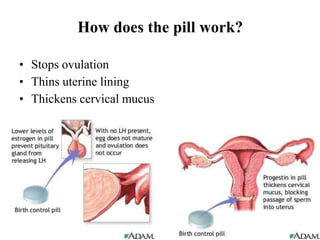
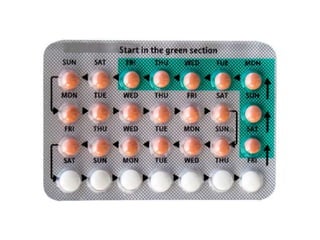
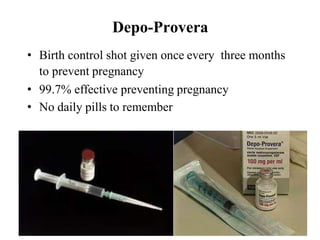
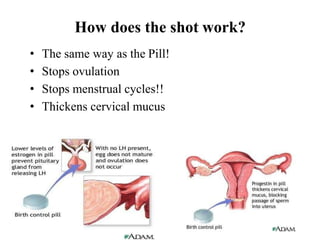
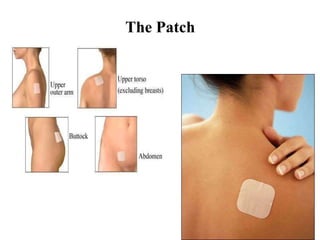
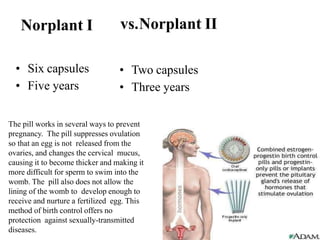
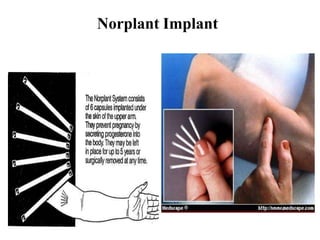
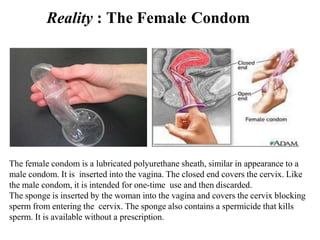
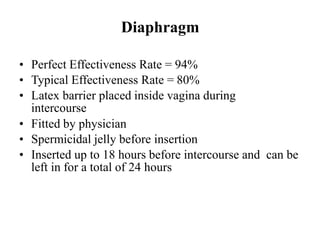
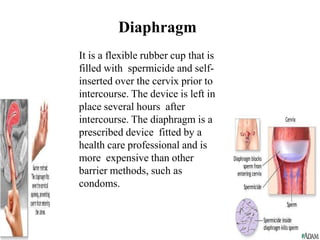
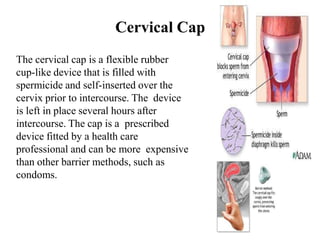
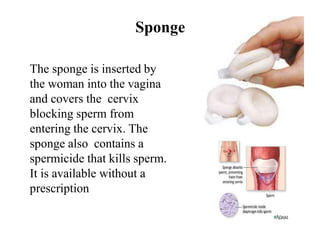
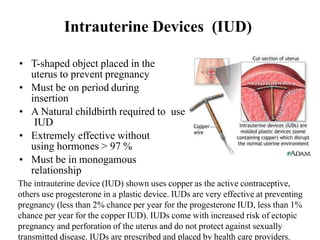
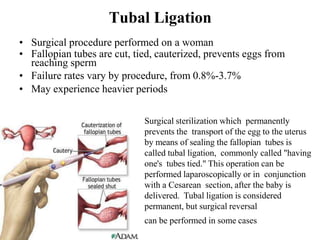
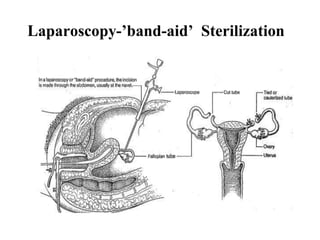
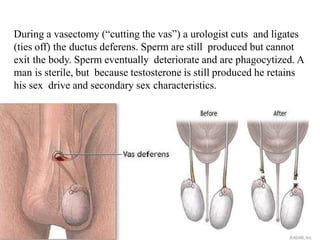
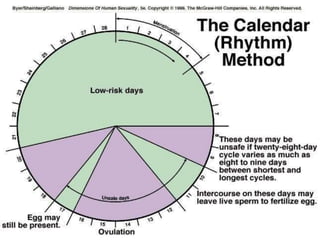
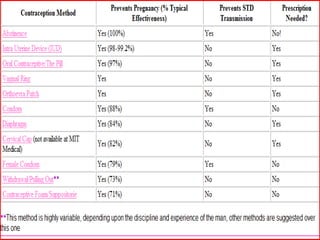
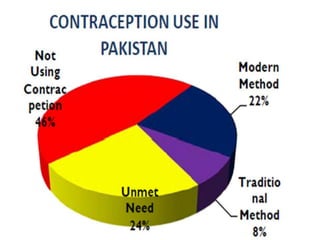
The document outlines family planning objectives, highlighting the importance of family planning methods, their effectiveness, and the consequences of population growth in Pakistan. It discusses various contraceptive methods, including hormonal, barrier, and permanent sterilization options, along with their benefits and side effects. Additionally, it addresses social, environmental, and health impacts of overpopulation and emphasizes the role of nurses in counseling and advising clients on family planning.