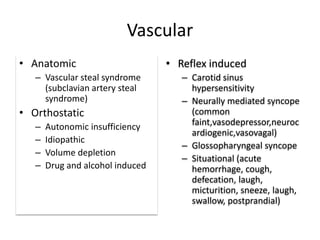
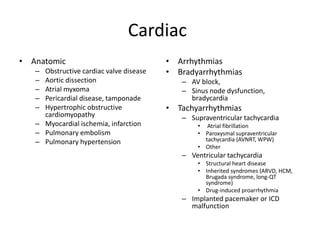
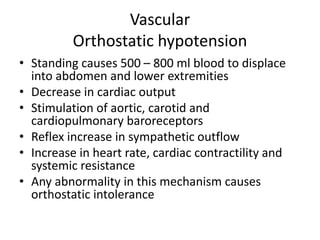
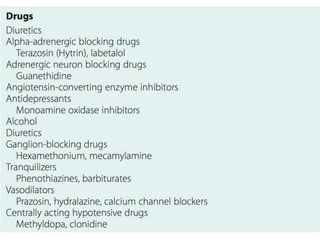
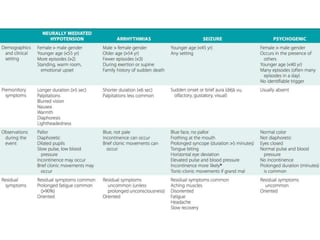
Syncope is a transient loss of consciousness due to transient global cerebral hypoperfusion. It is characterized by rapid onset, short duration, and spontaneous recovery. The most common causes are reflex-mediated syncope and orthostatic hypotension, which account for one-third of syncopal episodes. Evaluation involves detailed history taking and physical examination, including orthostatic vital signs and carotid sinus massage. Tilt table testing can be used to confirm neurogenic causes when initial evaluation is insufficient.