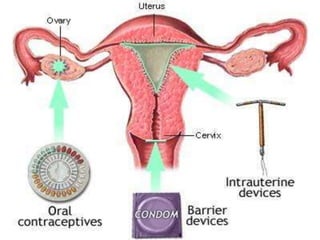
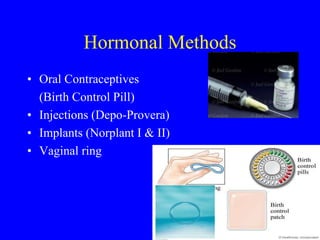
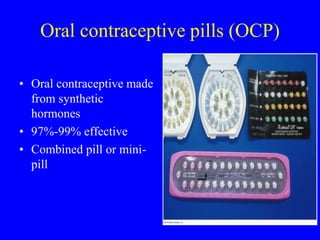
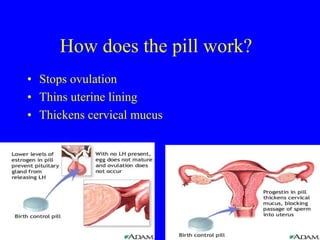
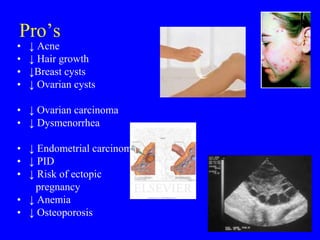
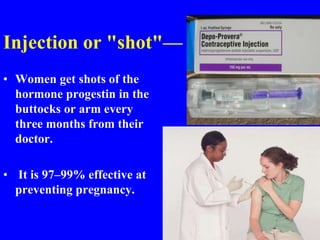
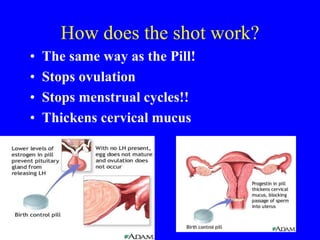
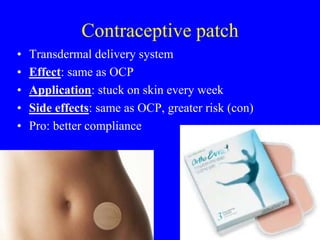
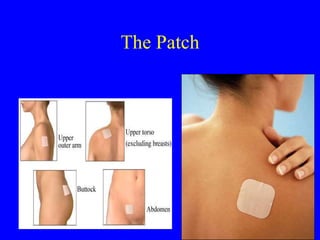
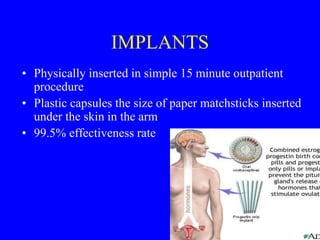
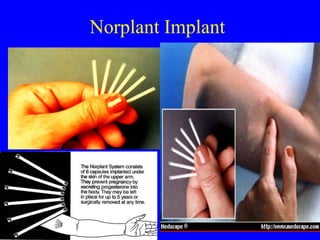
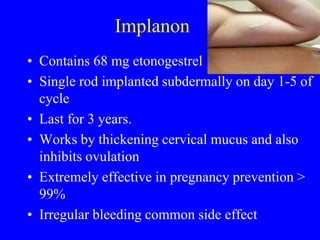
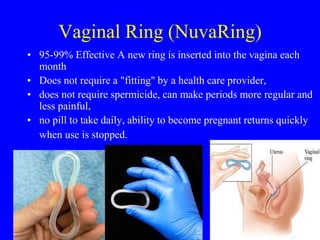
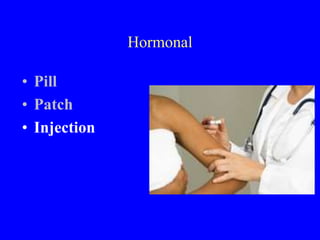
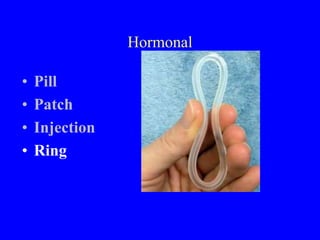
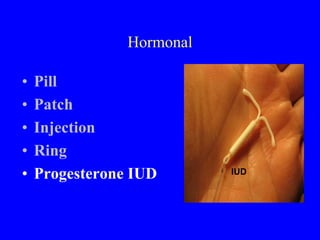
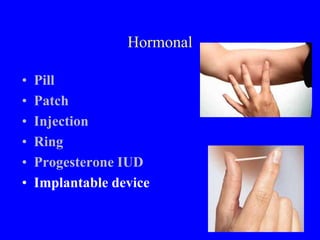
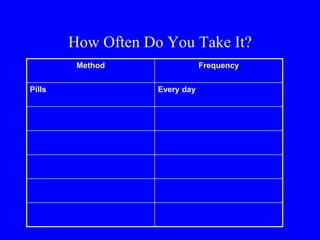
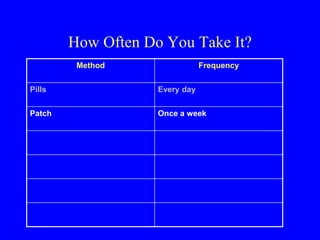
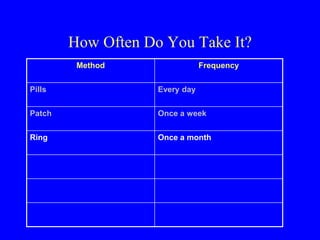
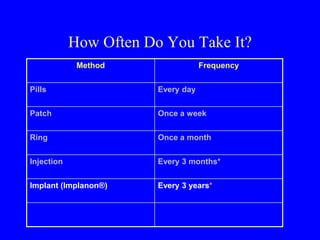
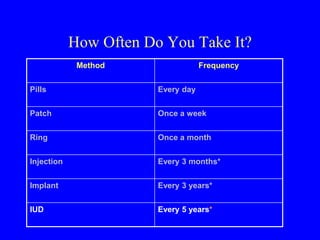
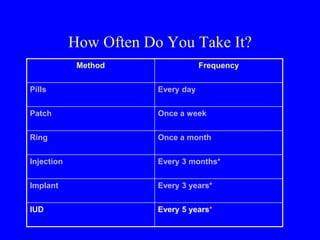
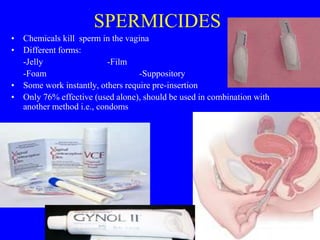
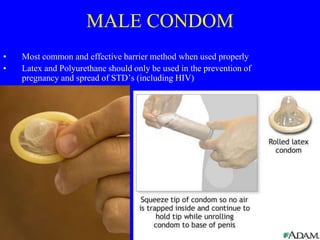
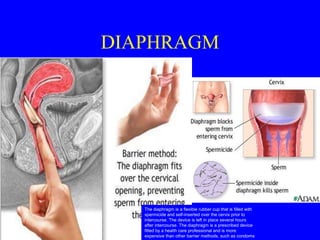
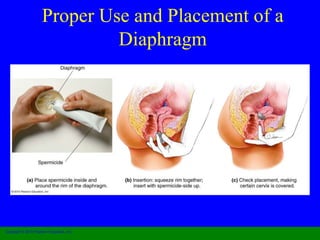
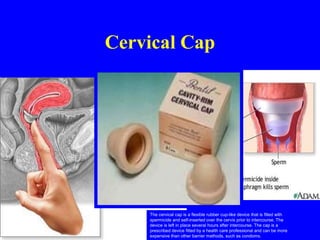
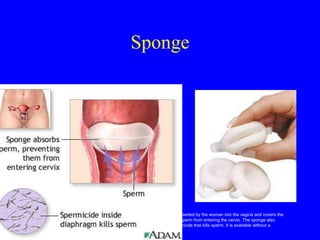
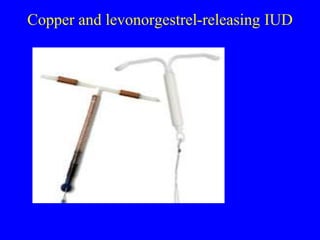
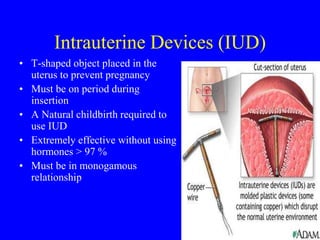
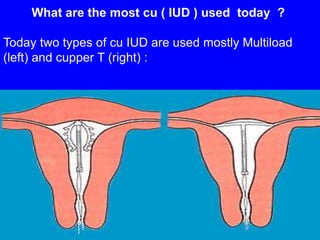
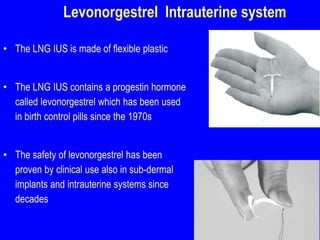
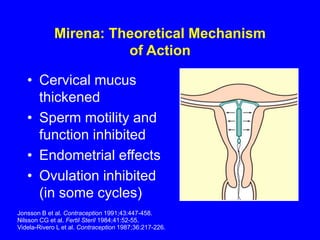
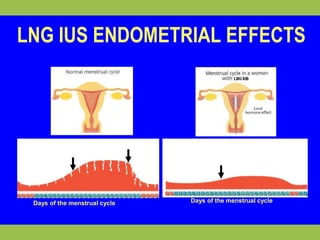
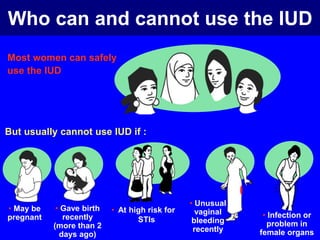
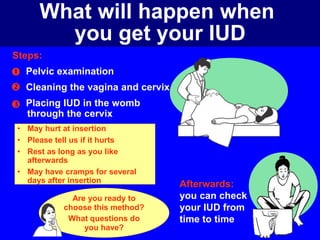
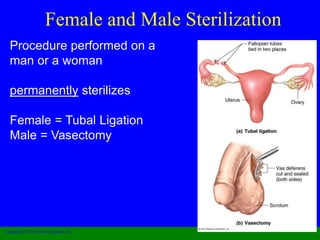
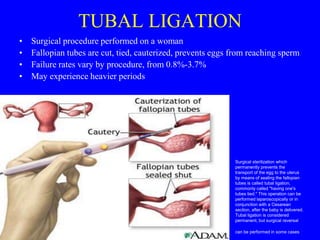
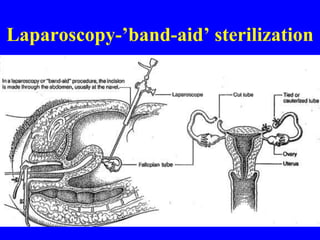
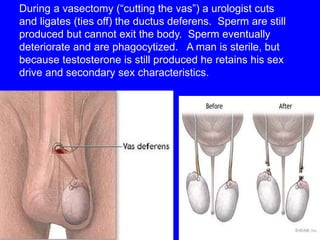
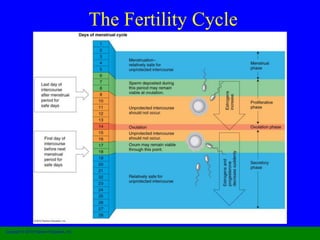
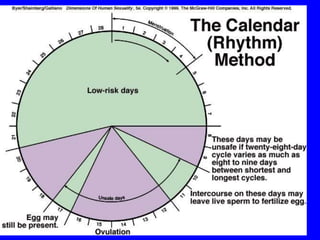
This document provides information on various contraceptive methods. It discusses hormonal methods like oral contraceptives (birth control pills), injections (Depo-Provera), implants (Norplant), and the vaginal ring. It also covers barrier methods, including condoms, diaphragms, spermicides, and cervical caps. Surgical sterilization options for both females (tubal ligation) and males (vasectomy) are described. The document concludes with behavioral methods like withdrawal and fertility awareness/natural family planning. Considerations for choosing a method include effectiveness, cost, safety, comfort/ease of use, and future fertility.