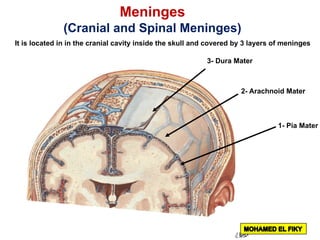
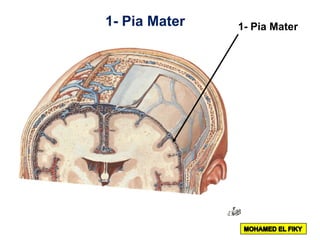
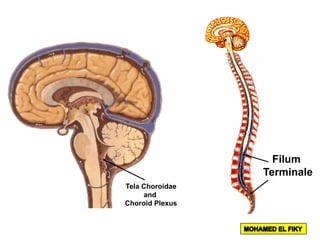
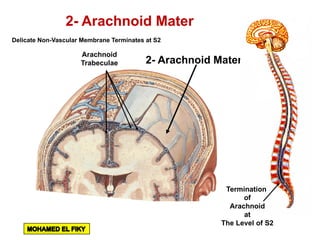
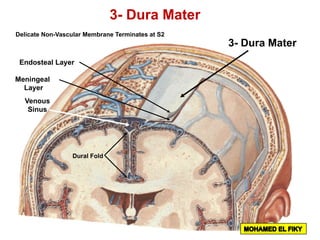
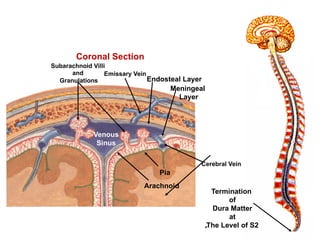
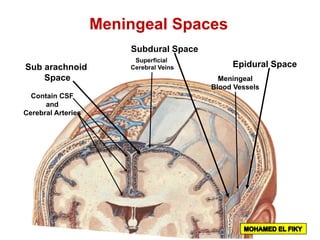
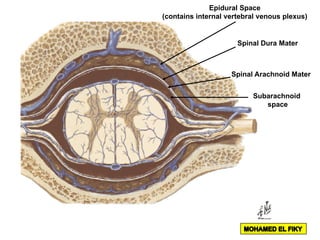
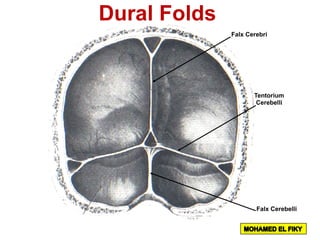
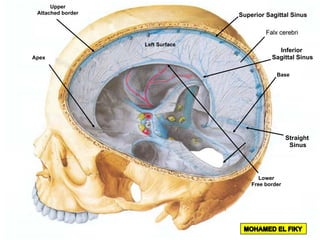
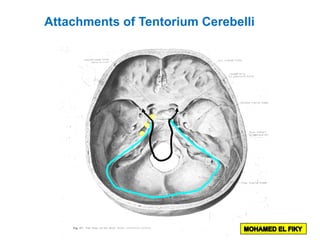
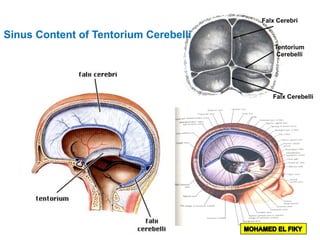
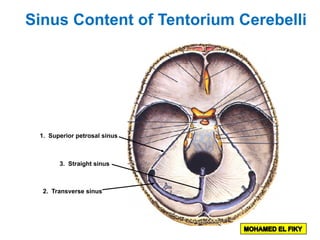
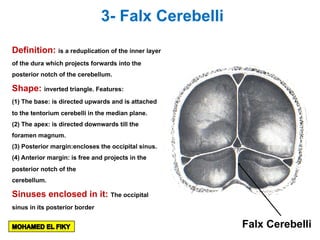
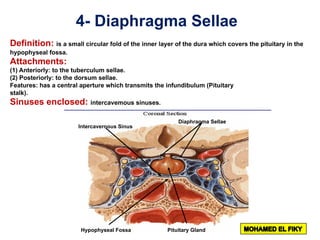
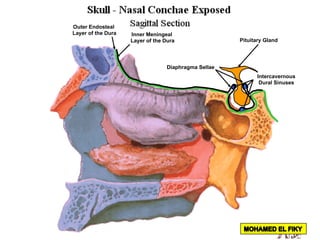
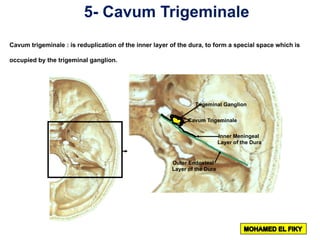
The document discusses the coverings and folds of the central nervous system. It describes the three layers of meninges - pia mater, arachnoid mater, and dura mater - that cover the brain and spinal cord. It then examines several dural folds in more detail, including the falx cerebri, tentorium cerebelli, falx cerebelli, diaphragma sellae, and cavum trigeminale. It notes the sinuses contained within these folds and their attachments. Finally, it provides brief descriptions of the nerve and blood supply to the dura.