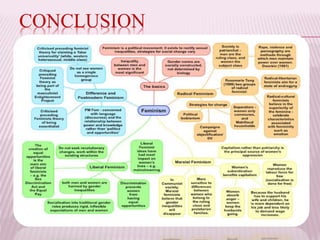
Feminism is a collection of movements and ideologies that work to establish political, social, and economic rights for women. The document outlines the history and waves of feminism, including the first wave in the late 19th century which focused on women's suffrage, and the second wave in the 1960s which aimed to end patriarchy and gain rights to education and careers for women. It also discusses feminist theory, different feminist movements and ideologies, and the phases of feminism in India from British colonization to independence to modern times. The overall goals of feminism have been to understand and critique gender inequality and power imbalances in society.






![FEMINIST THEORY
Feminist Theory is the
extension of feminism
into theoretical or
philosophical fields.
It encompasses work in
a variety of disciplines:]
I. Anthropology
II. Sociology
III. Economics and
women’s studies
IV. Literary criticism, art
history and
philosophy
Feminist theory aims to understand
gender inequality and focuses on
gender politics, power relations. While
providing a critique of these social and
political relations, much of feminist
theory also focuses on women interest
and rights.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/feminism-210530052806/85/Feminism-7-320.jpg)