The document discusses PID controllers and their origins. It provides information on:
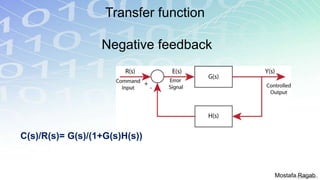
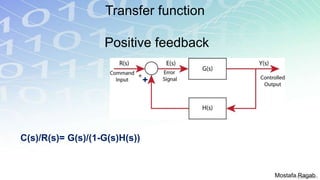
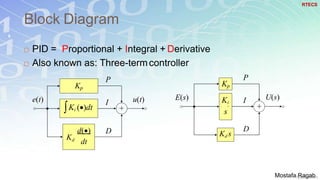
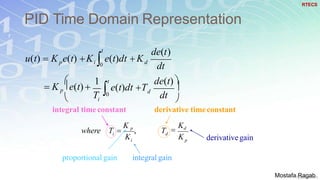
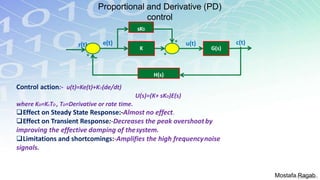
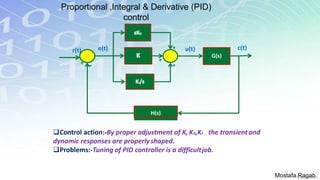
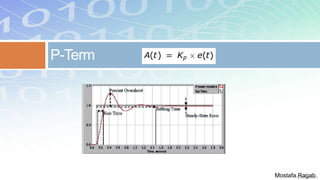
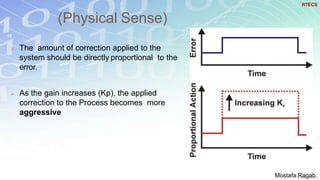
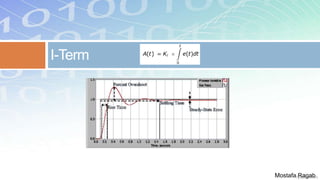
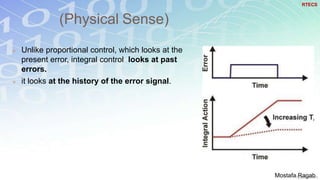
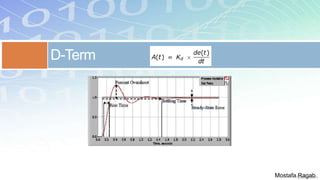
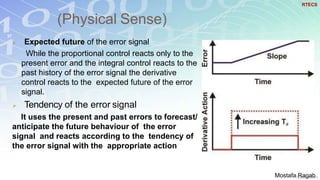
1) The basic components and functions of PID controllers, including proportional, integral and derivative terms that react to error, accumulated error over time, and rate of change of error respectively.
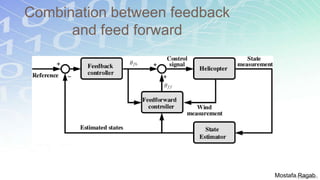
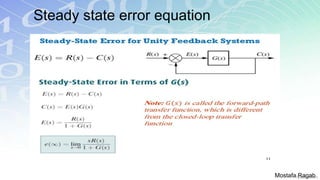
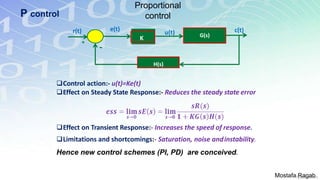
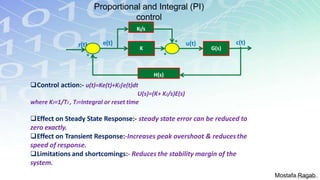
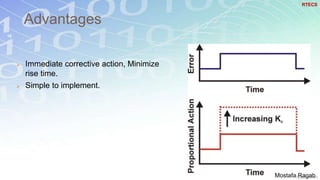
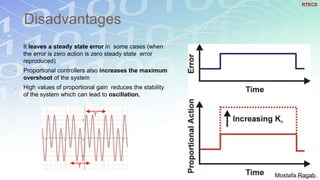
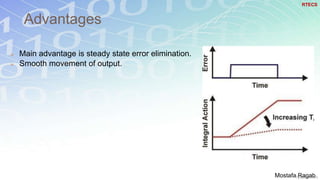
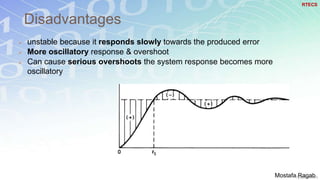
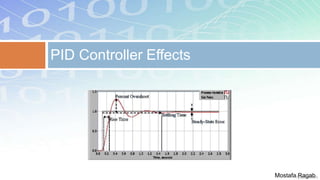
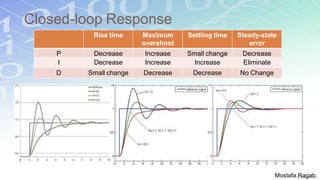
2) The benefits and limitations of proportional, integral and derivative control modes individually and in combination. PID controllers can reduce rise time, settling time and steady state error.
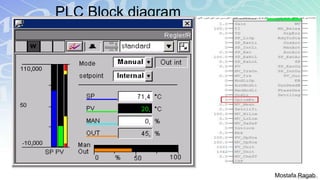
3) Applications of different PID variations and guidelines for controller design depending on process characteristics like temperature, flow or liquid level control.
4) Tips for designing PID controllers including obtaining an open-loop response and adjusting gains to achieve desired closed-loop performance.