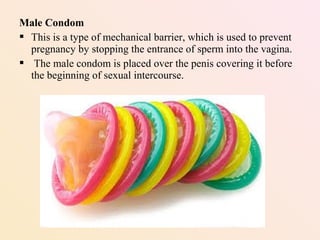
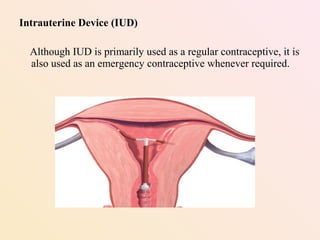
The document discusses various birth control methods, categorizing them into contraception, contragestation, and surgical or chemical processes. It outlines reversible and permanent methods, including hormonal methods, barrier methods, and emergency contraceptives, detailing their efficacy and usage. Additionally, it addresses side effects, health considerations, and the impacts of birth control on fertility.