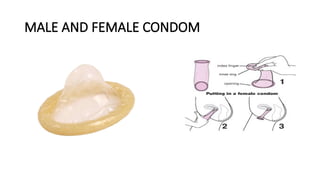
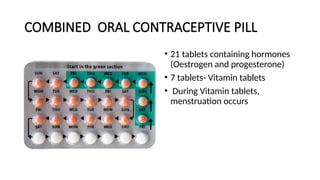
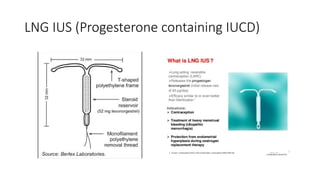
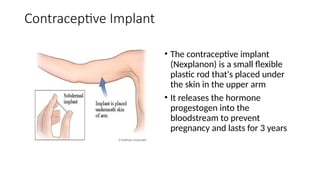
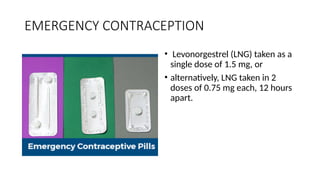
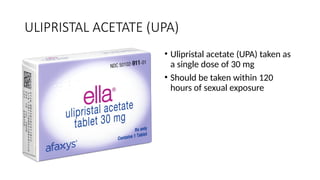
The document outlines various contraceptive methods including barrier methods like male and female condoms, oral contraceptive pills, progestin-only pills, contraceptive injections, intrauterine devices, contraceptive implants, vaginal rings, diaphragms, surgical sterilization, and emergency contraception. It details the mechanisms of action, effectiveness, benefits, and contraindications for each method. Significant pros and cons are discussed, providing a comprehensive overview of the available contraceptive options.