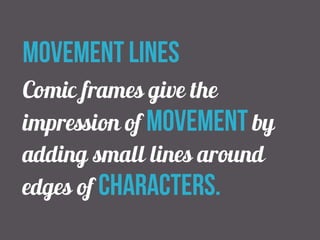
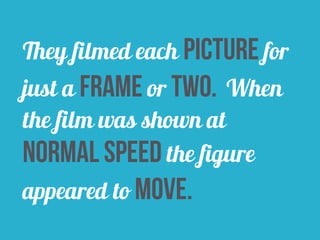
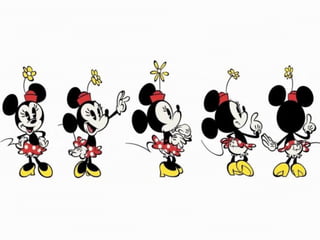
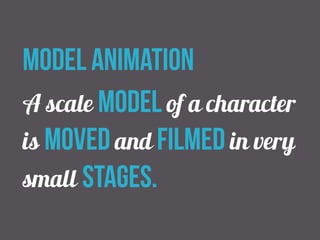
The document discusses comics, cartoons, and animation. It identifies three lesson objectives: 1) identify codes and conventions, 2) understand how they attract audiences, and 3) identify animation types and effects. It discusses character types like heroes and villains. It also outlines techniques used in comics like speech bubbles and thought bubbles. Finally, it describes animation techniques such as line drawing, model animation, and computer-generated imagery.