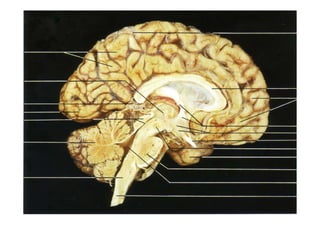
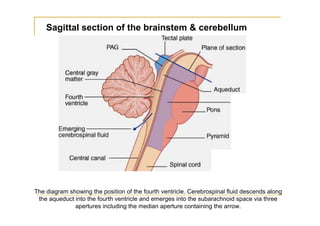
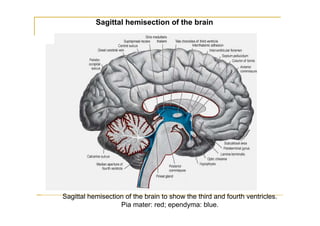
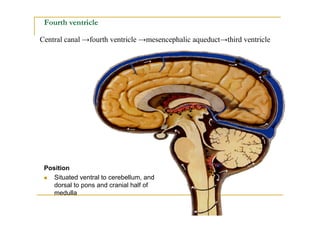
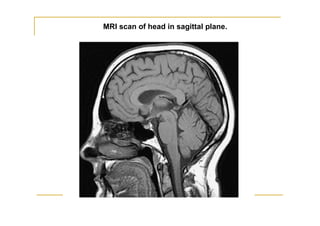
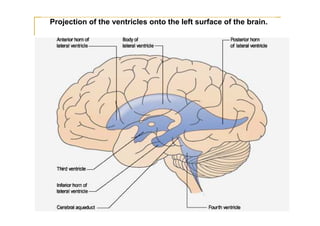
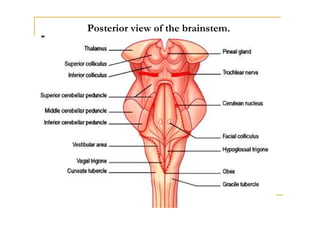
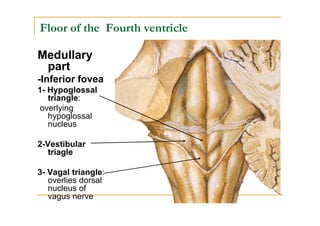
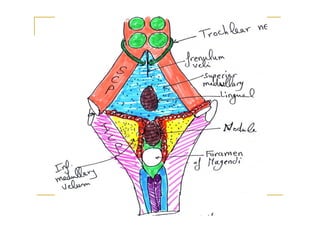
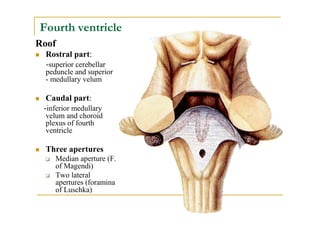
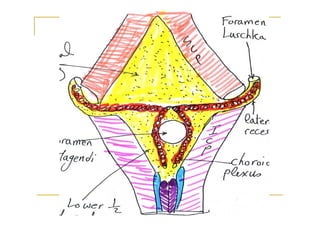
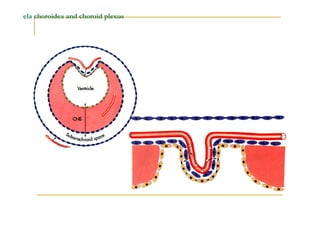
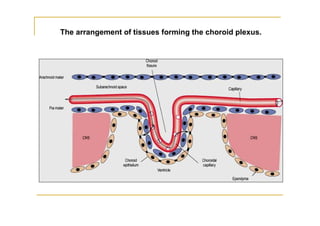
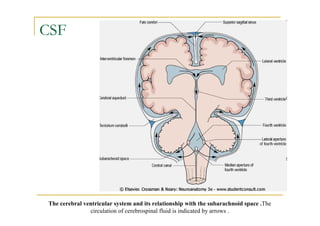
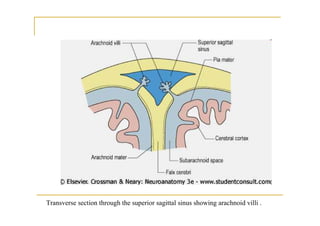
The fourth ventricle is located ventral to the cerebellum and dorsal to the pons and medulla. It is bounded laterally by the gracile and cuneate tubercles and inferior cerebellar peduncles, and superiorly by the superior cerebellar peduncle. Its roof is formed by the superior cerebellar peduncle and medullary velum. Its floor contains landmarks like the median sulcus, facial colliculus, and hypoglossal triangle. Cerebrospinal fluid circulates from the fourth ventricle through the median aperture and exits into the subarachnoid space through the foramina of Luschka and Magendi.