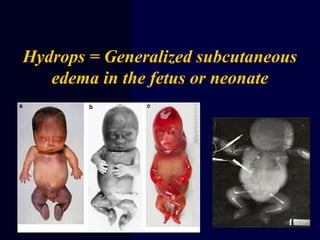
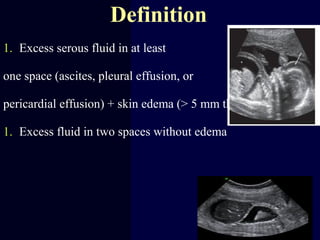
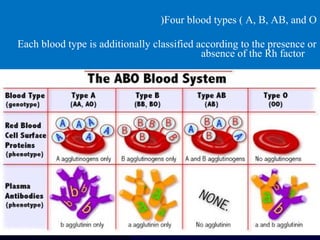
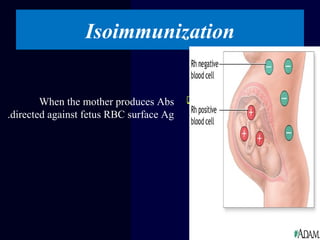
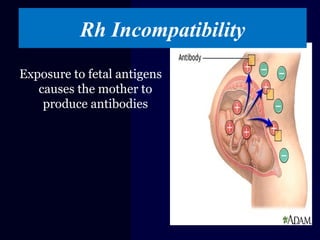
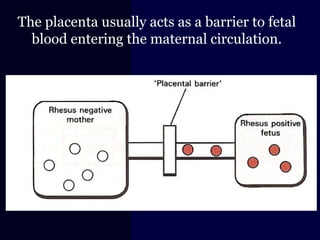
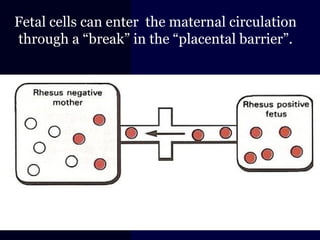
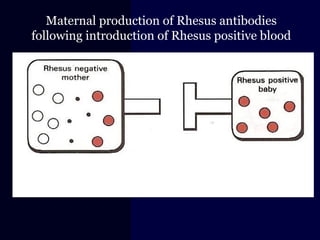
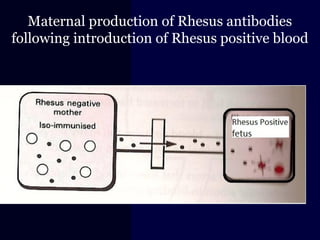
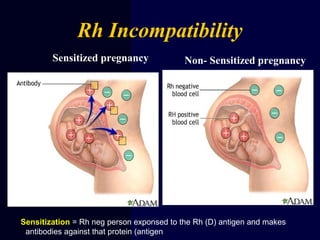
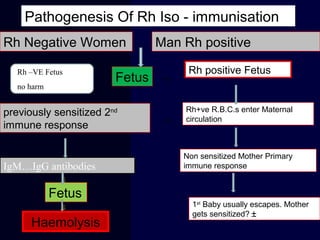
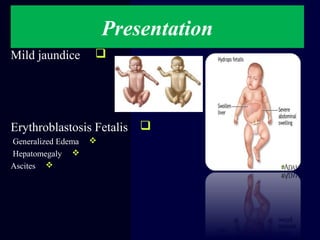
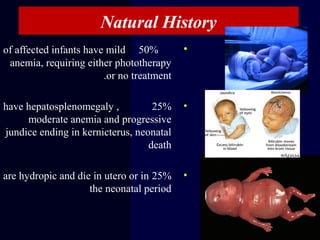
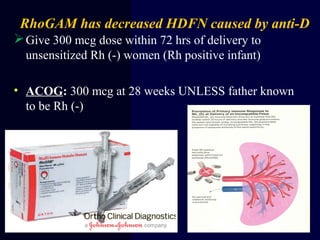
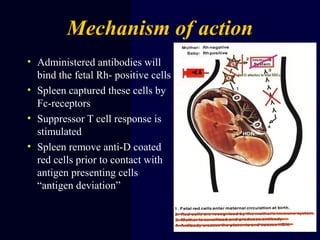
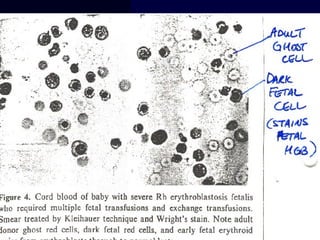
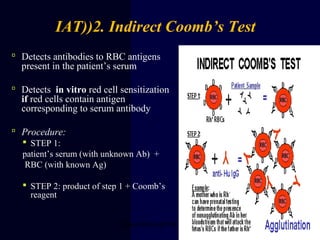
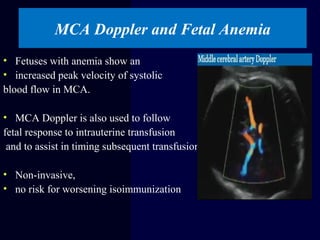
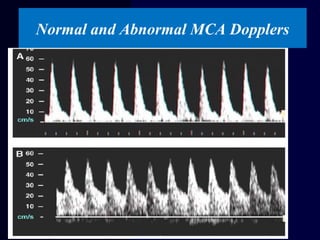
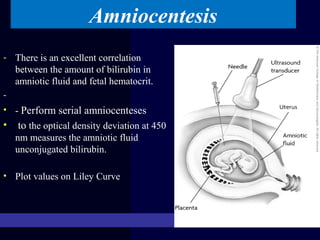
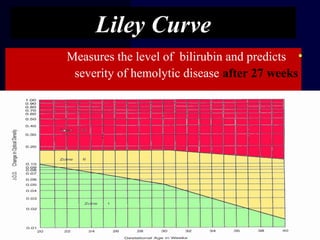
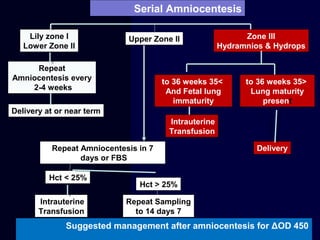
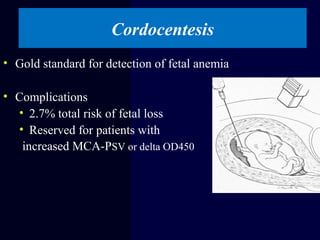
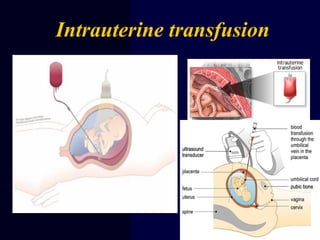
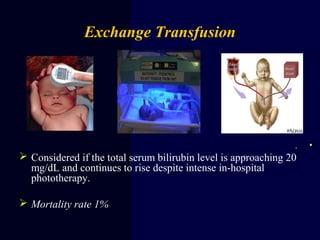
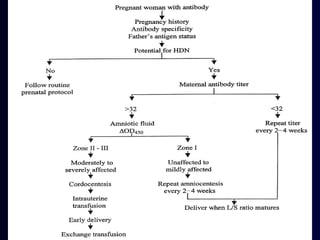
Hydrops fetalis is characterized by excess serous fluid in fetal or neonatal spaces and is primarily non-immune (90%) with various etiologies including hematologic, cardiovascular, infection, chromosomal, and more. The management of Rh incompatibility involves the administration of Rhogam to prevent hemolytic disease in sensitized pregnancies, and monitoring can include tests like the Kleihauer-Betke test and MCA Doppler for fetal anemia. Preventive measures, timely diagnosis, and appropriate interventions are crucial for managing potential complications and outcomes associated with hydrops fetalis.