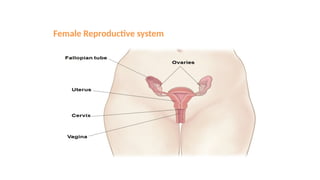
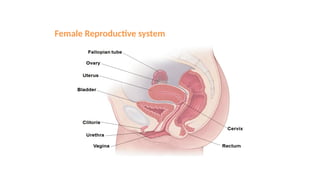
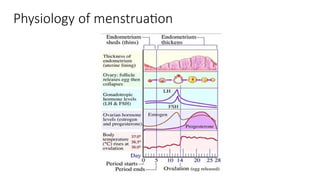
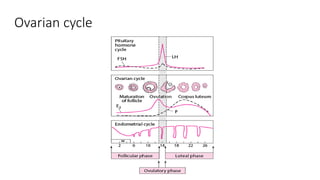
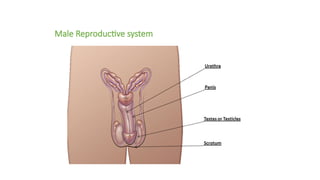
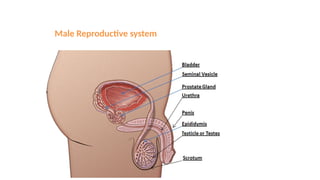
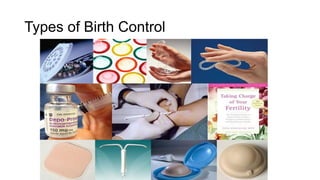
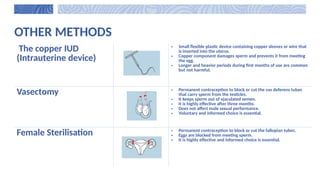
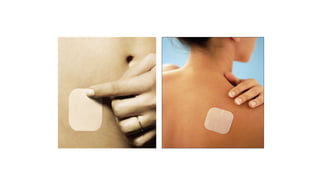
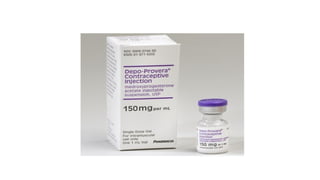
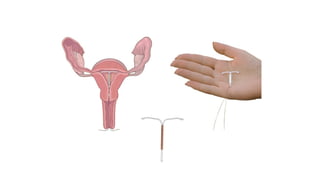
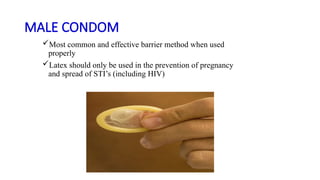
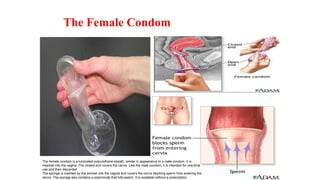
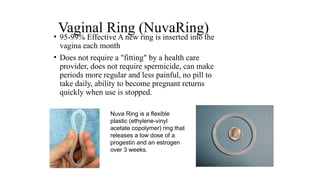
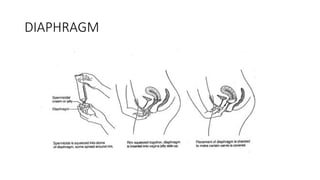
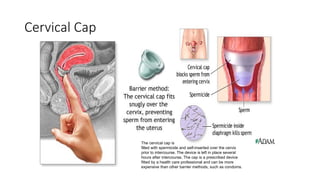
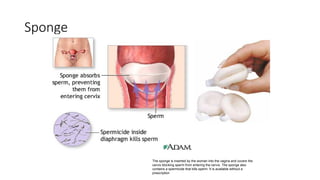
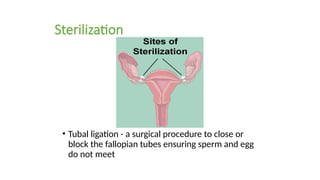
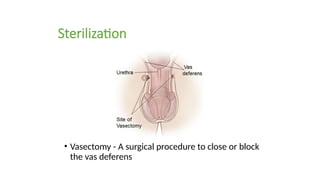
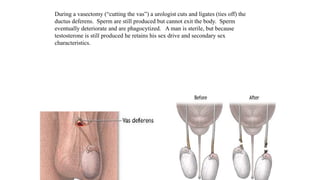
The document covers the various methods of contraception and family planning, aiming to dispel misconceptions and provide accurate information. It discusses hormonal and barrier methods, their effectiveness, and the importance of personalized counseling for individuals, especially those who use drugs. The document also emphasizes the necessity of dual protection strategies to prevent STIs and unintended pregnancies, highlighting that no contraceptive method is completely effective.