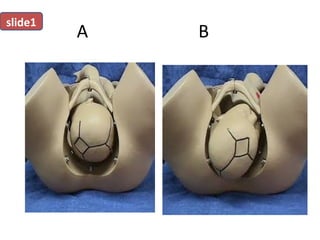
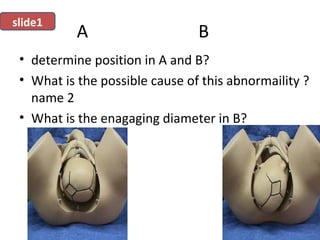
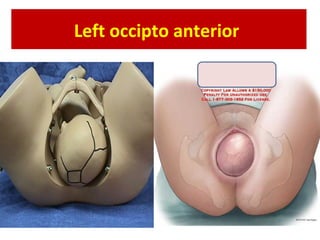
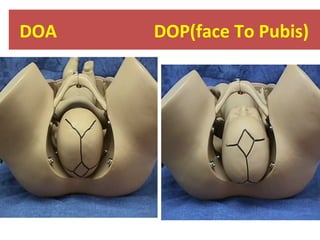
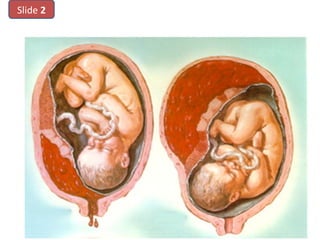
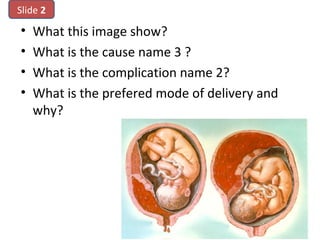
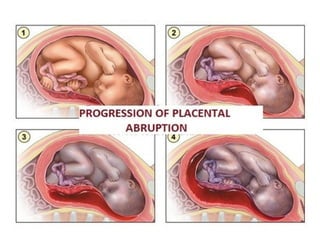
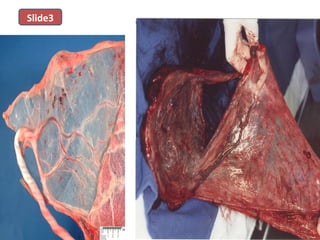
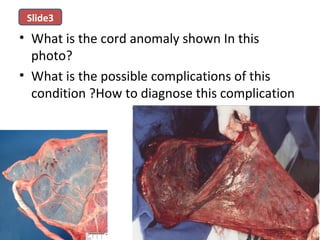
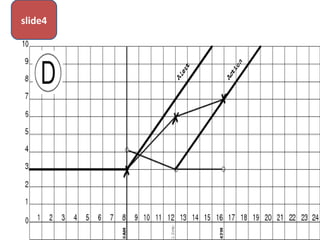
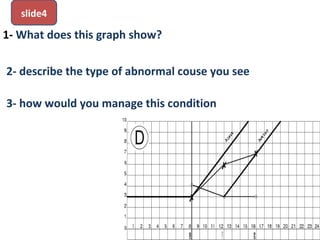
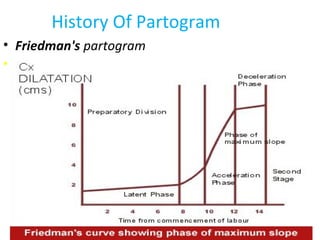
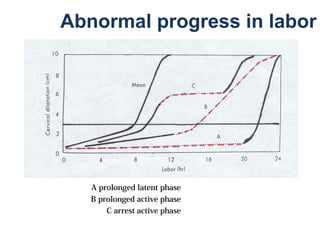
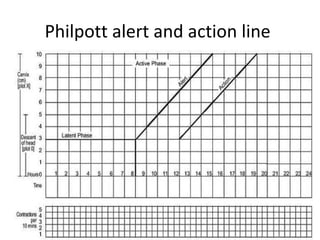
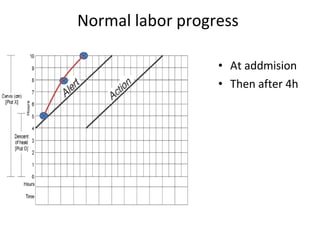
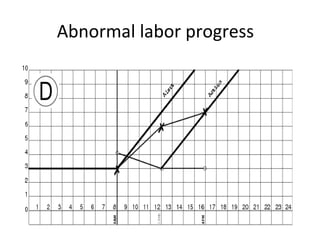
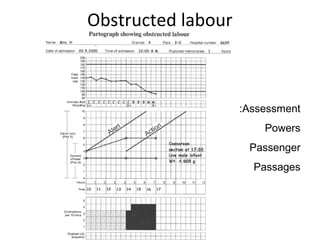
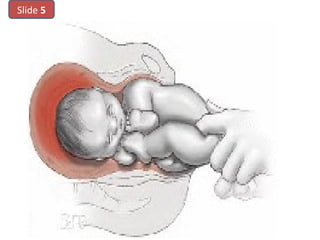
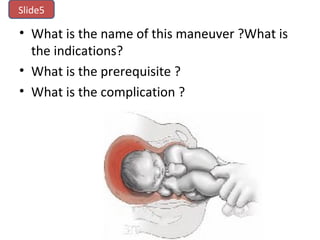
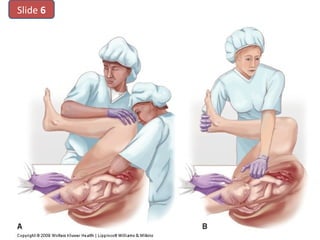
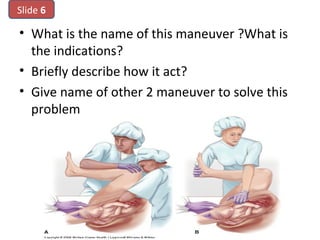
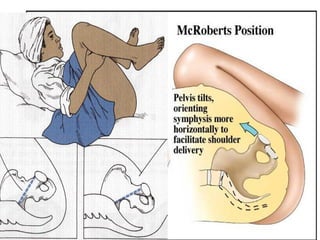
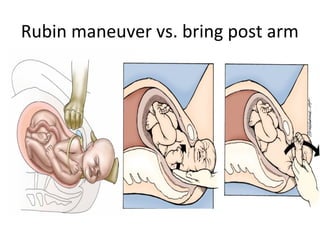
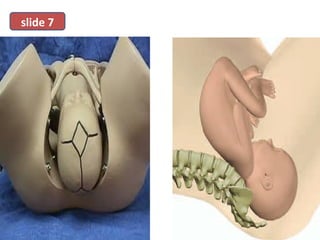
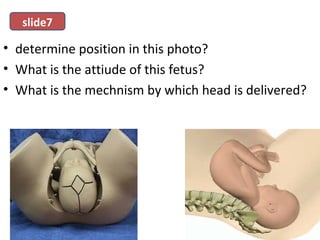
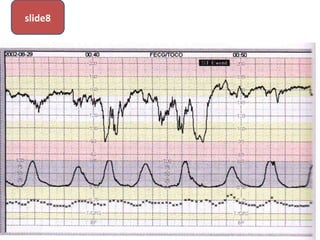
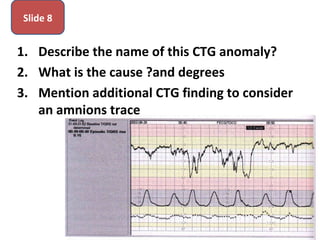
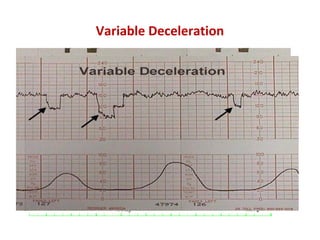
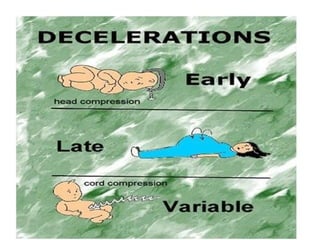
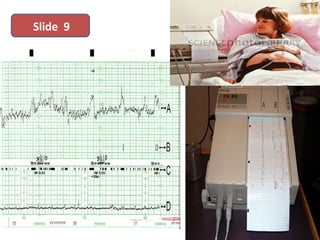
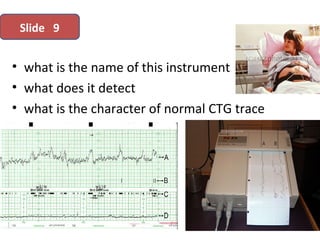
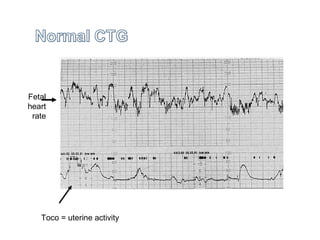
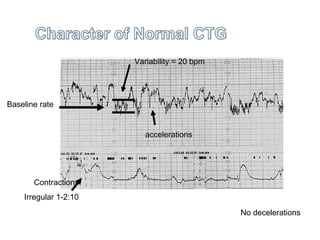
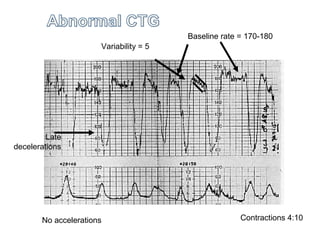
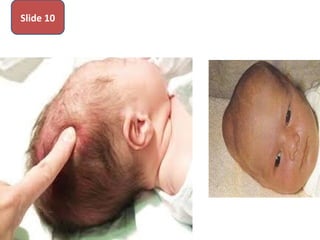
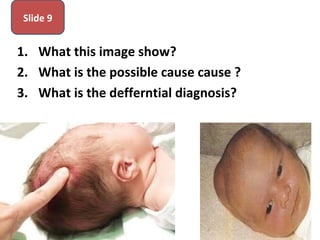
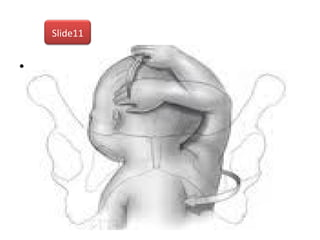
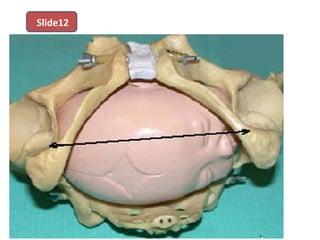
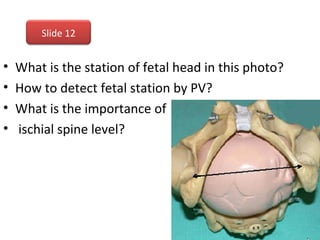
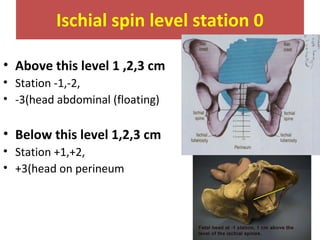
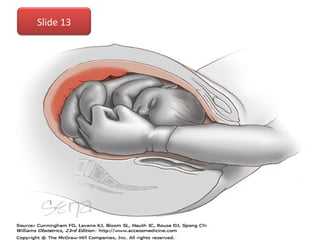
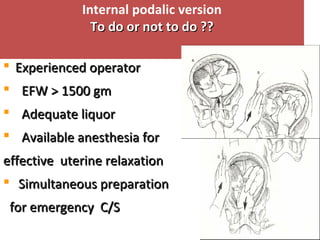
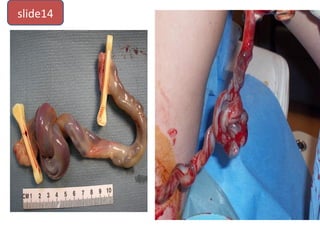
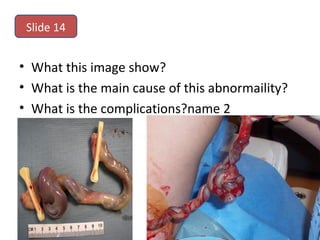
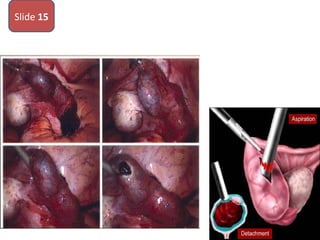
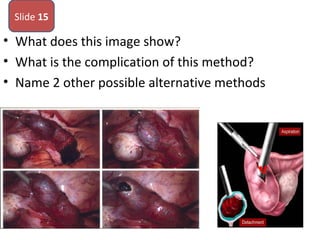
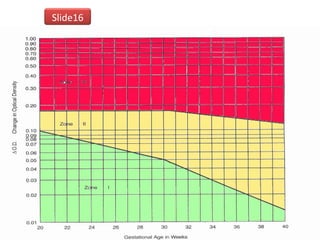
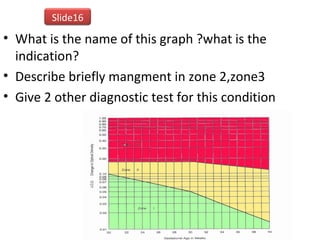
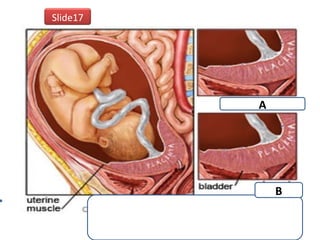
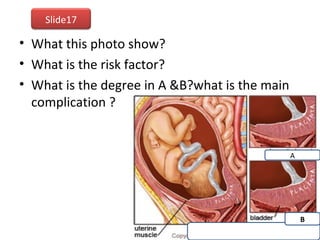
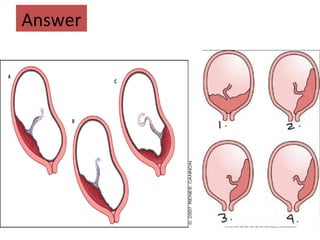
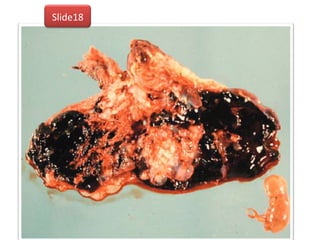
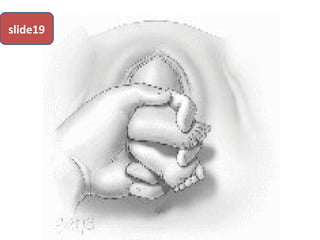
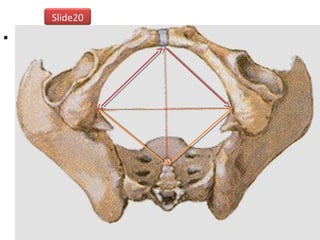
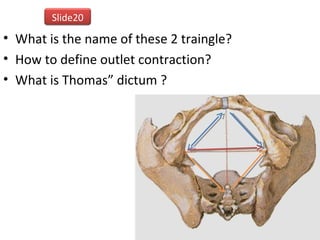
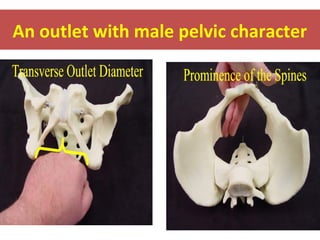
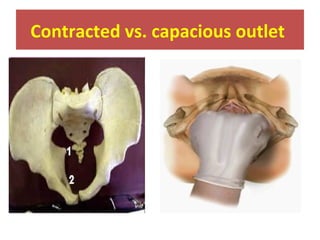
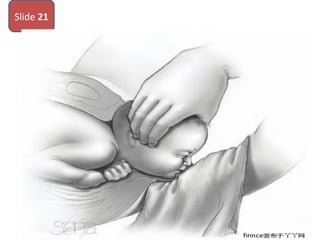
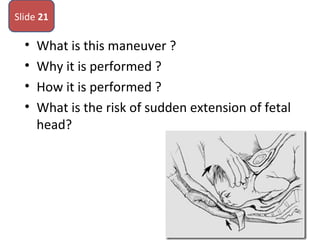
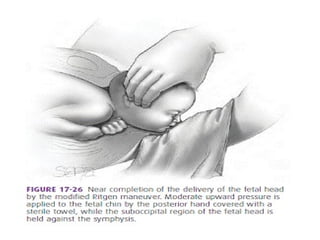
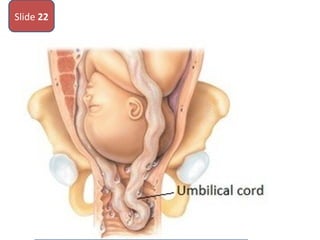
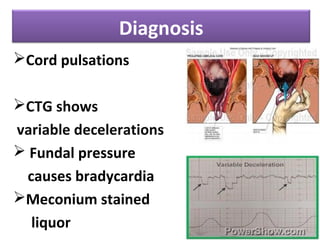
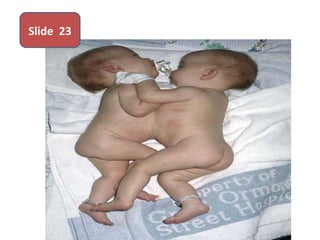
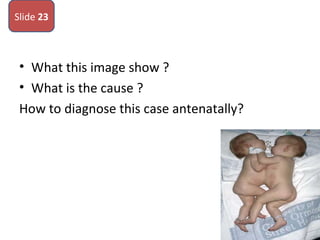
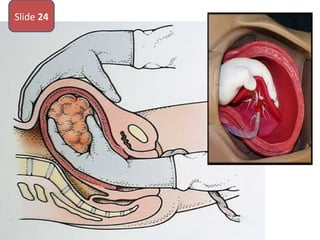
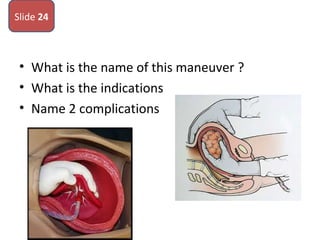
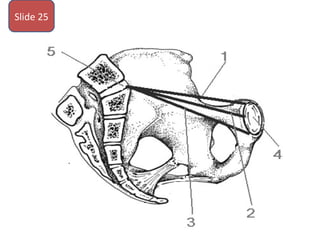
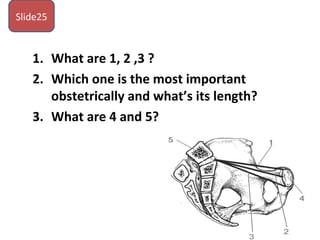
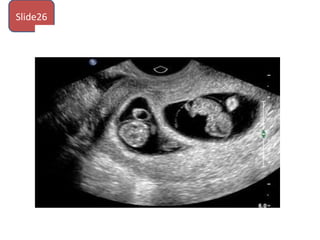
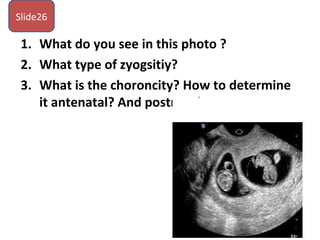
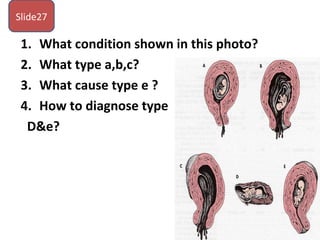
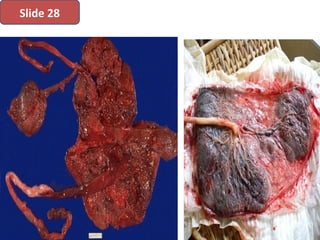
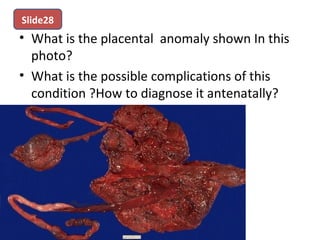
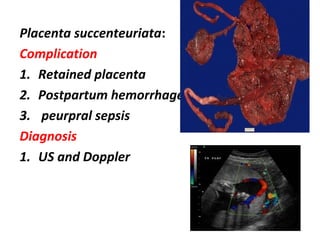
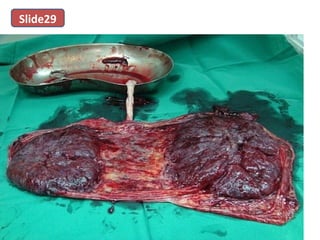
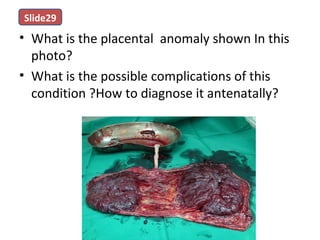
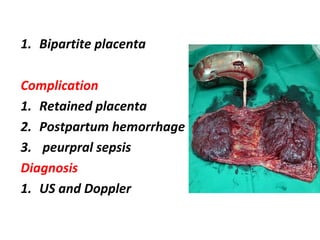
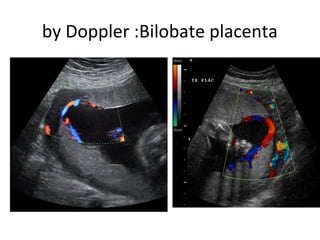
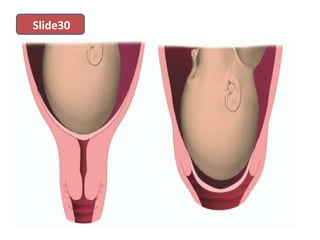
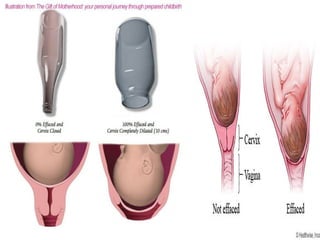
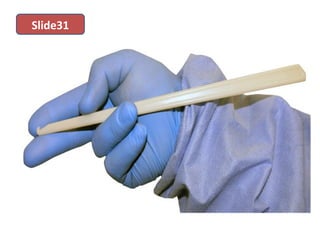
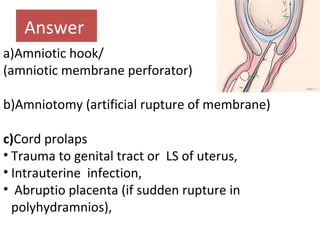
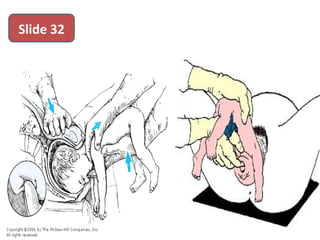
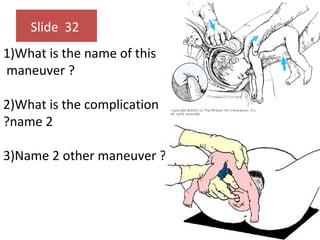
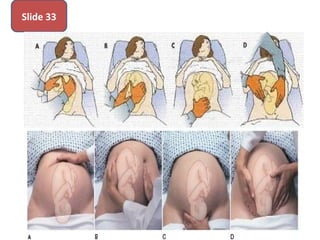
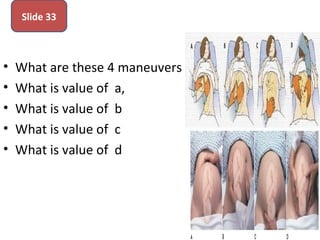
The document covers various obstetrics and gynecology topics, highlighting maneuvers and assessments related to labor and delivery. It discusses different complications, diagnostic methods, and management strategies for various conditions observed in fetal monitoring and delivery processes. The information is structured in a slide-based format with specific questions aimed at evaluating understanding of these concepts.