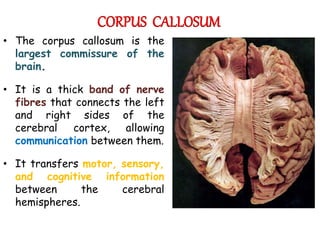
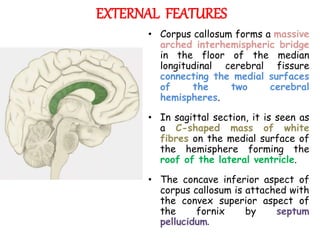
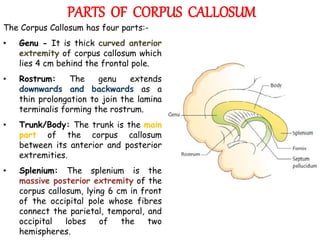
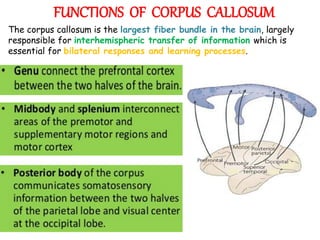
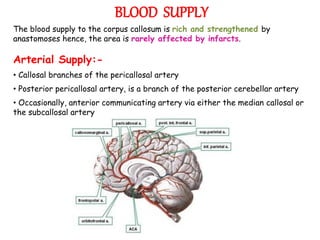
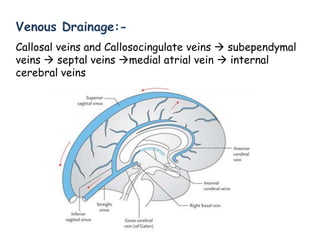
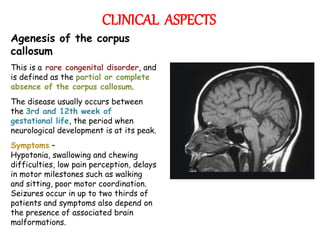
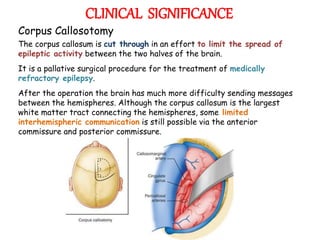
The corpus callosum is the largest commissure in the brain, connecting the left and right cerebral hemispheres and facilitating communication for motor, sensory, and cognitive processes. It comprises four parts: genu, rostrum, trunk, and splenium, and is well-supplied with blood, minimizing infarct risks. Clinical conditions related to the corpus callosum include agenesis, impingement syndrome, and disconnection syndrome, affecting visual perception, motor skills, and interhemispheric communication.