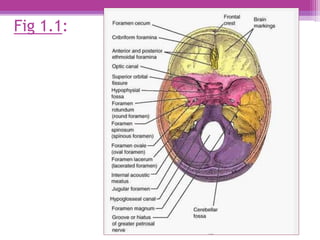
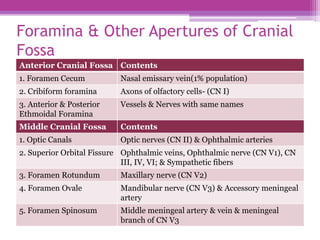
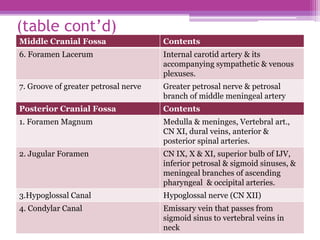
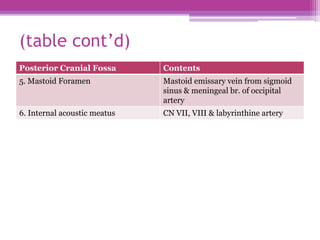
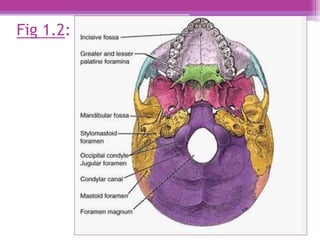
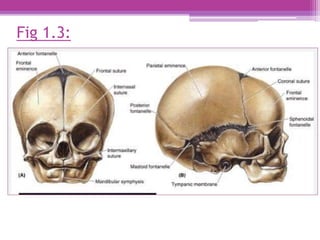
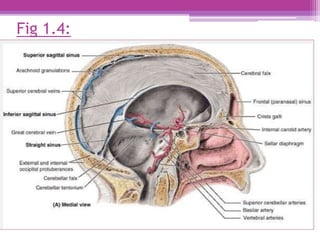
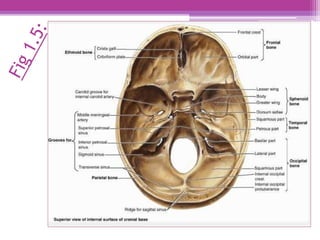
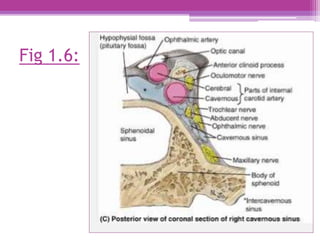
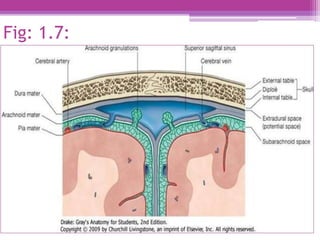
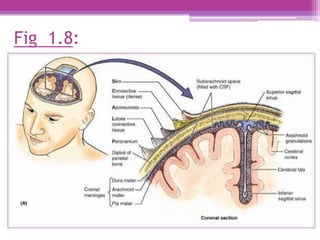
The internal surface of the cranial base has three large depressions called cranial fossae: the anterior, middle, and posterior cranial fossae. The anterior fossa is the highest and lodges parts of the frontal lobes. The middle fossa is butterfly-shaped and contains the sella turcica. The posterior fossa is the largest and deepest, lodging the cerebellum, pons, and medulla oblongata. Various foramina and sinuses penetrate the cranial fossae to allow passage of nerves, vessels and CSF. Dural folds such as the falx cerebri and tentorium cerebelli further subdivide the cranial cavity.