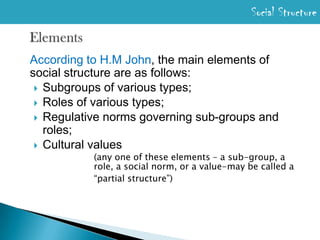
The document defines key concepts related to social structure and anomie. It discusses how social structure refers to the arrangement of persons in institutionally defined relationships and includes subgroups, roles, norms, and cultural values. Anomie is defined as a lack of norms or their breakdown, which was first introduced by Durkheim to explain deviant behavior resulting from changes in society. Merton later adopted the idea of anomie to develop strain theory, defining it as a discrepancy between social goals and legitimate means to achieve them. The document also discusses how communalism and casteism can lead to a state of normlessness or anomie.