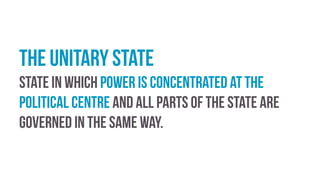
The British constitution is an uncodified system comprised of written and unwritten rules. It has adapted over time through incremental reforms rather than by replacing the existing framework. Recent reforms have included devolving some powers to Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland; incorporating the European Convention on Human Rights; and establishing independent electoral authorities. However, parliamentary sovereignty, the concentration of power in Westminster, and an outdated electoral system remain ongoing weaknesses according to critics of the traditional British constitutional model.