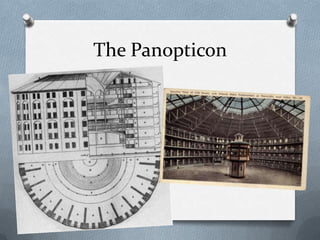
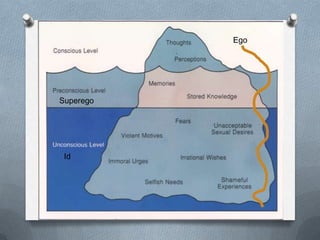
This document discusses deviance and social control. It defines deviance as variations from social norms and expectations. While some deviance is normal, too much or extreme deviations can disrupt social order. Deviance performs functions like defining norms but can also have dysfunctions. Society uses internal and external social controls like sanctions to encourage conformity. Theories of deviance include strain theory, conflict theory, and symbolic interactionist perspectives like differential association theory and labeling theory.