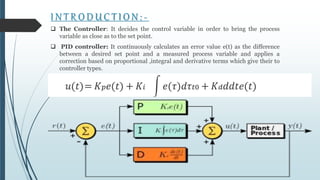
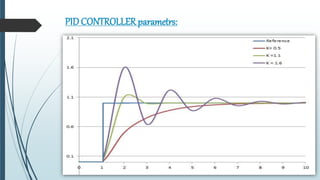
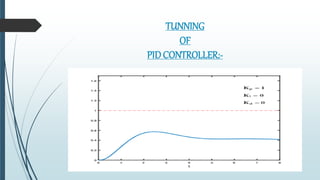
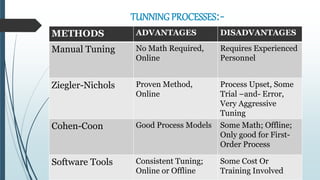
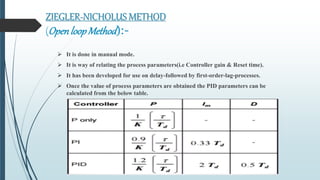
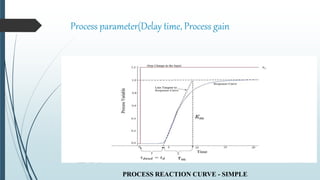
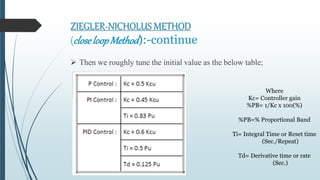
This document discusses tuning PID controllers. It introduces PID controllers and their proportional, integral and derivative terms. It describes different tuning methods, focusing on the Ziegler-Nicolas tuning method. This method relates process parameters like delay time and gain to PID parameters. It involves adjusting the proportional band until oscillations occur, then using those values to calculate initial PID settings according to provided tables. The goal of tuning is to optimize rise time, overshoot, settling time, steady state error and stability.