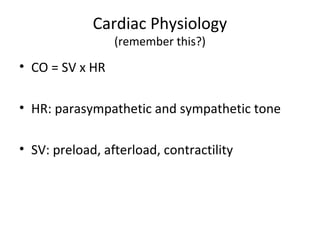
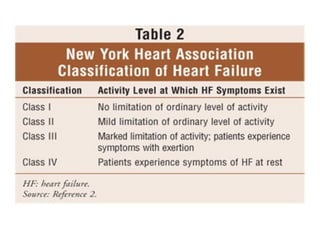
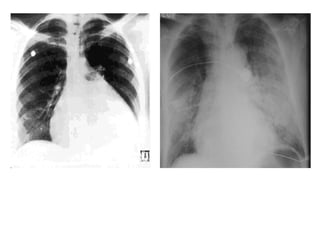
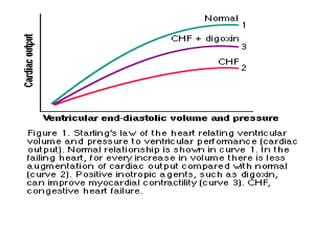
This document provides information on congestive heart failure (CHF), including its definition, pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, causes, precipitating factors, evaluation, monitoring, and management. CHF can be caused by conditions that weaken the heart muscle such as heart attacks or cardiomyopathy. It occurs when the heart cannot pump sufficiently due to problems with its electrical or mechanical function. Management involves treating underlying causes, reducing preload and afterload on the heart, and increasing cardiac contractility and output with medications, oxygen, and potentially devices like intra-aortic balloon pumps.