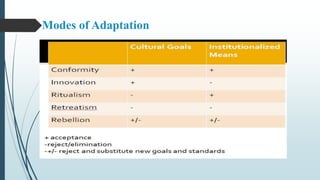
Strain theory posits that societal pressure to achieve socially accepted goals through legitimate means can create strain, leading to deviant or criminal behaviors. Emile Durkheim first developed the concept of anomie to describe a lack of social norms. Robert Merton expanded on this, arguing that a disjunction between cultural goals and legitimate means of achieving them can result in innovation (crimes), ritualism, retreatism, or rebellion. Albert Cohen focused on how status frustration from blocked opportunities can lead to reaction formation and delinquent subcultures. Criticisms argue these theories may overdetermine criminal behavior and not account for alternative value systems.