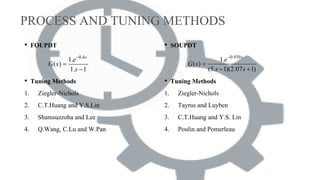
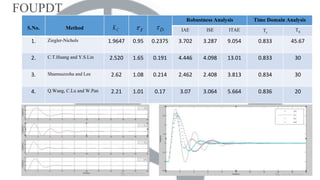
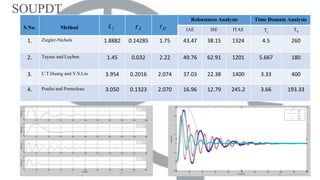
This document compares different PID controller tuning methods for first-order and second-order unstable processes with dead time (FOUPDT and SOUPDT). It analyzes the Ziegler-Nichols, C.T. Huang and Y.S. Lin, Shamsuzzoha and Lee, and Q. Wang et al. tuning methods for FOUPDT processes, finding that the Shamsuzzoha and Lee method provides the best response with minimum IAE, ISE, and ITAE. For SOUPDT processes, it analyzes the Ziegler-Nichols, Tayrus and Luyben, C.T. Huang and Y.S. Lin, and P

![PID CONTROLLER
• It is most commonly used in control process for better stability of the process
• It combines the beneficial features of PD and PI controller
• It gives lower overshoot
• It eliminate derivative and proportional Kick
• It gives direct and reverse action
• It consist automatic and manual control modes
• It has lower rise and settling time
• In chemical industry desired output (product) of the process needed in small time with out taking any
deficiency
G(s) is transfer function of PID controller and , , are controller parameter
1
( ) [1 ]C D
I
G s K s
s
CK I D](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conferencegoa-170228144913/85/Comparison-of-PID-controller-tuning-methods-for-unstable-systems-3-320.jpg)