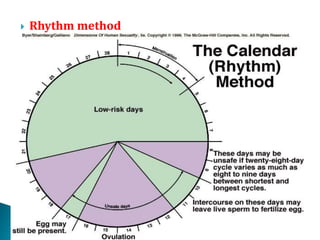
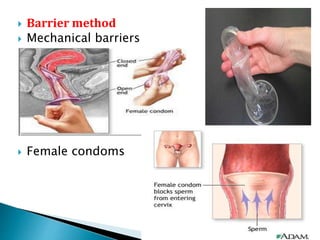
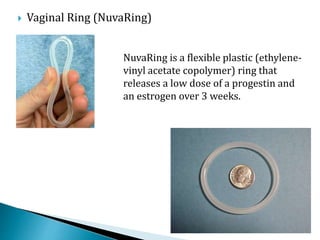
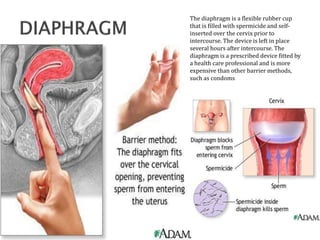
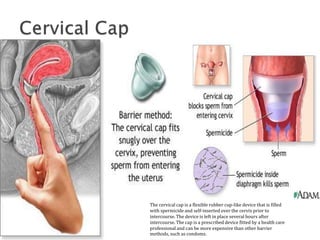
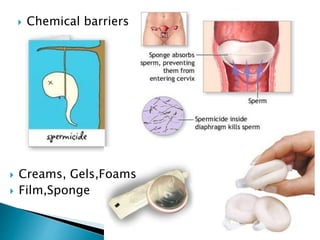
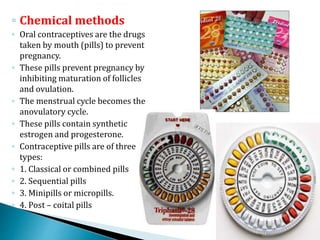
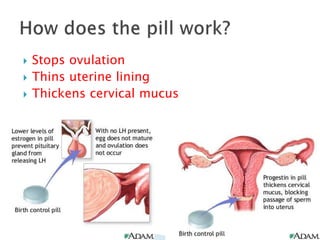
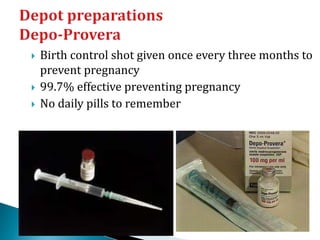
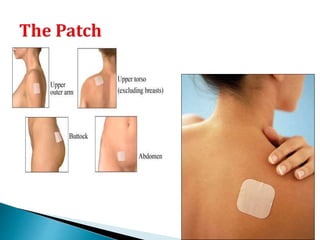
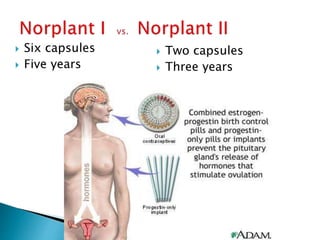
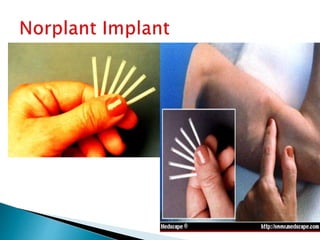
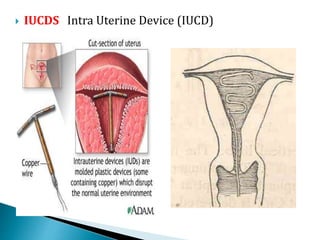
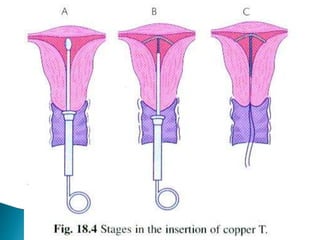
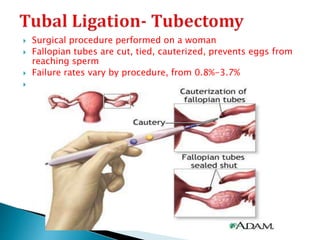
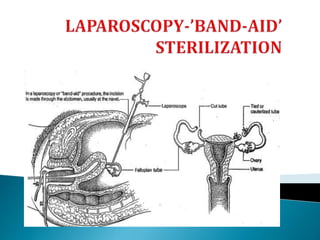
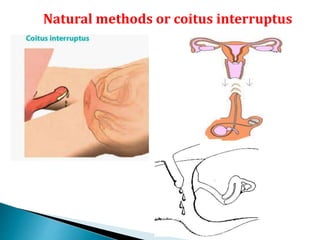
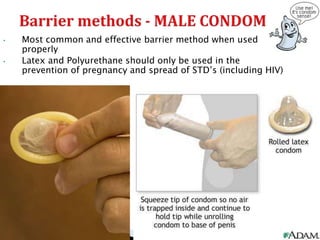
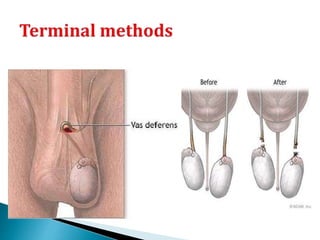
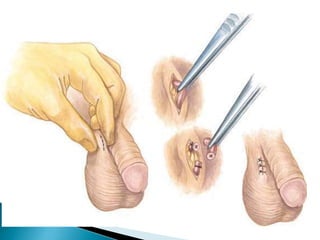
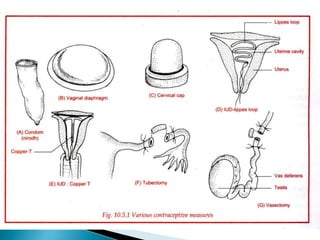
This document summarizes various contraceptive methods for both males and females. It discusses spacing methods like barrier methods (condoms, diaphragms, cervical caps), chemical methods (pills, injections, implants), and IUDs. It also covers terminal methods for permanent contraception like tubal ligation and vasectomy. It provides details on how different contraceptives work, their effectiveness in preventing pregnancy, and important benefits and risks to consider. A wide range of options are presented to suit different individual needs and circumstances for family planning and birth control.