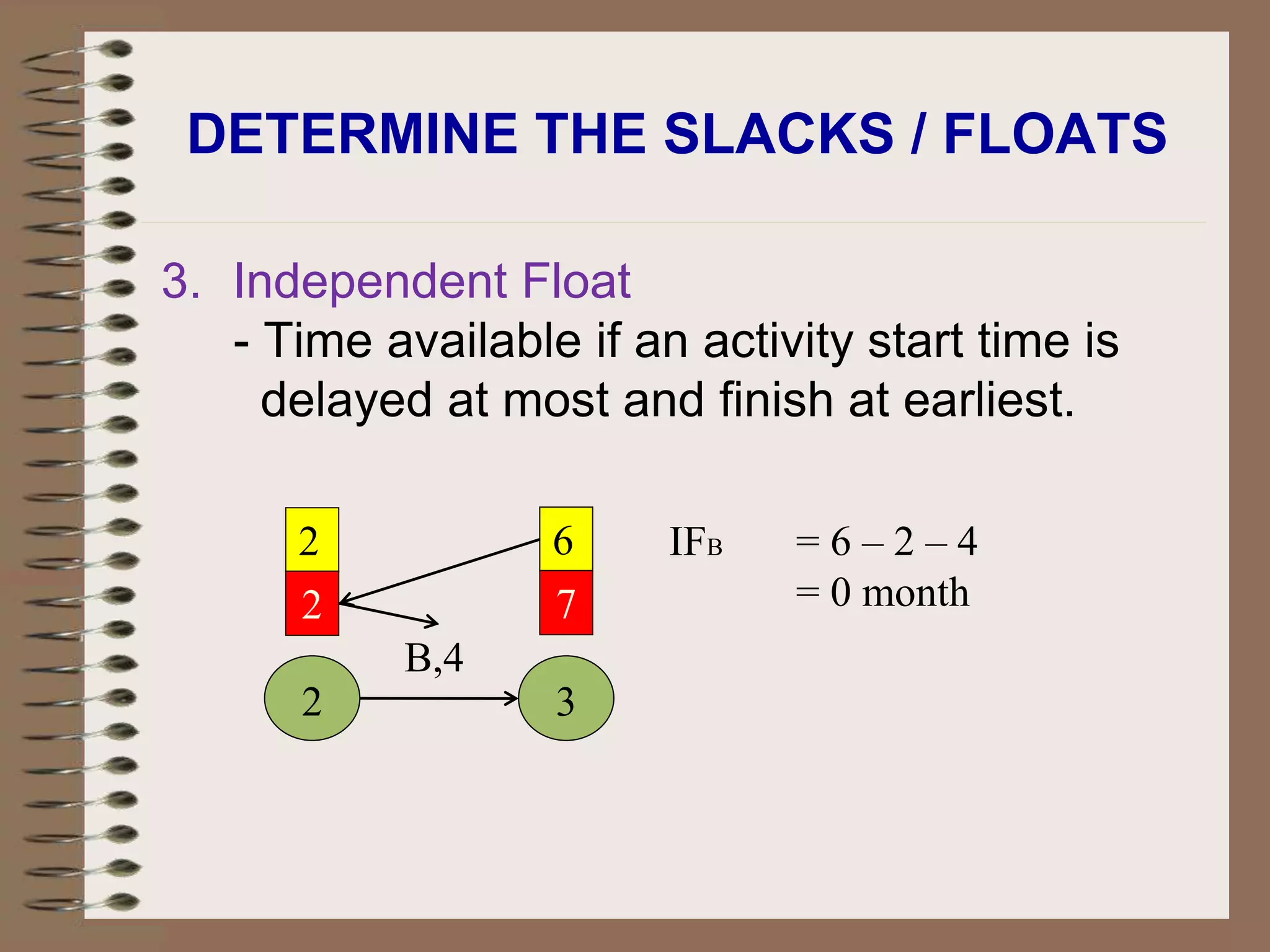
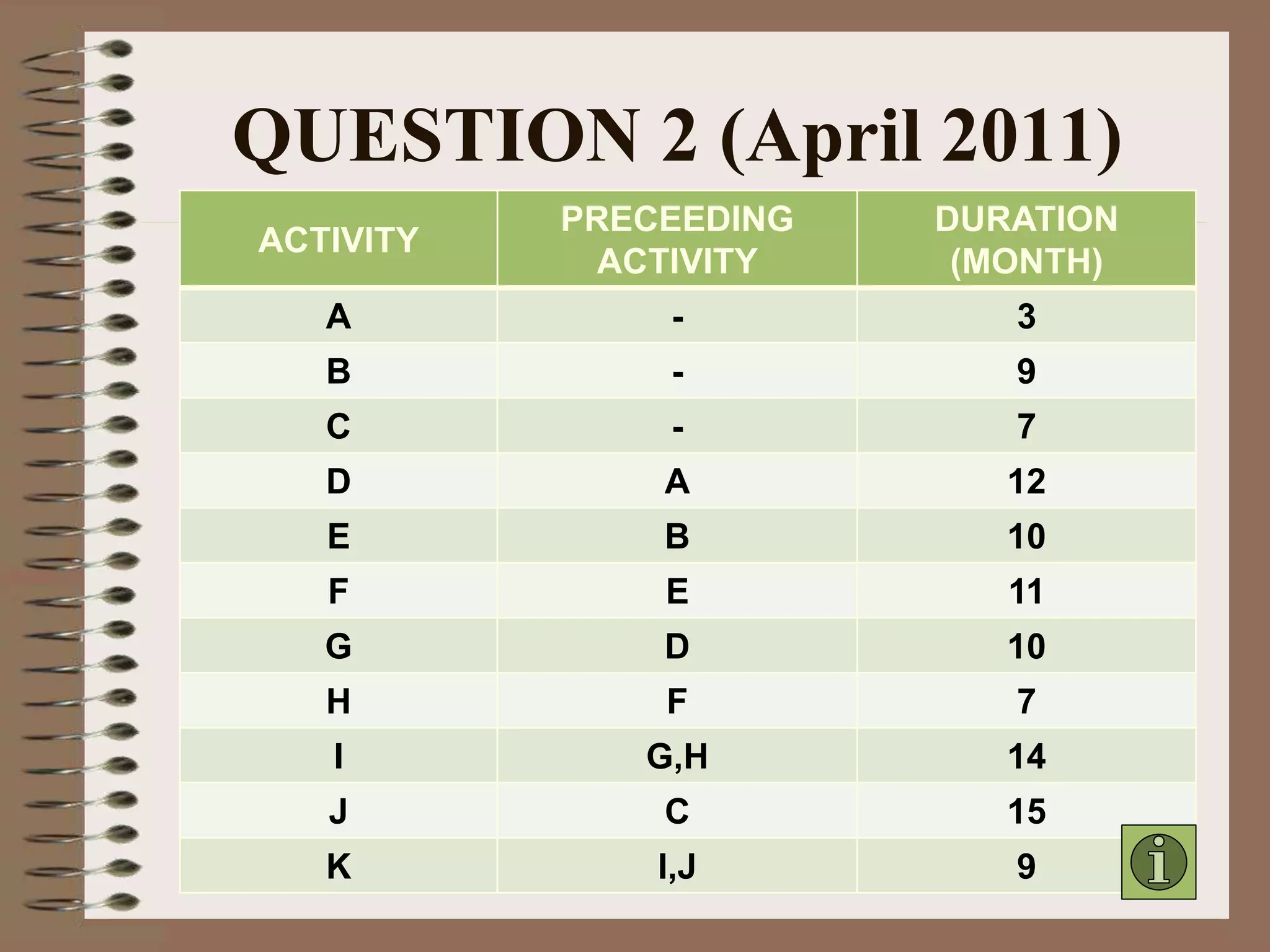
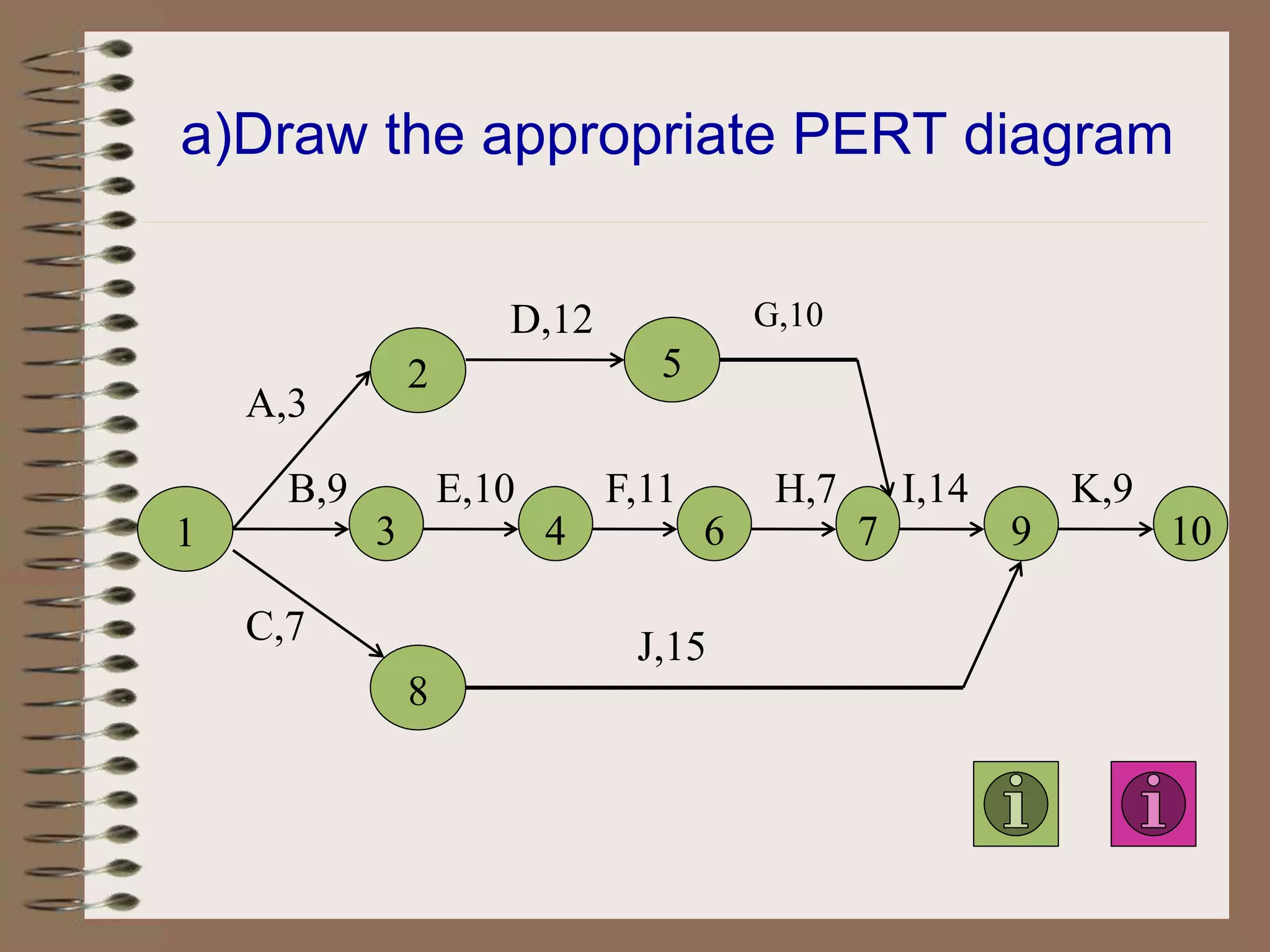
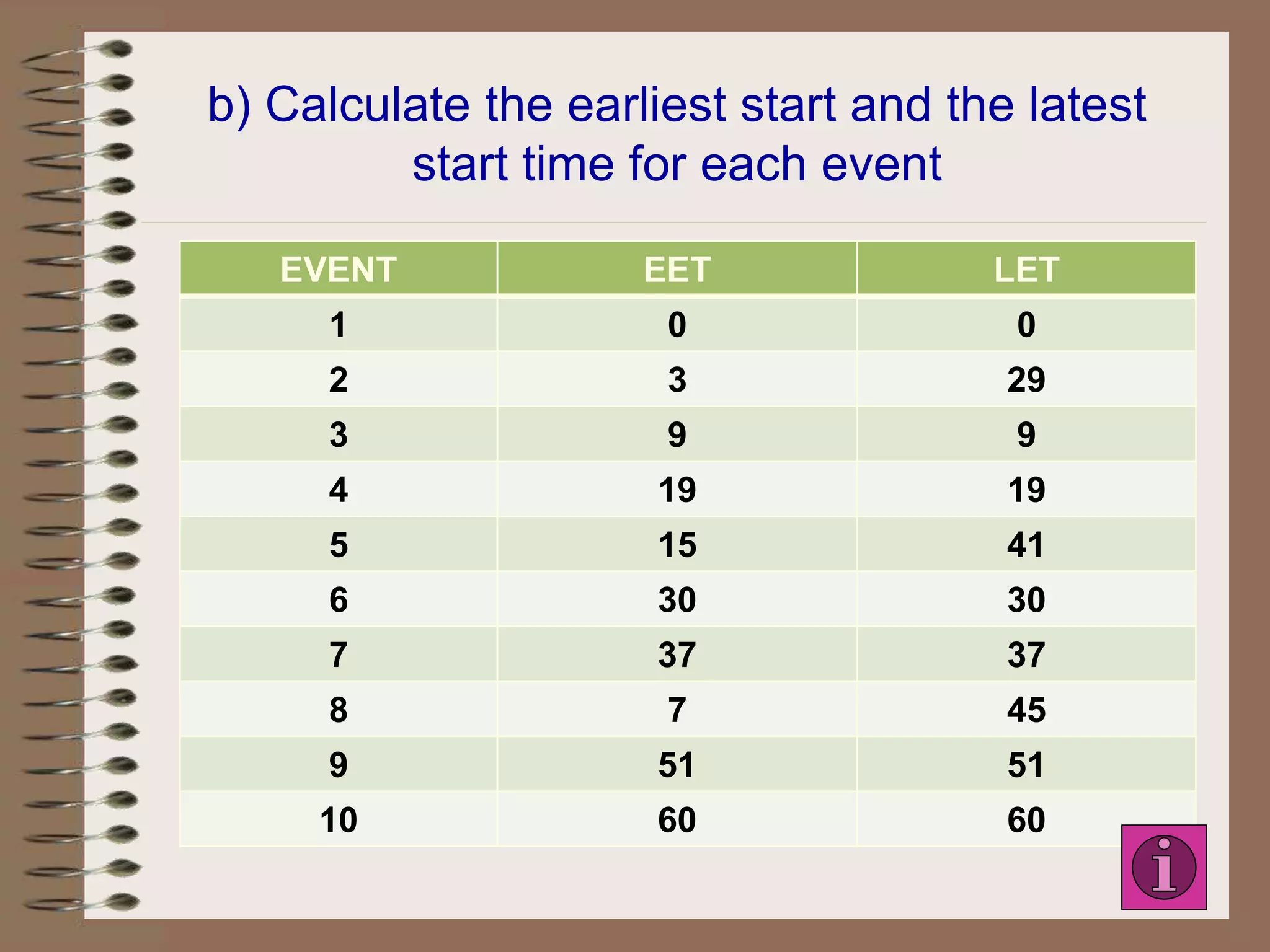
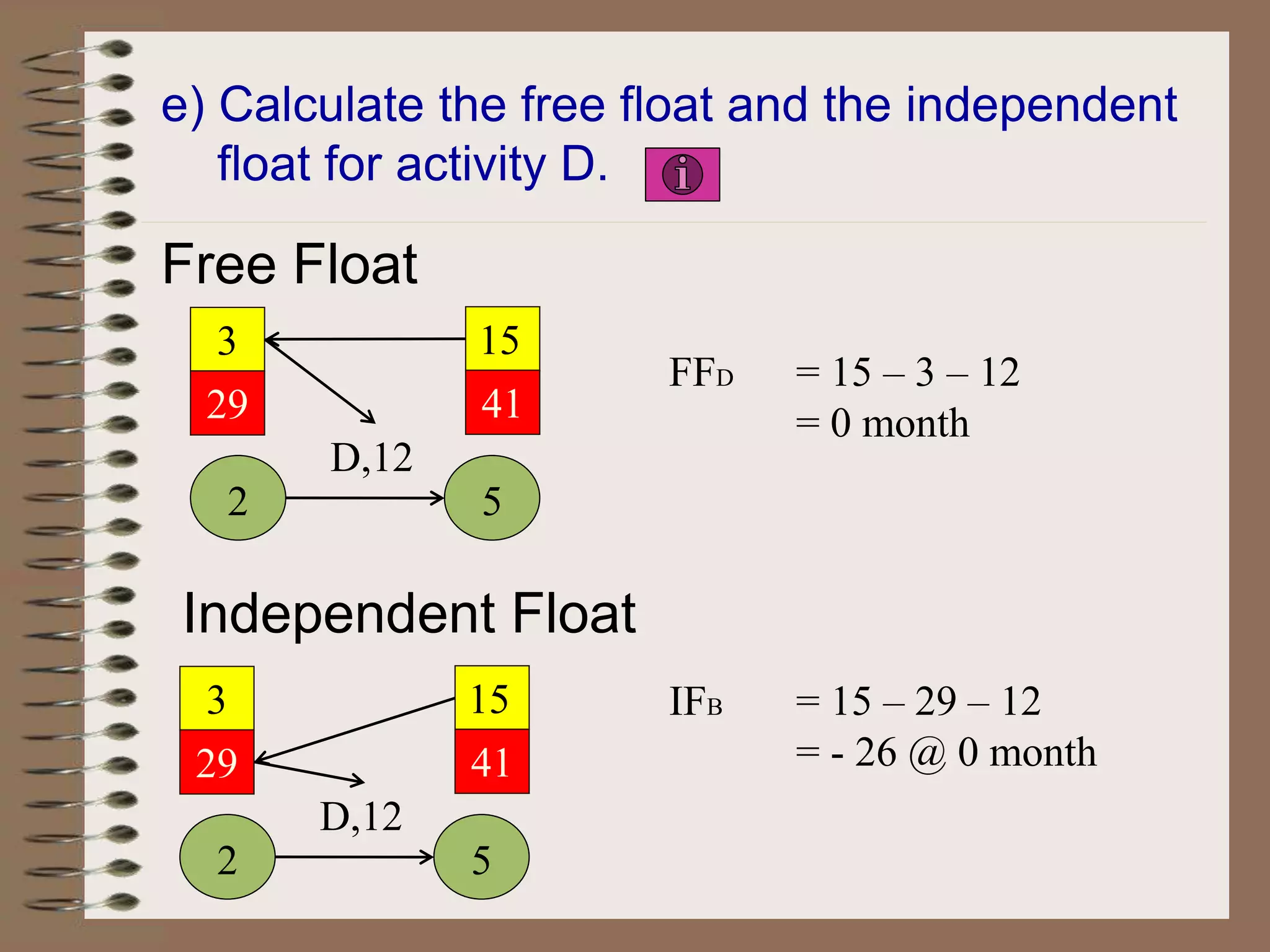
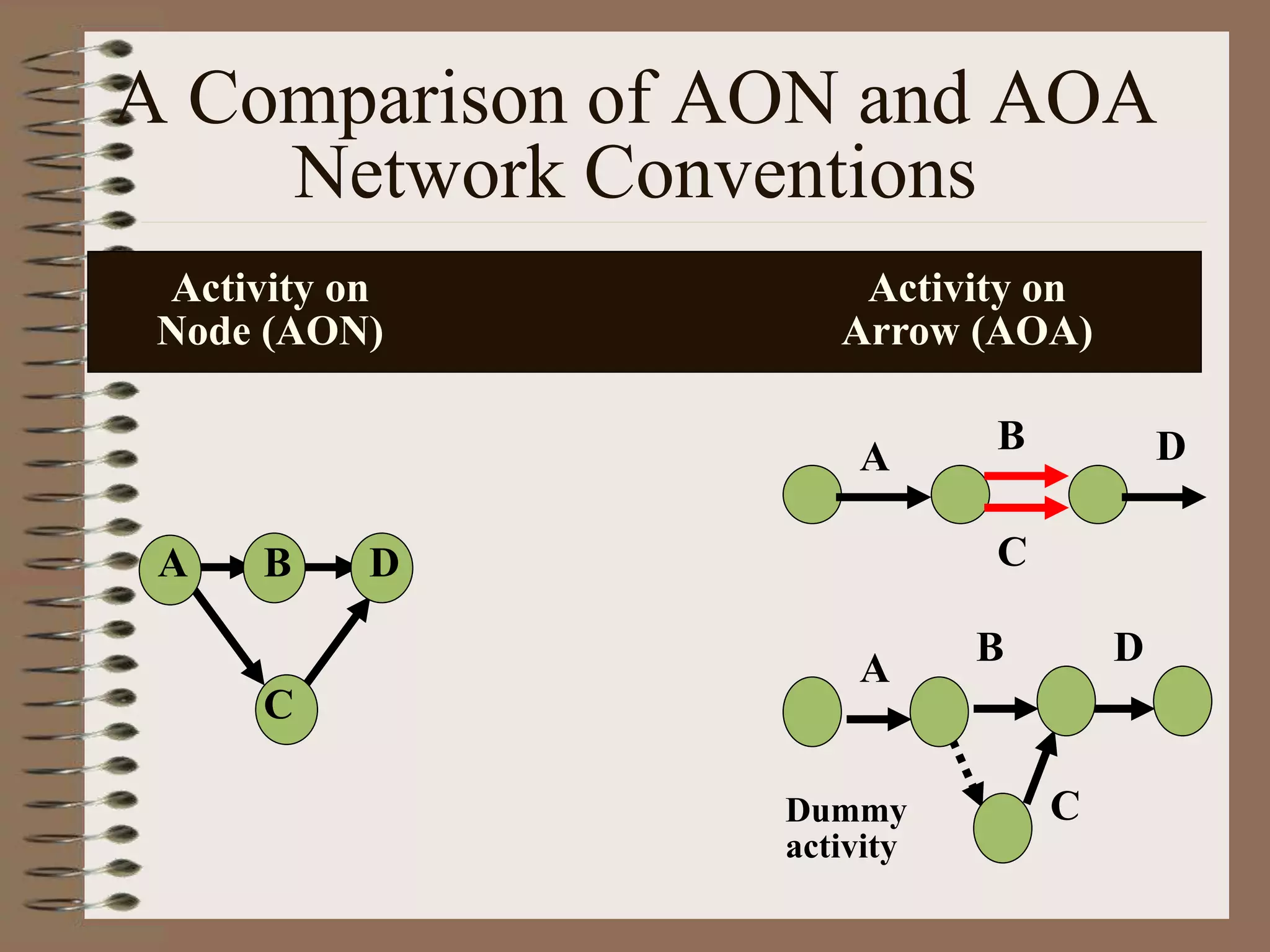
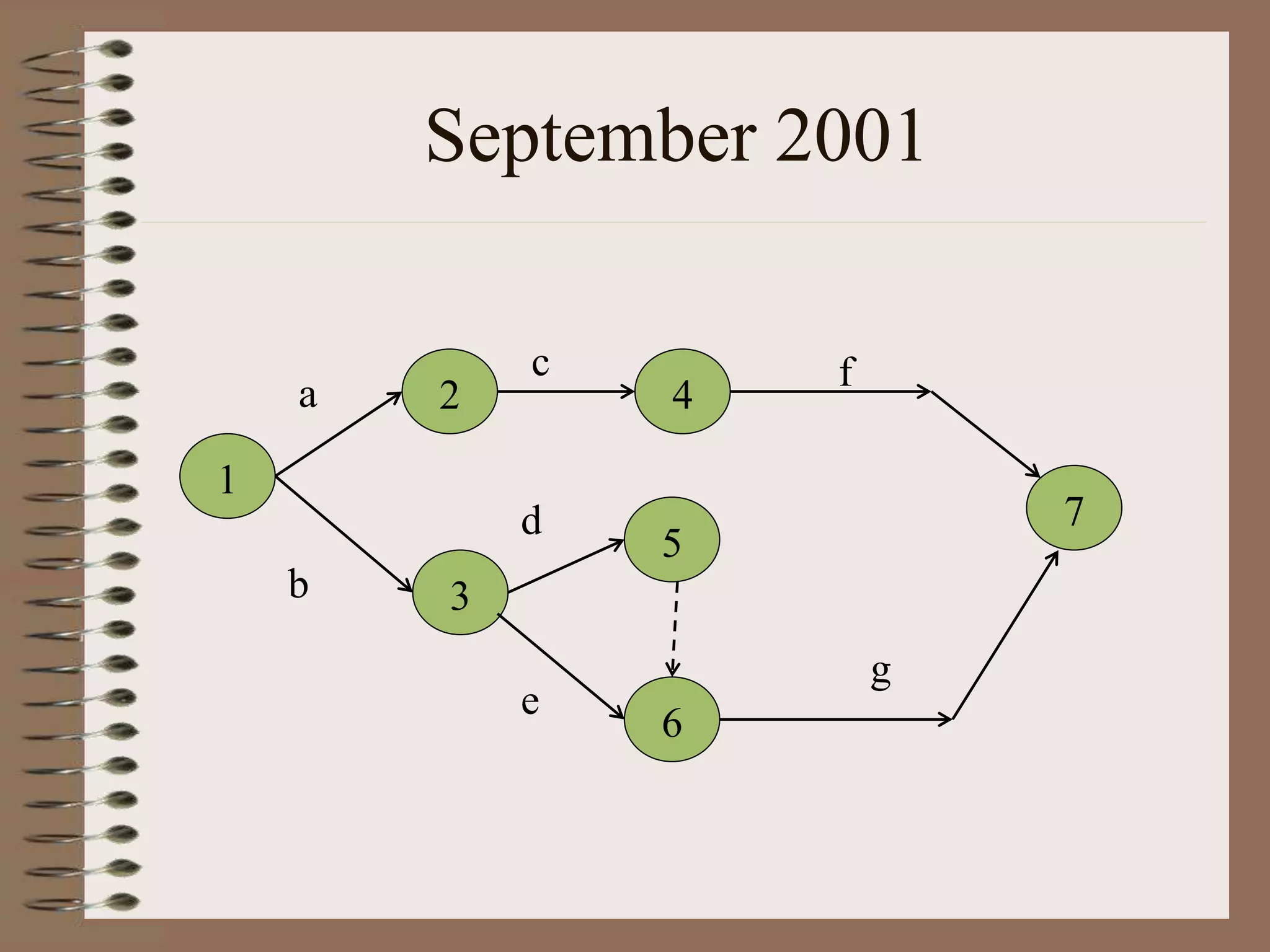
This document discusses project management and the critical path method technique. It defines project management as planning, directing, and controlling resources to meet time, cost, and technical constraints. The critical path method allows project managers to identify the critical activities and completion time of a project by determining the earliest and latest times of each activity. The document provides examples of constructing critical path networks and calculating key timing metrics to schedule and control a project.