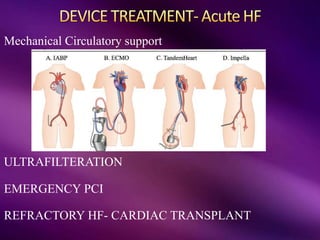
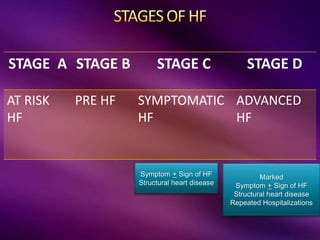
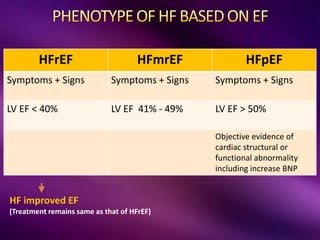
The document provides a comprehensive overview of heart failure (HF), including its definitions, classifications, prevalence rates, pathophysiology, and diagnostic criteria. It distinguishes between chronic and acute HF, outlines various clinical presentations and diagnostic tests, and emphasizes the importance of objective evidence of cardiac dysfunction. Treatment strategies, including pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions, are also detailed, focusing on improving patient outcomes and managing related comorbidities.

















![BNP [ >35 pg/mL CHF] [ >100 pg/dLAHF ]
NT Pro BNP [ > 125 pg/mL CHF] [ >400 pg/dLAHF ]
Released from failing heart (sensitive marker for HF)
• Support diagnosis of HF
• Prognosis
• GDMT
• Falsely elevated in acute cardiac illness,
critical illness, Sepsis, PE, AKI
BIOMARKERS: Troponin T (Ischemia)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heartfailureapproachclassoct2022-221010162630-93065ec8/85/Heart-Failure-Approach-class-pptx-20-320.jpg)