1. The document discusses the dural venous sinuses, their characteristics, classification, and the cavernous sinus in detail.
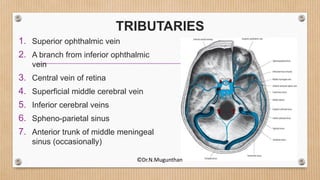
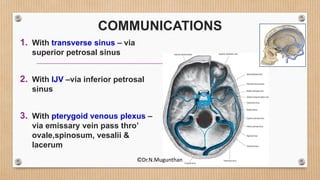
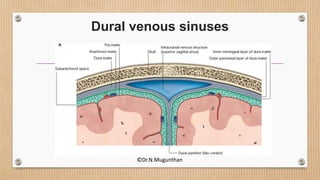
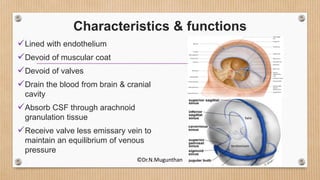
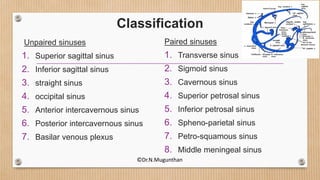
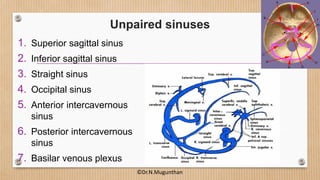
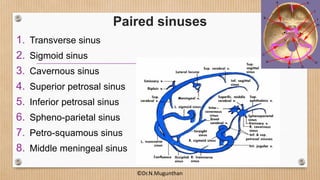
2. The dural venous sinuses drain blood from the brain and cranial cavity, absorb CSF, and receive valveless emissary veins. They are classified into unpaired and paired sinuses.
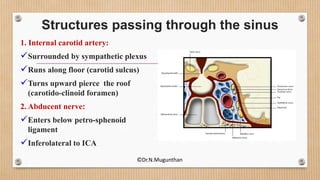
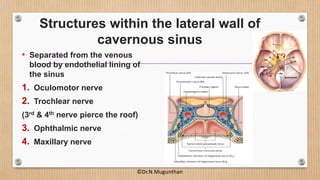
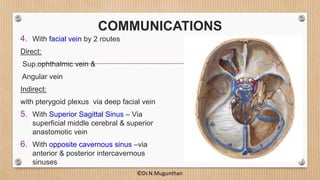
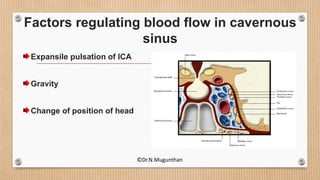
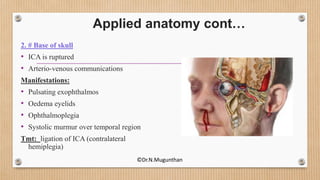
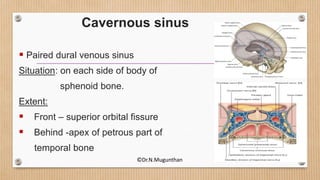
3. The cavernous sinus is a paired dural venous sinus located near the sphenoid bone. It contains the internal carotid artery and cranial nerves III and IV. Thrombosis or rupture of the cavernous sinus or internal carotid artery can cause symptoms like exophthalmos and ophthalmoplegia.


![RELATIONS
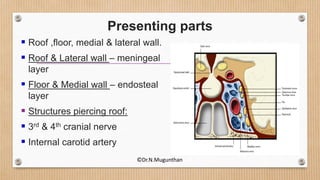
Superiorly:
• Optic chiasma
• ICA [after piercing roof -
backward & upward(Carotid siphon)]
Inferiorly:
• Sphenoidal air sinus
Medially:
• Pituitary gland
Laterally:
• Cavum trigeminale
• Temporal lobe (uncus)
©Dr.N.Mugunthan](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/duralvenoussinusescavernoussinus-dr-160307194205/85/Dural-venous-sinuses-cavernous-sinus-Dr-N-Mugunthan-11-320.jpg)