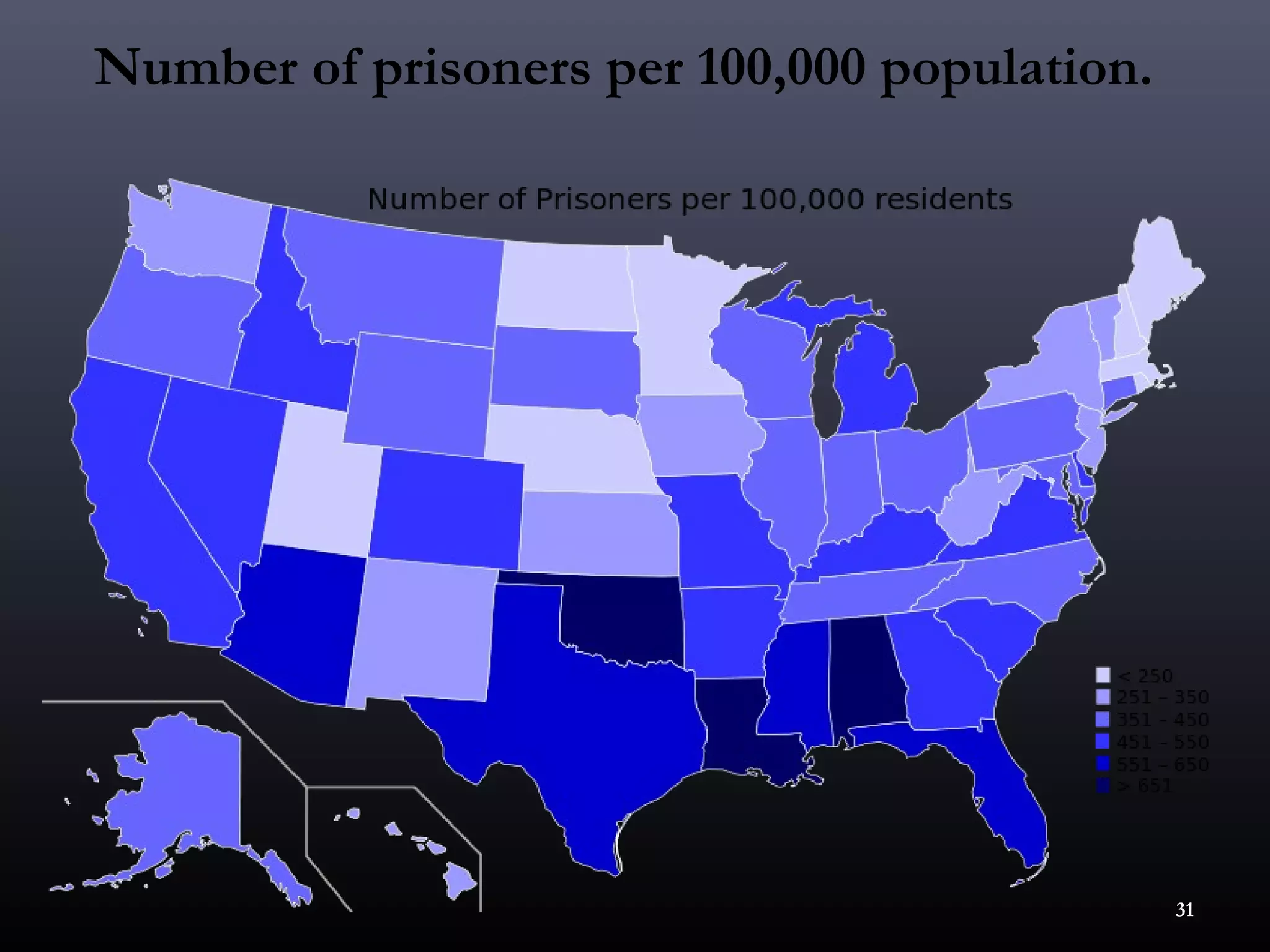
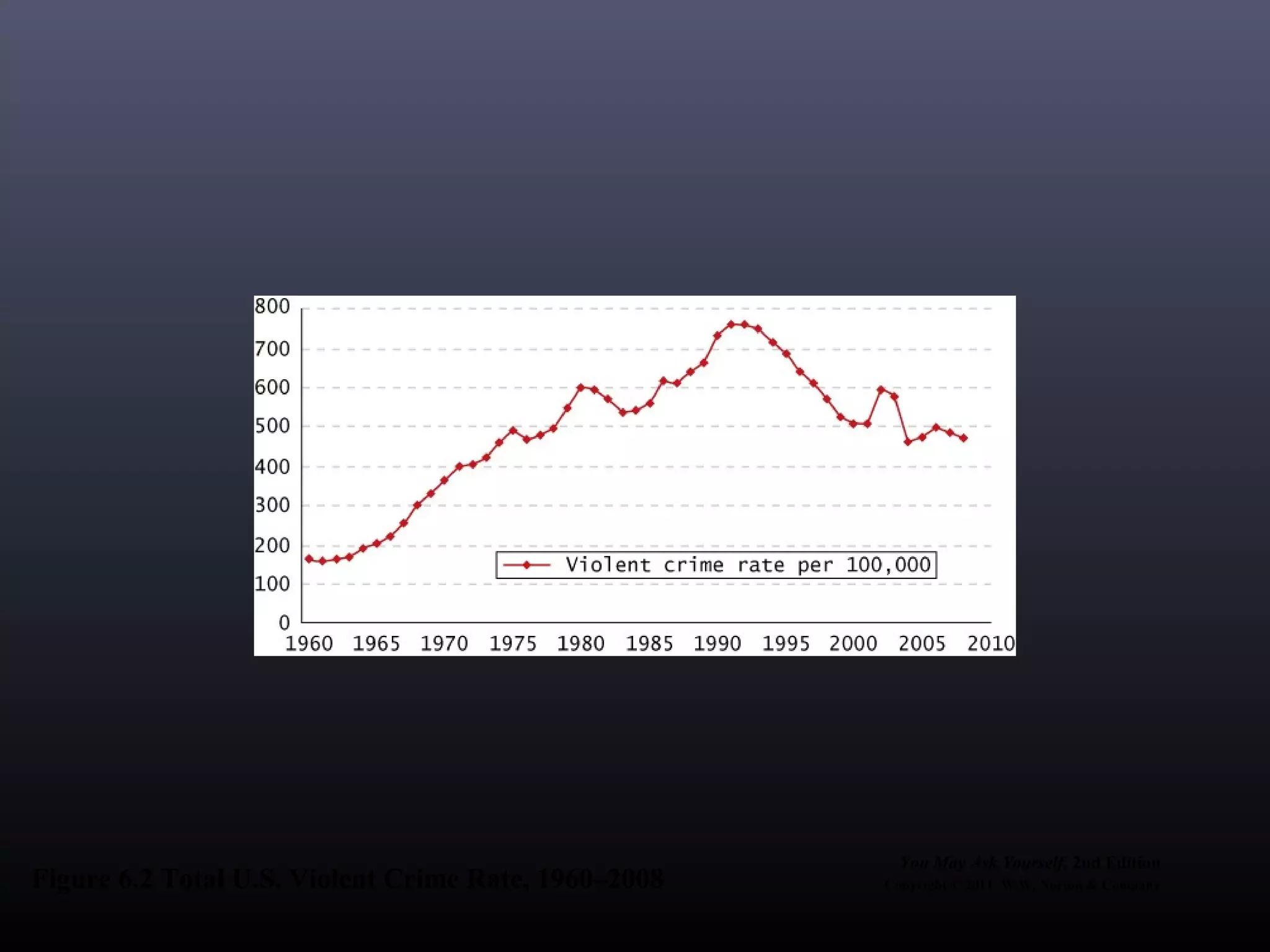
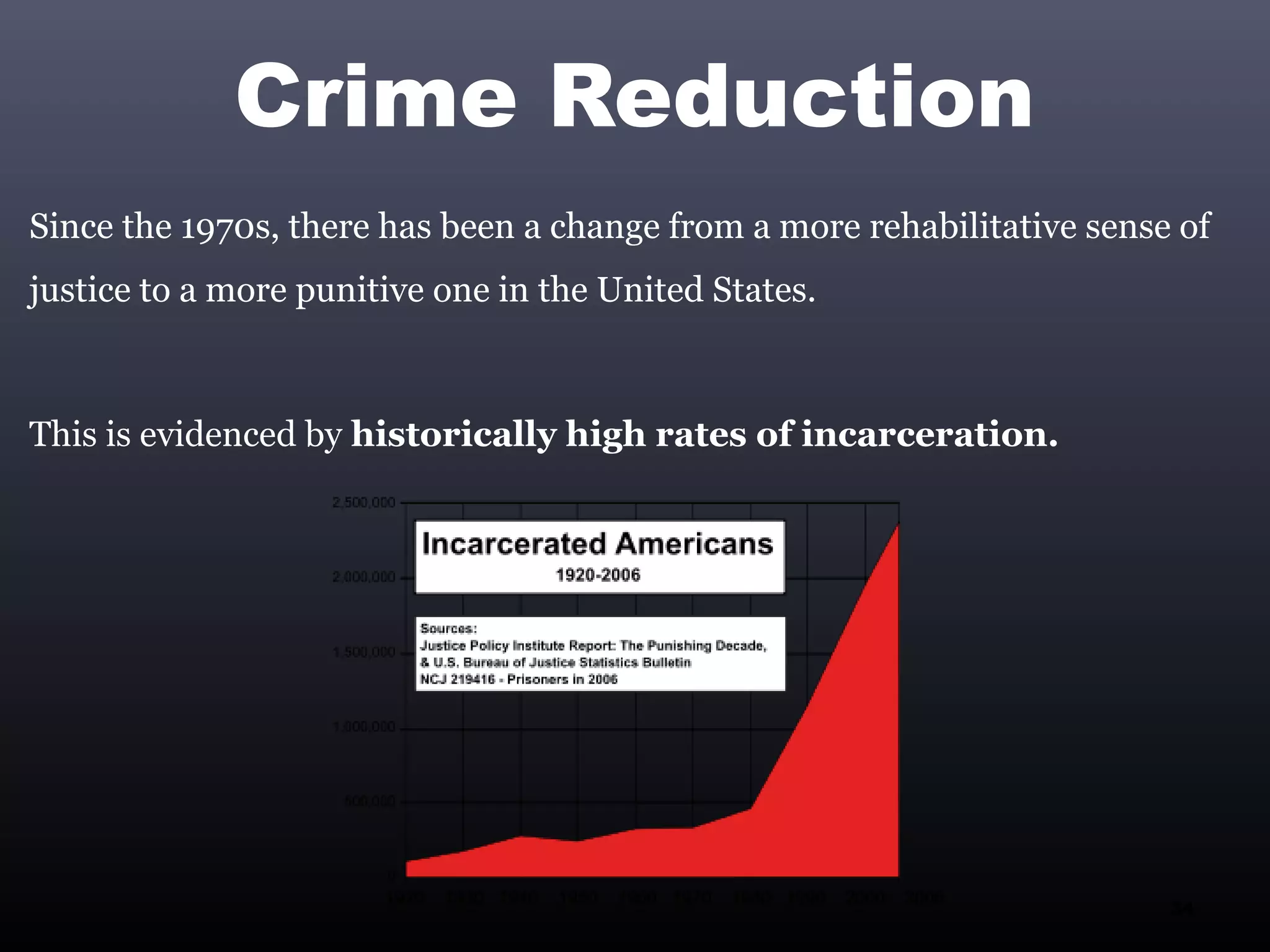
1) Social deviance refers to any violation of established social norms, ranging from minor informal transgressions to serious criminal acts. What is considered deviant can change over time.
2) Sociological theories of deviance examine how social norms are established and enforced through both informal social pressures and formal laws and punishments. They also seek to understand why some individuals violate norms.
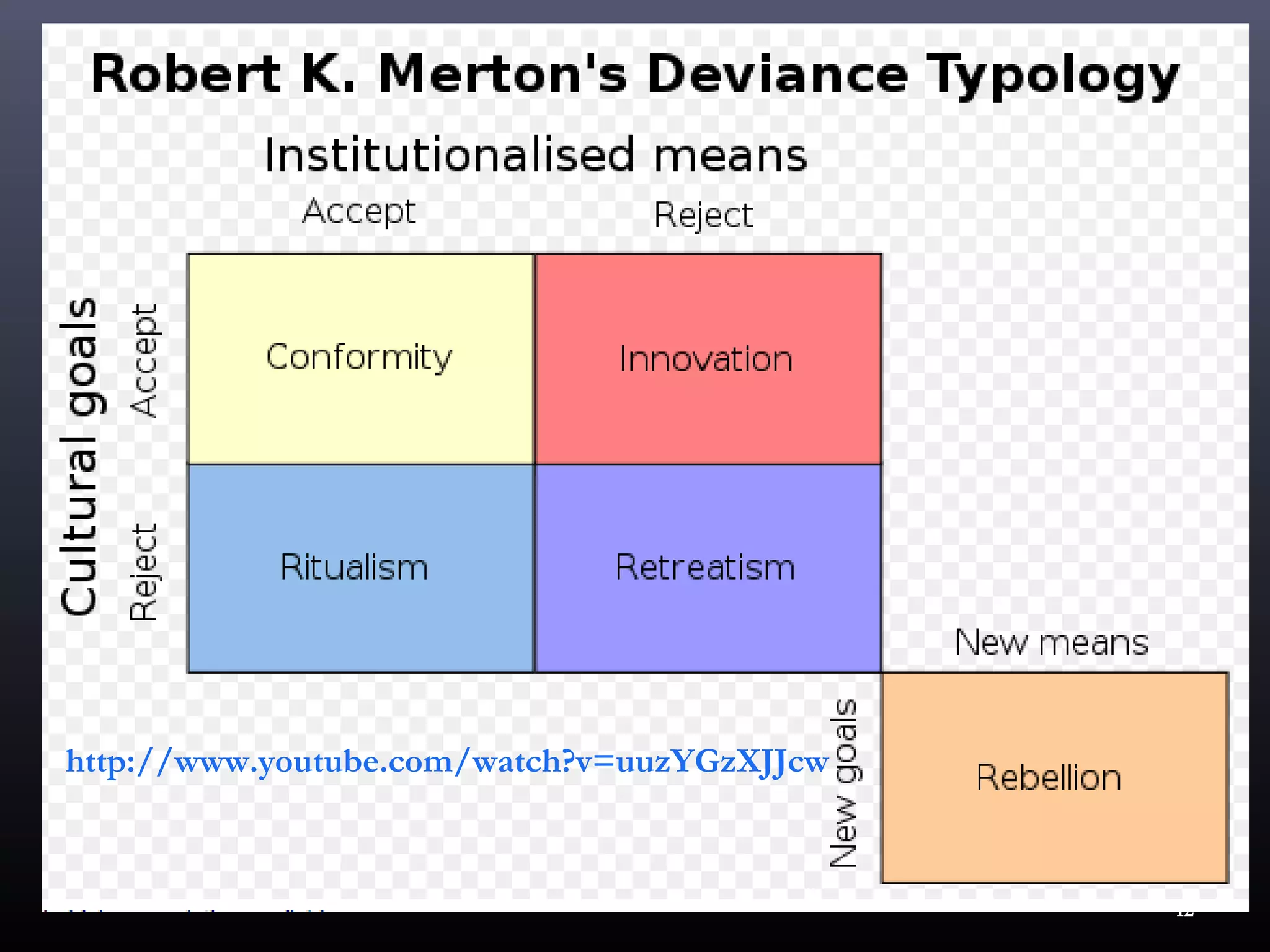
3) Symbolic interactionist theories focus on how social interactions and labels influence perceptions of deviance. They view deviance as a social construct rather than an intrinsic quality.