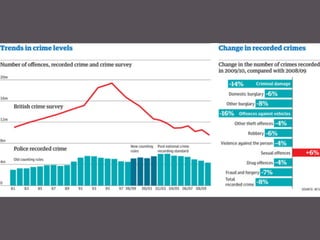
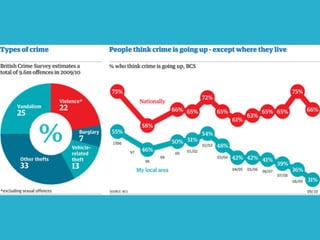
This document summarizes several key theories of crime and deviance from sociological perspectives, including functionalism, Marxism, interactionism, and feminism. It also discusses biological explanations, agencies of social control, and aspects of crime statistics and gender. Functionalism views deviance as having both dysfunctional and functional roles in society. Marxism sees crime and deviance examined through a conflict perspective. Interactionism focuses on the interaction between those defined as deviant and those defining them. Feminism challenges the neglect of gender in prior theories.