This document provides an overview of knowledge management and PID tuning methods, including:
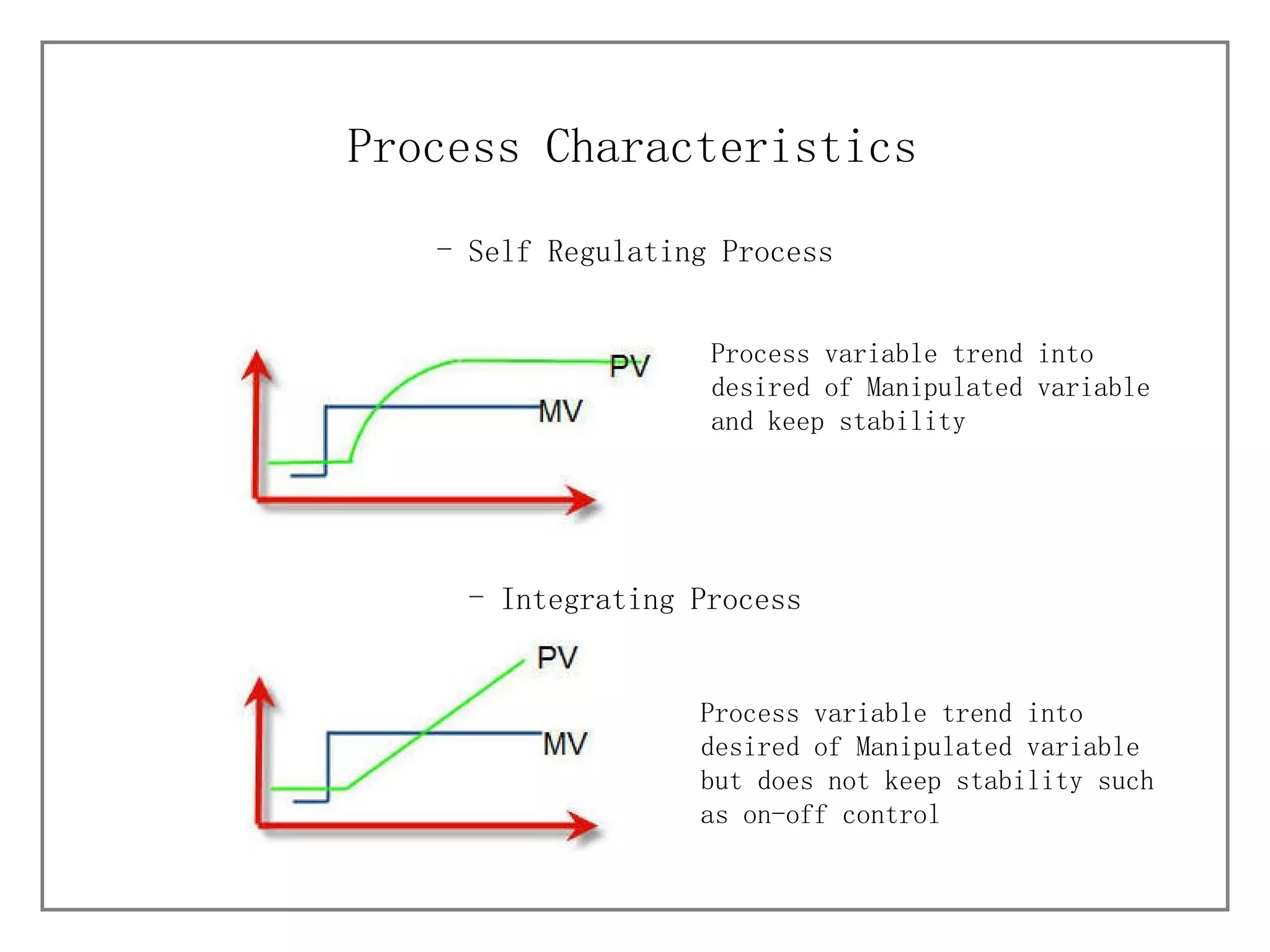
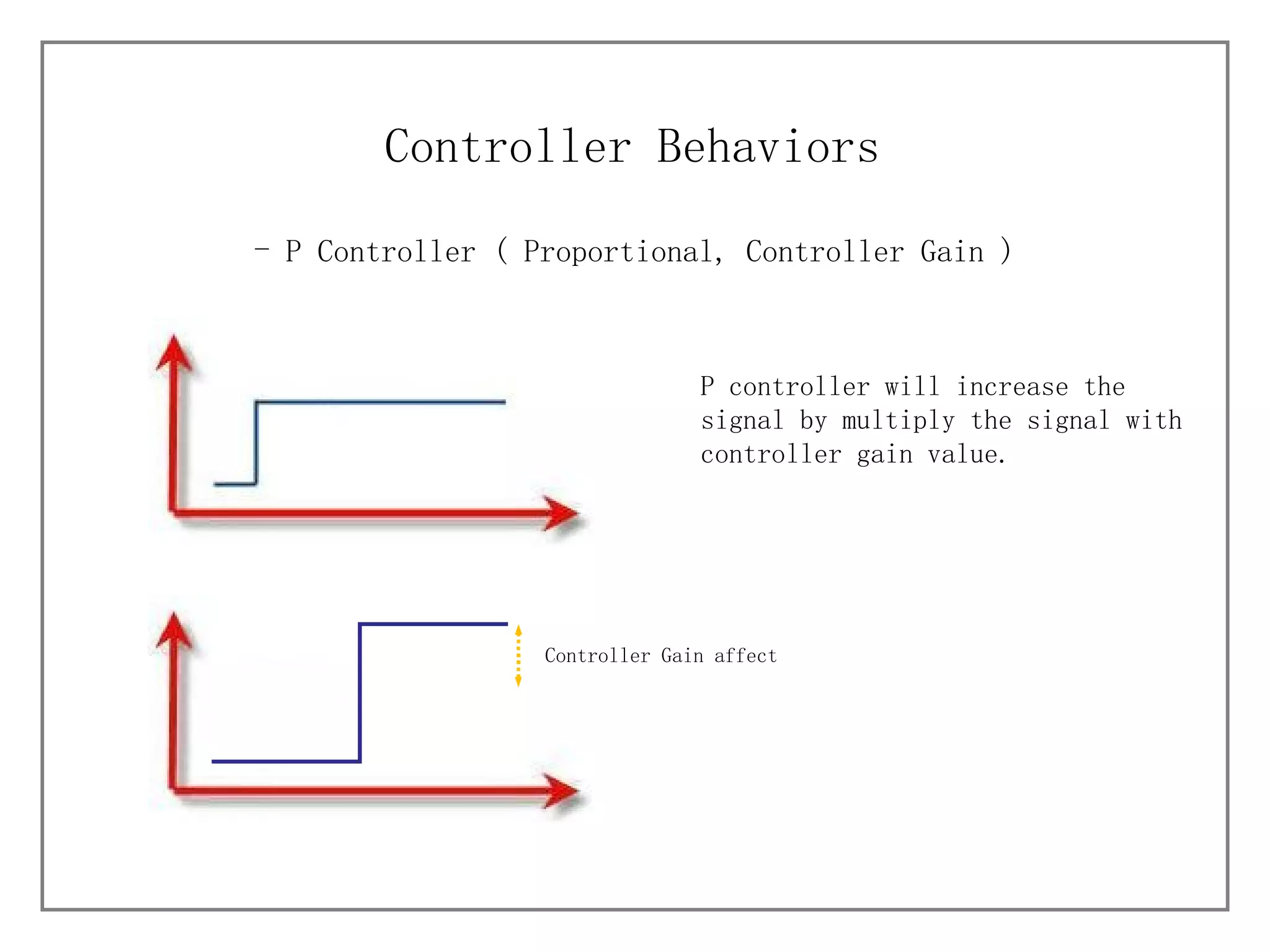
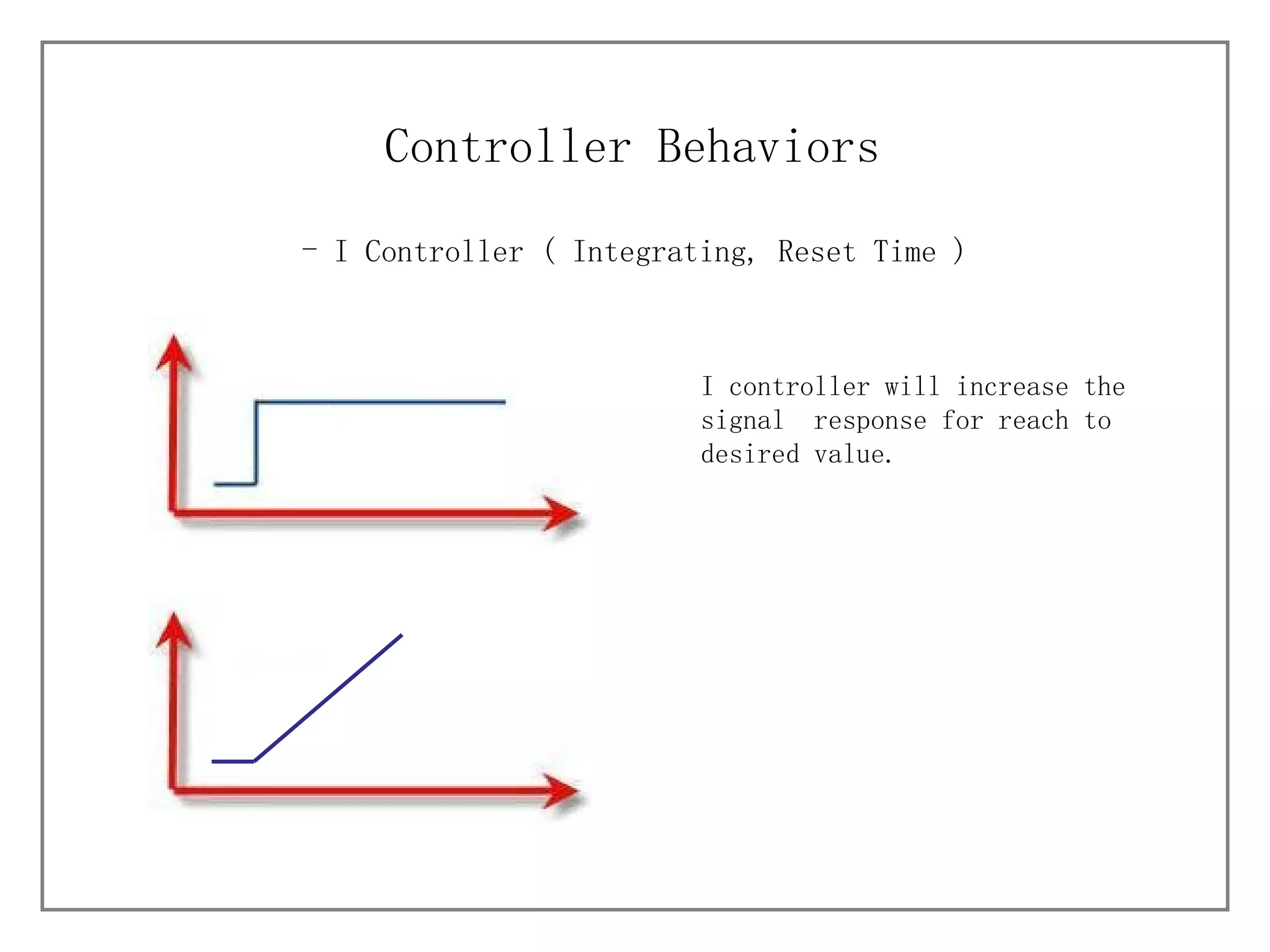
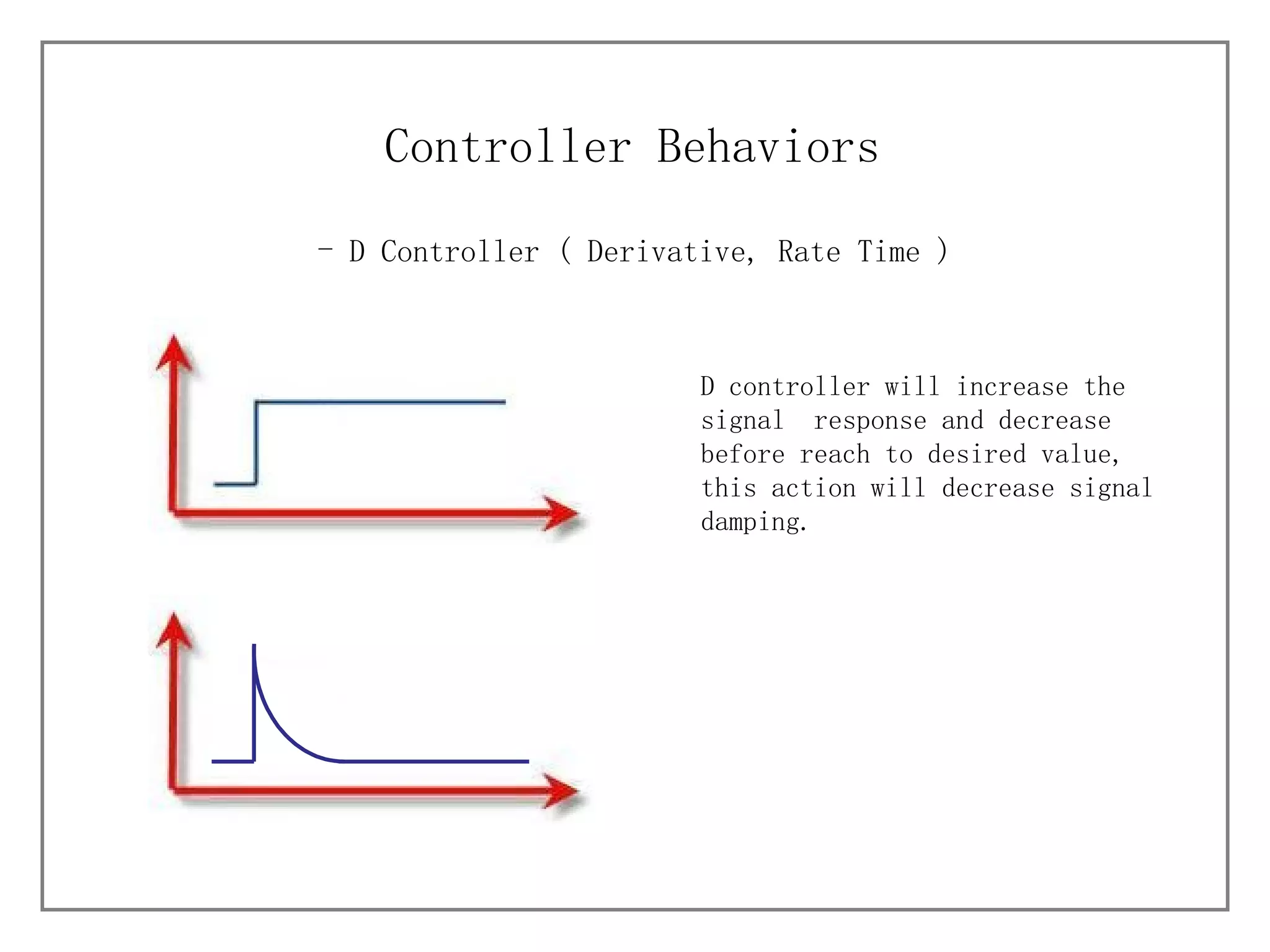
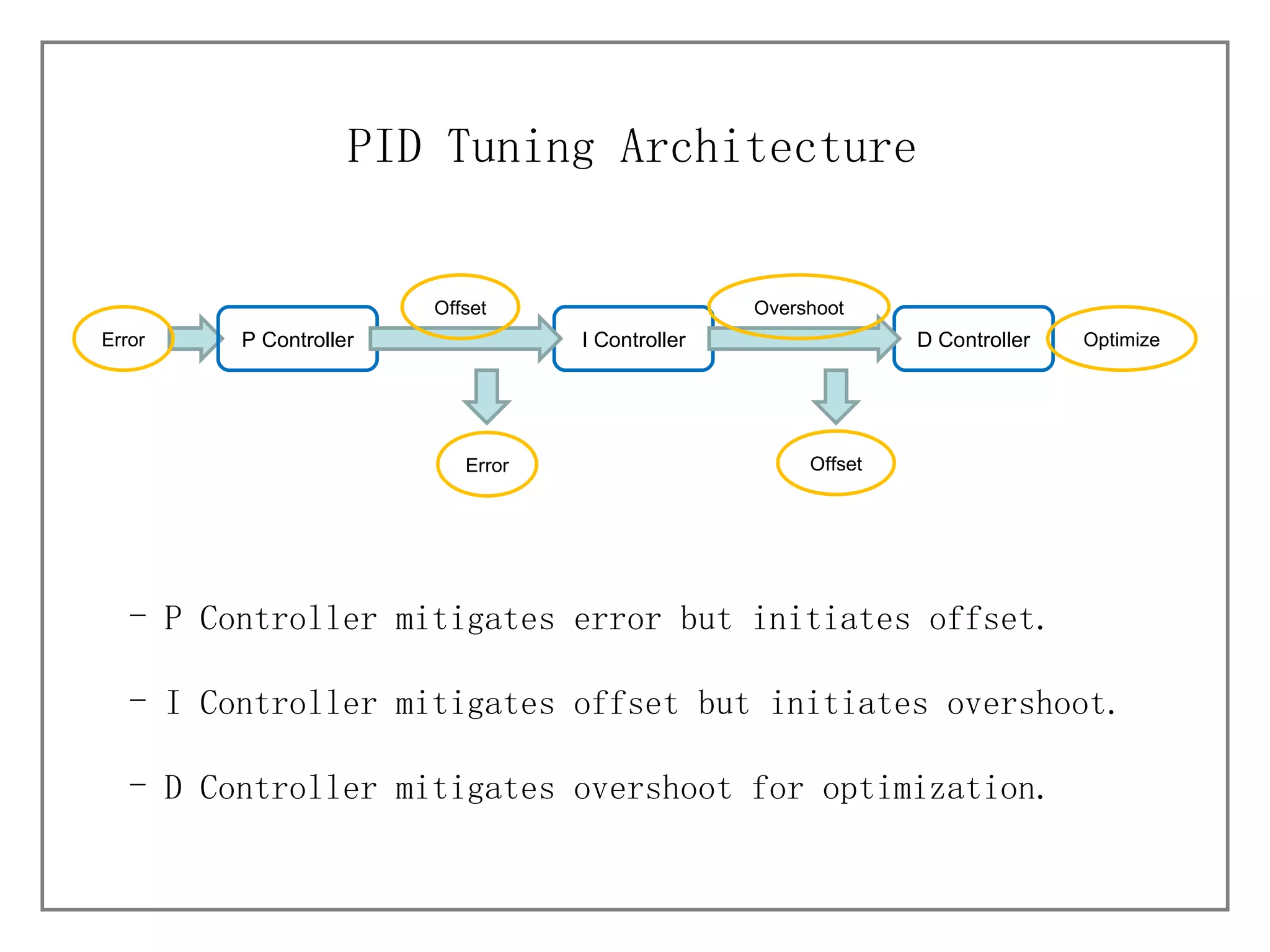
1) It describes different process characteristics and controller behaviors, and introduces common PID tuning methods like Ziegler-Nichols tuning.
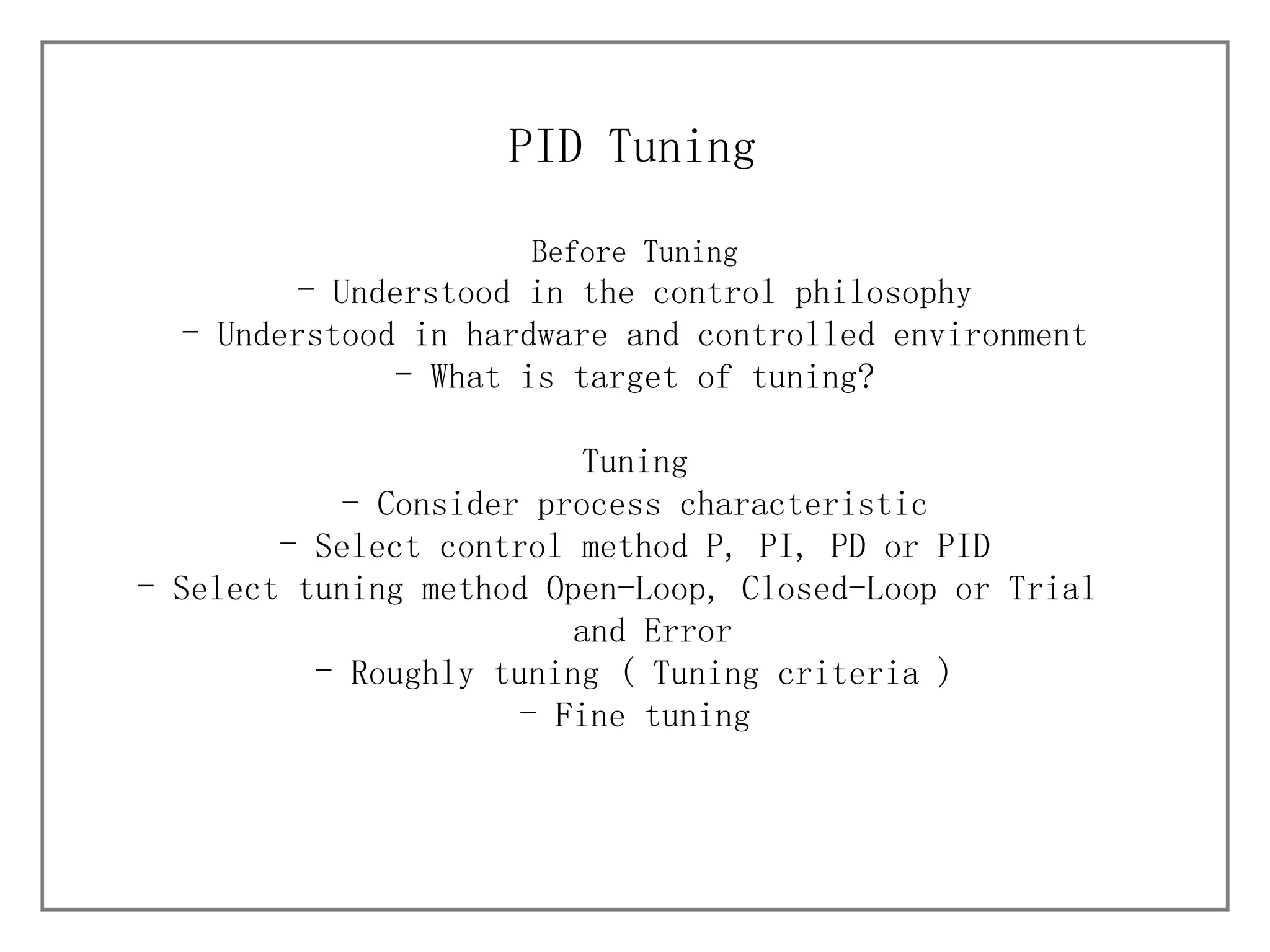
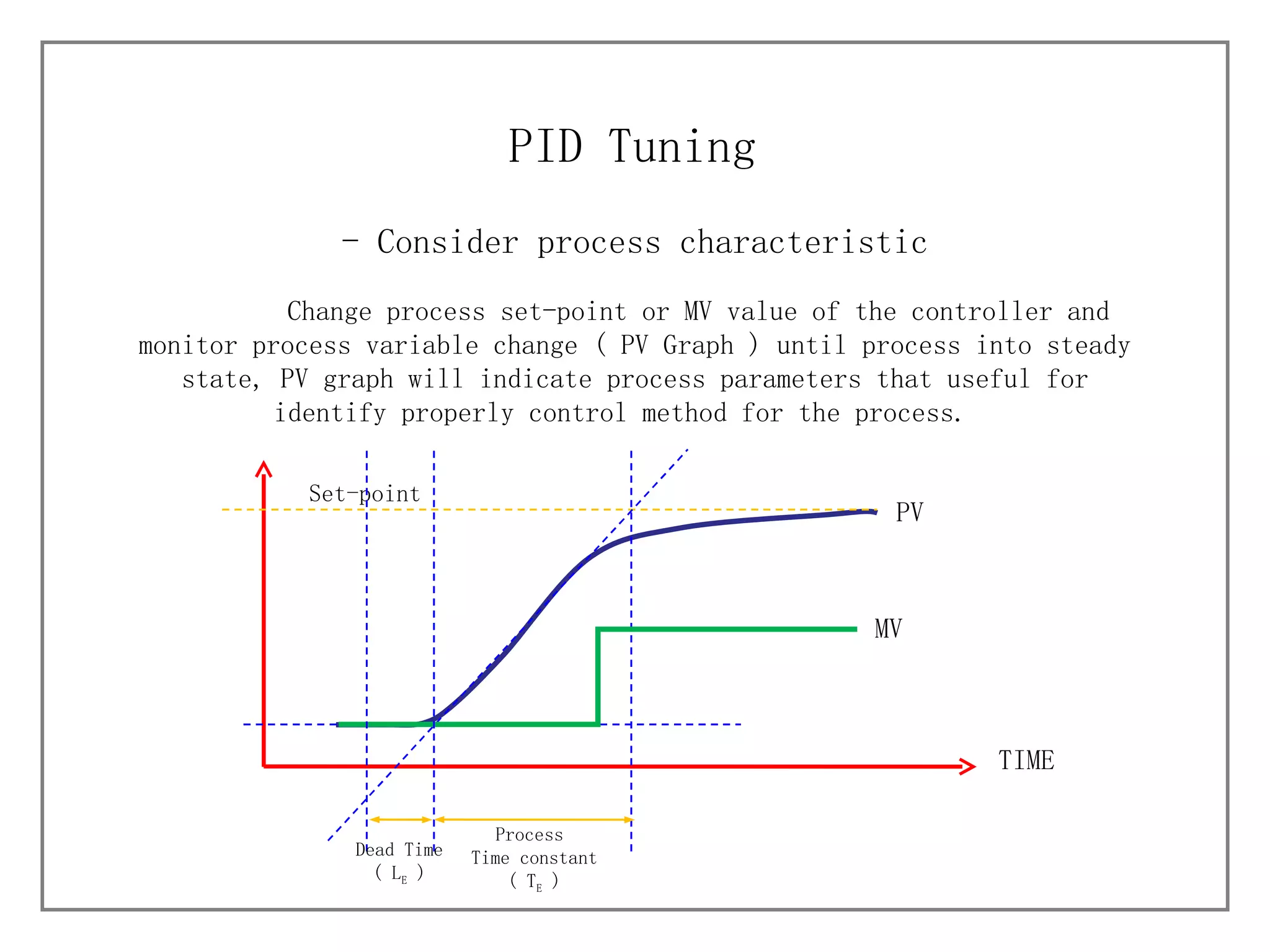
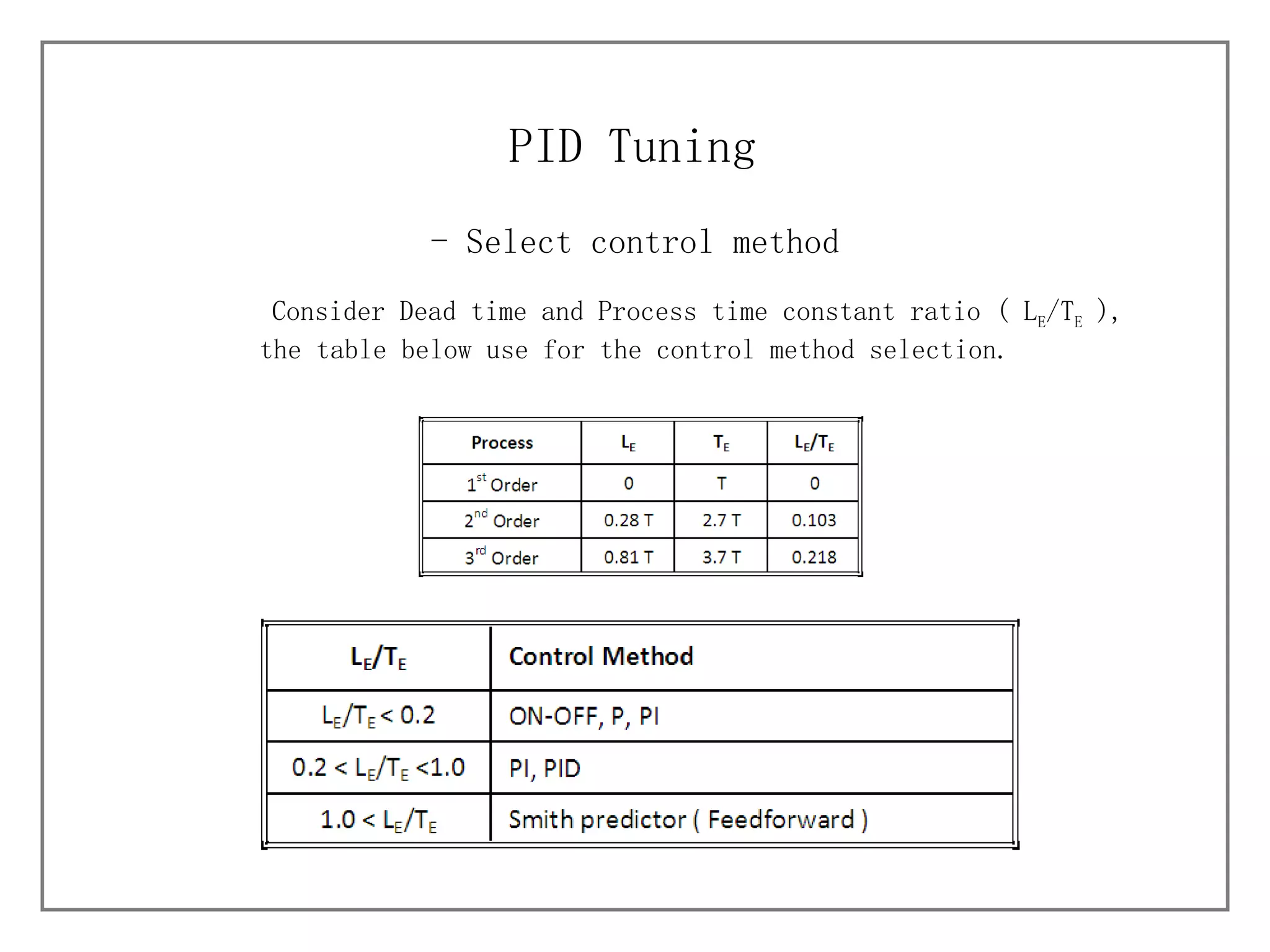
2) It outlines the steps for tuning a PID controller, including understanding the process, selecting a control method, tuning approach, and initially and finely tuning parameters.
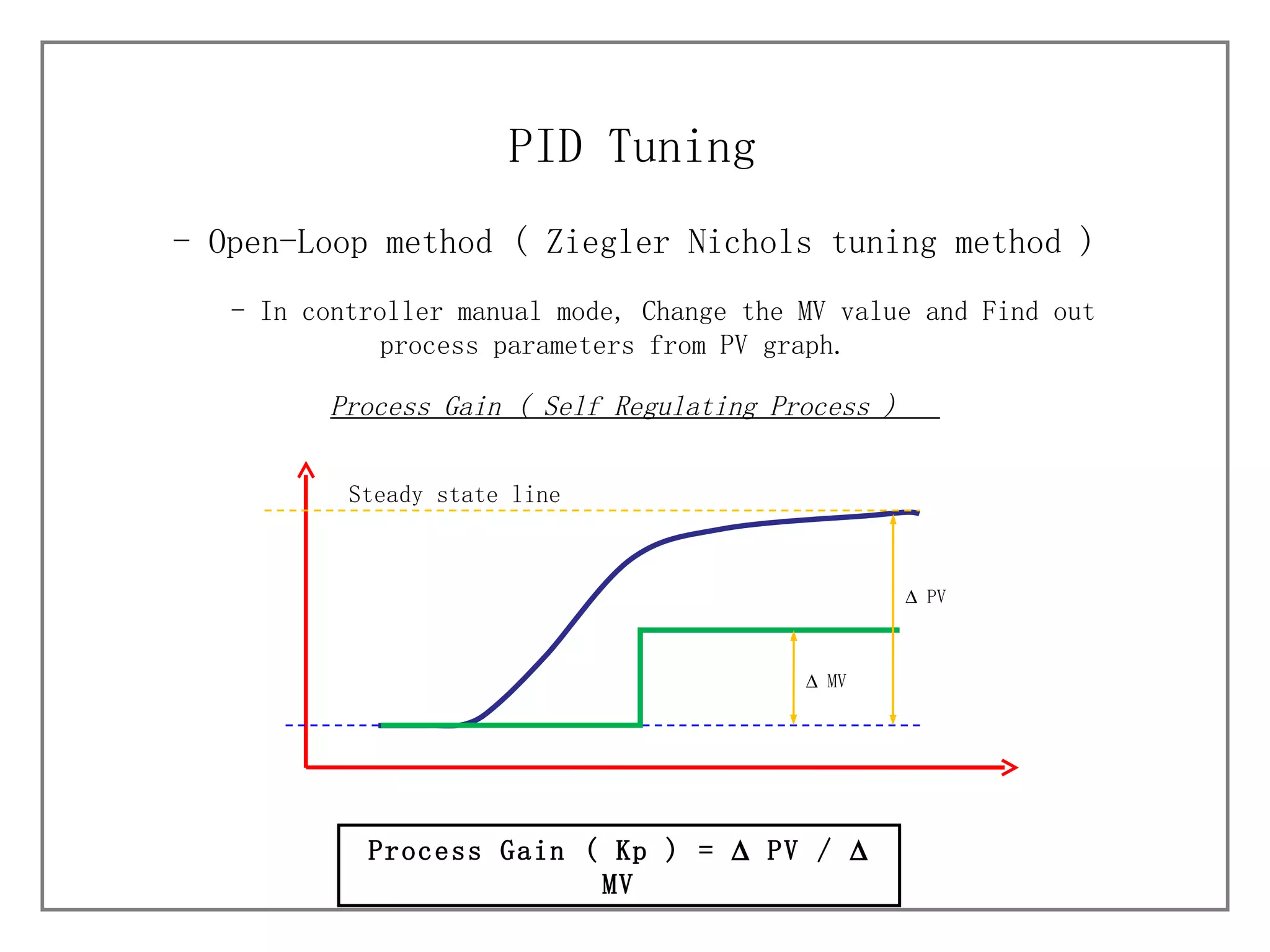
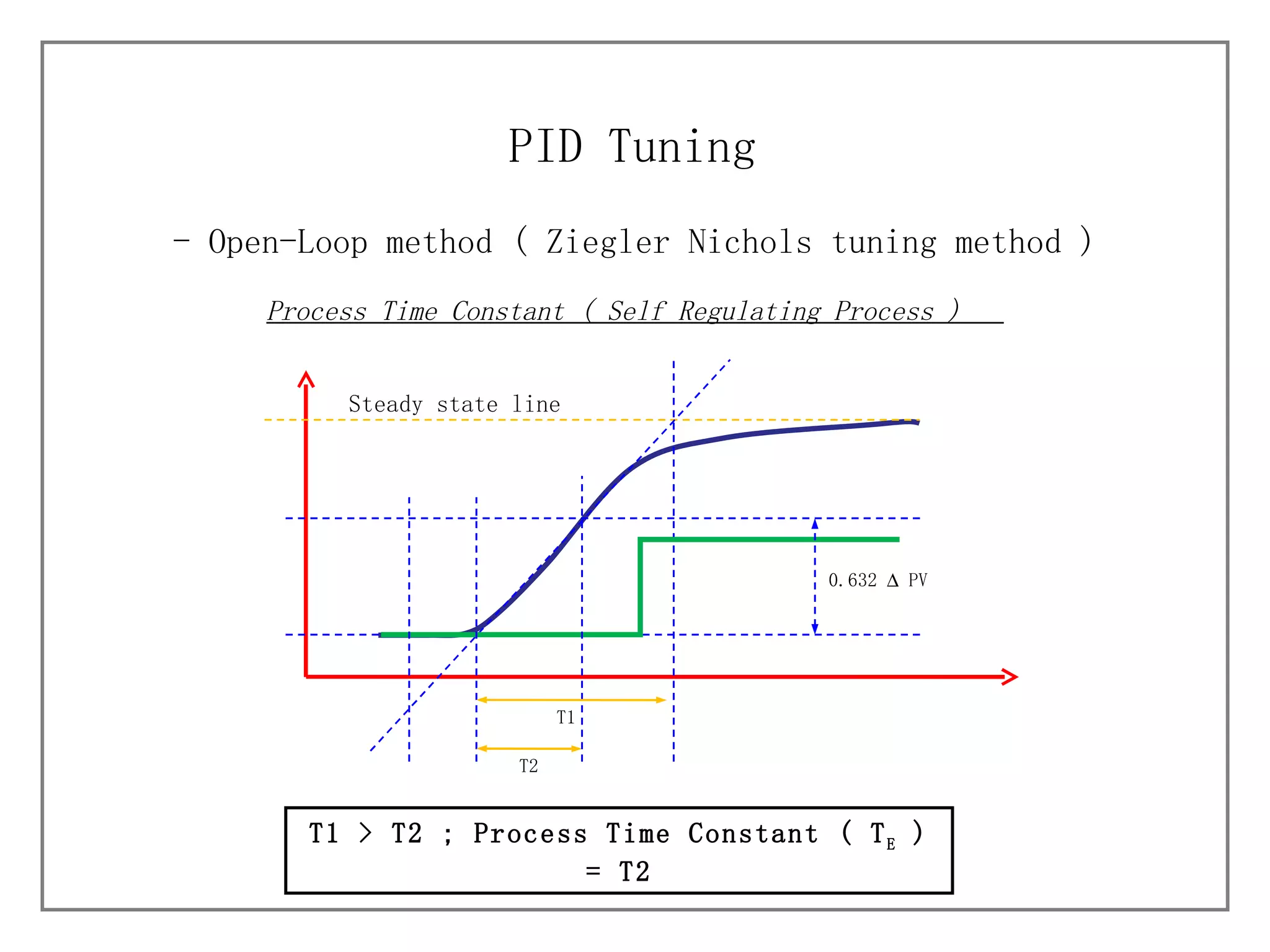
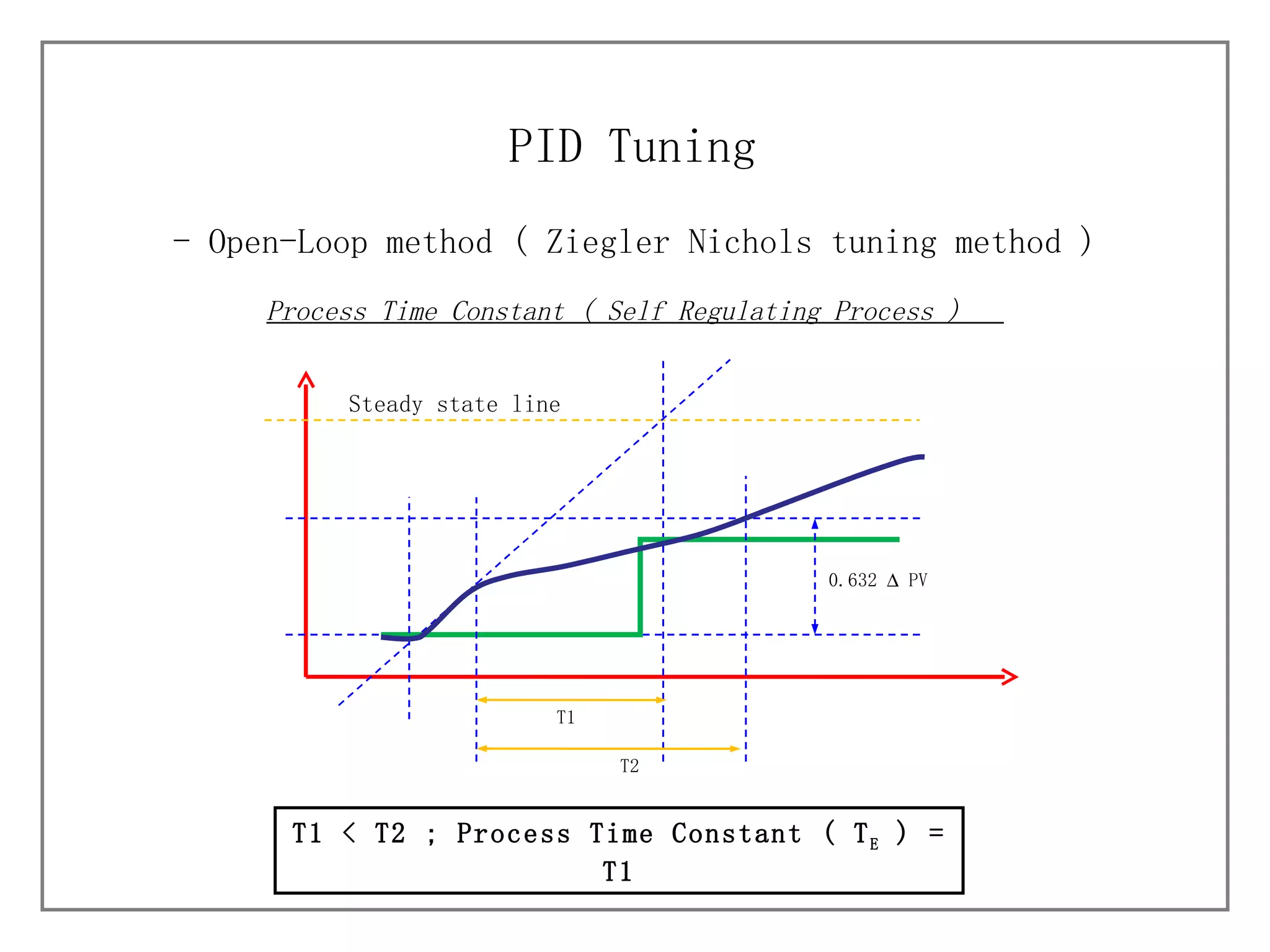
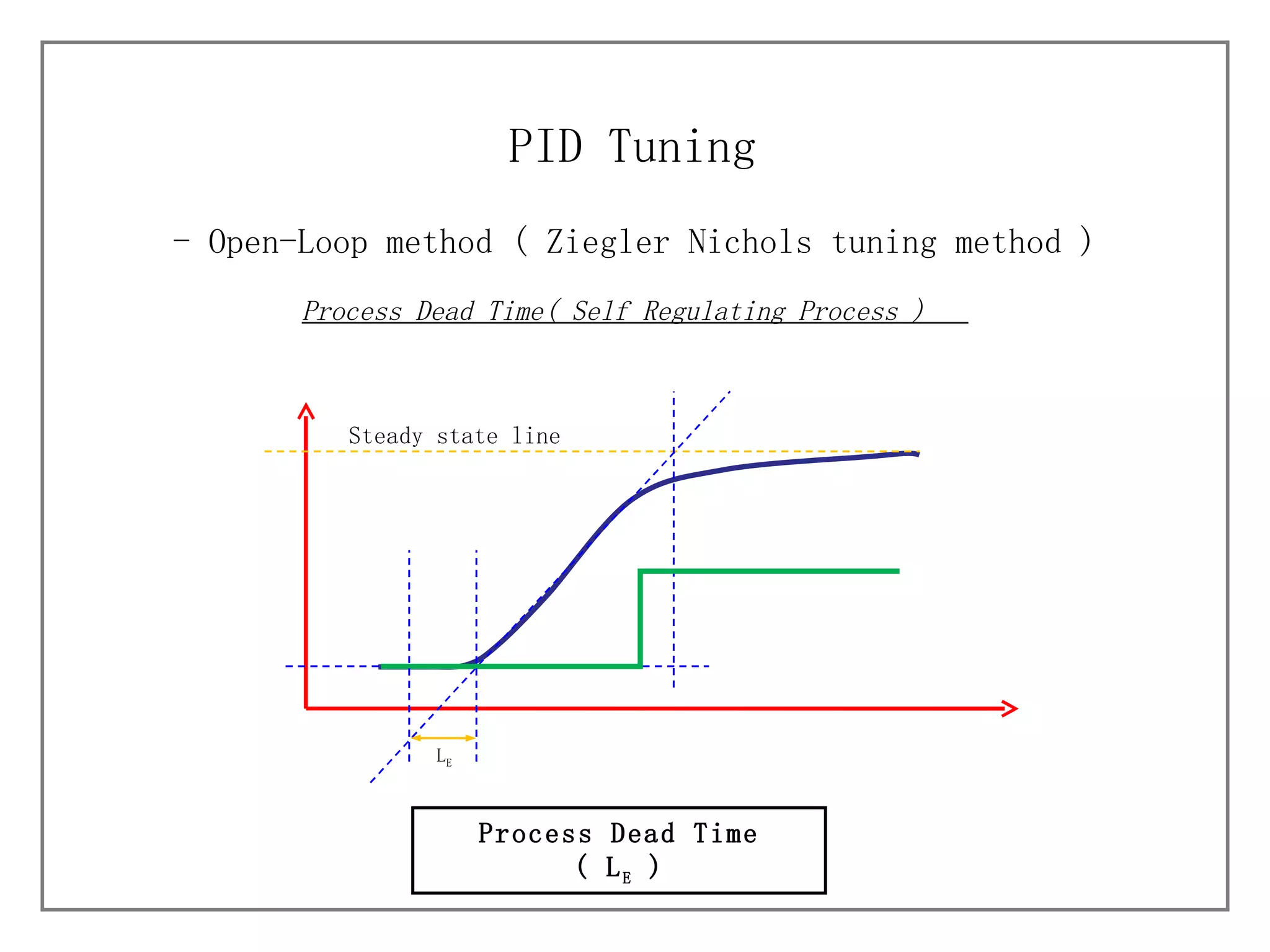
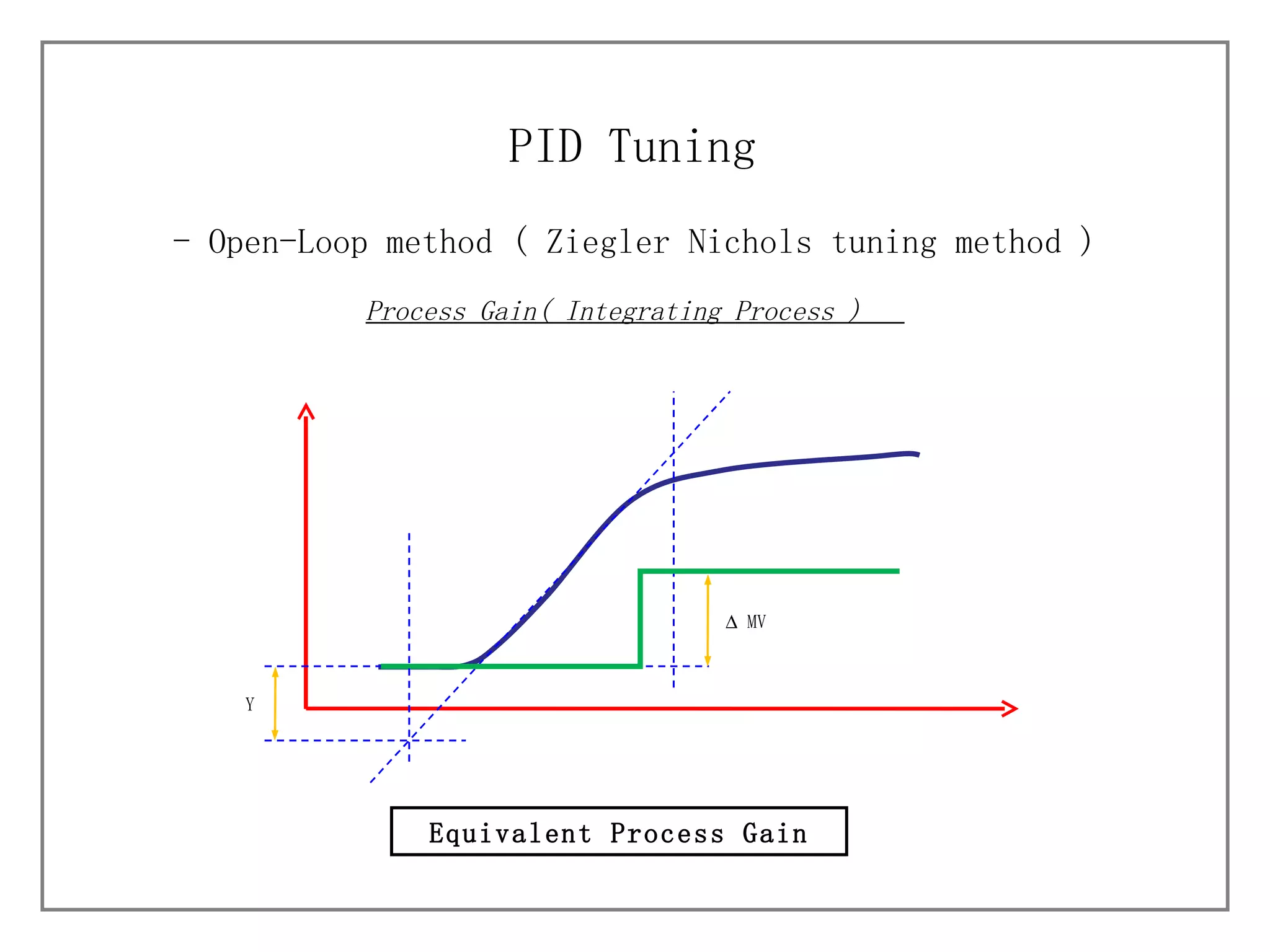
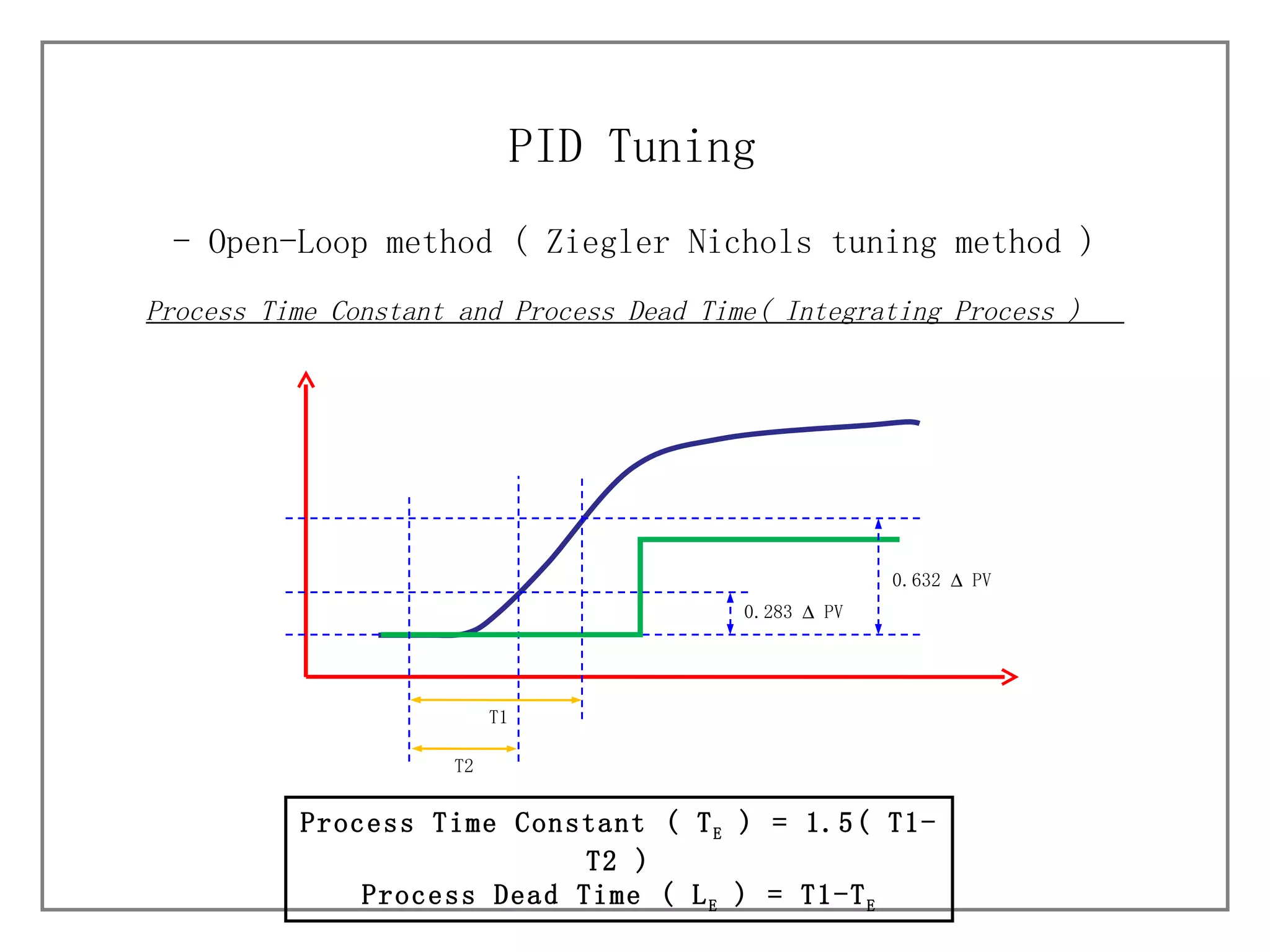
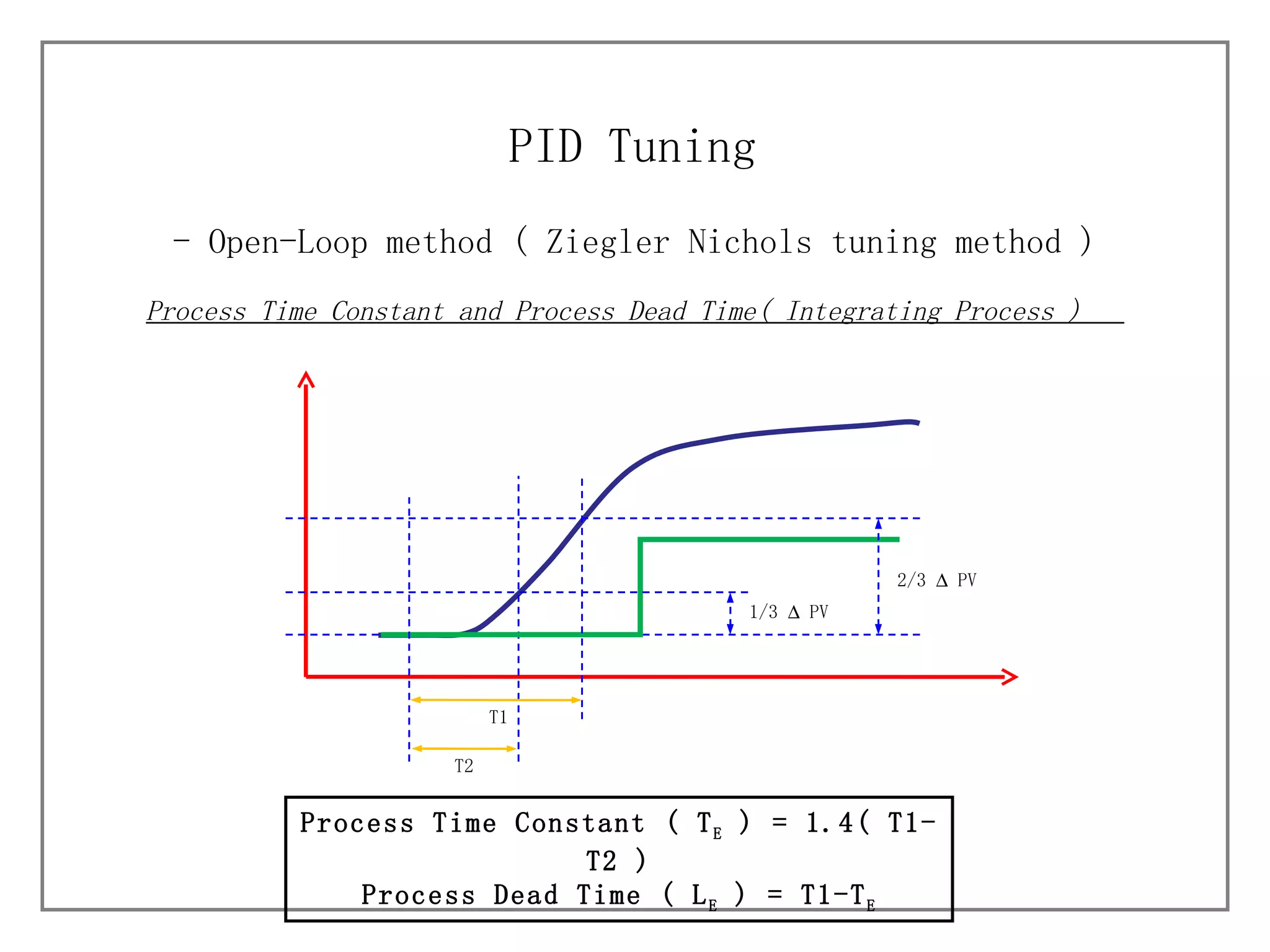
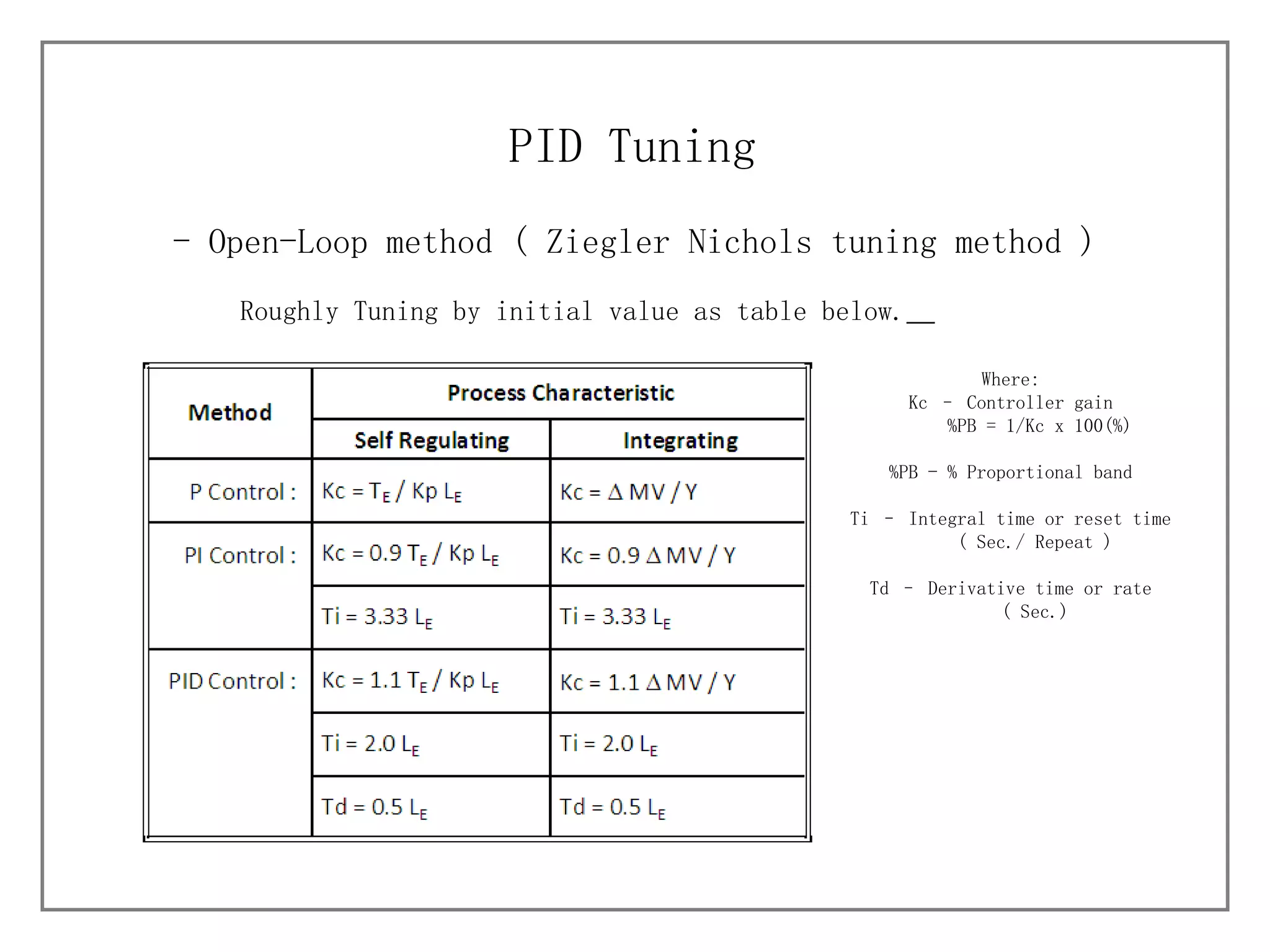
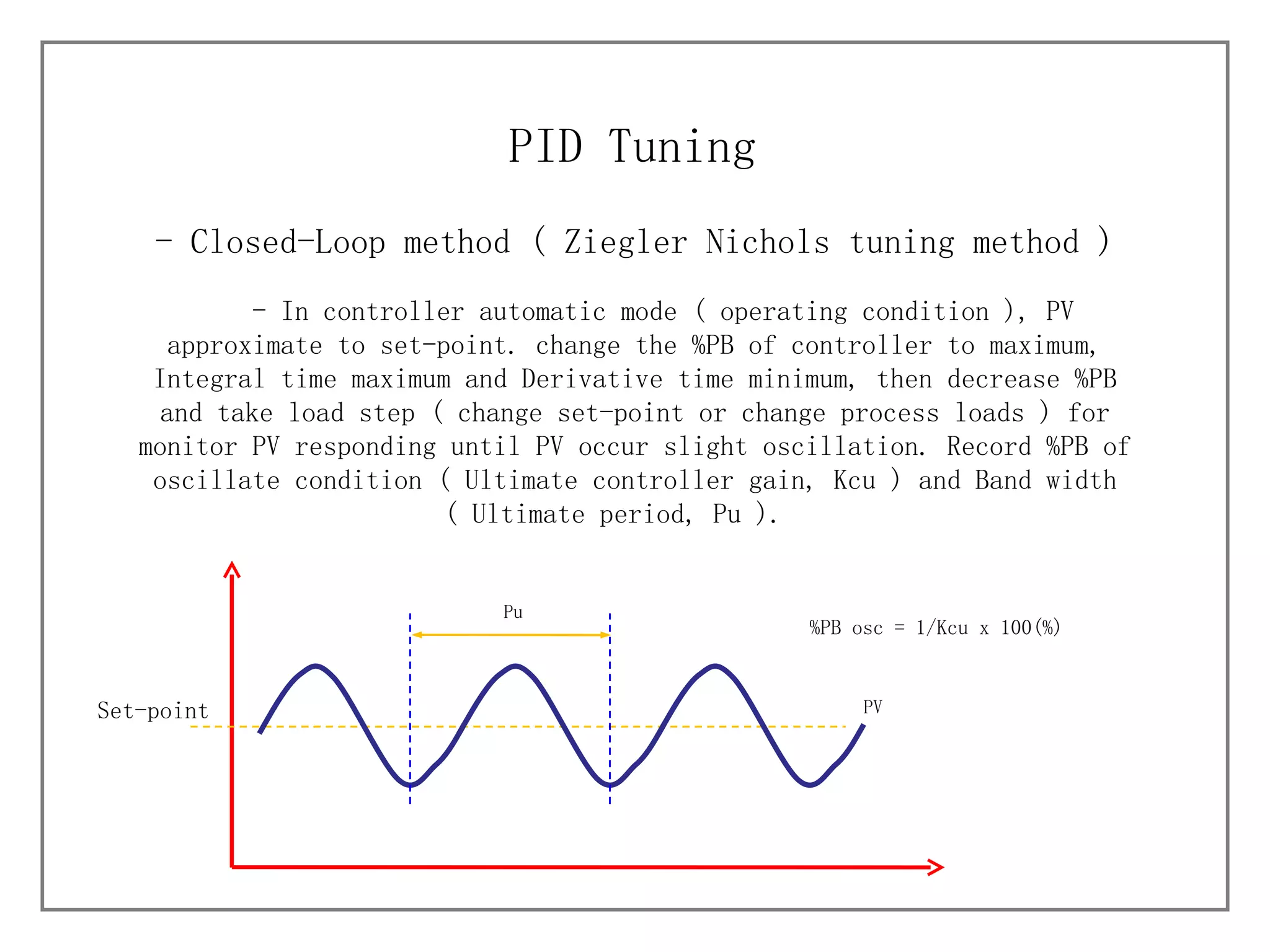
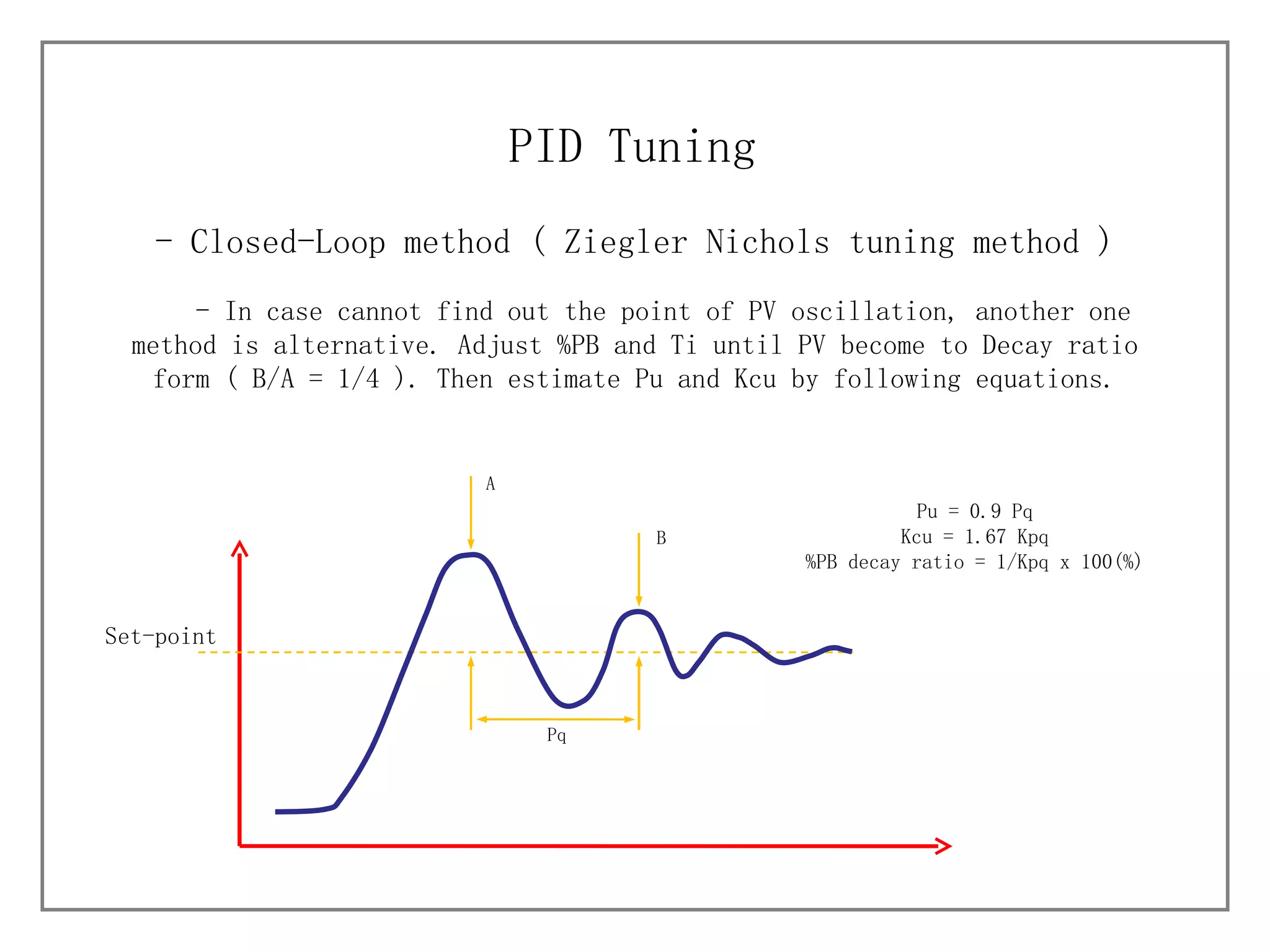
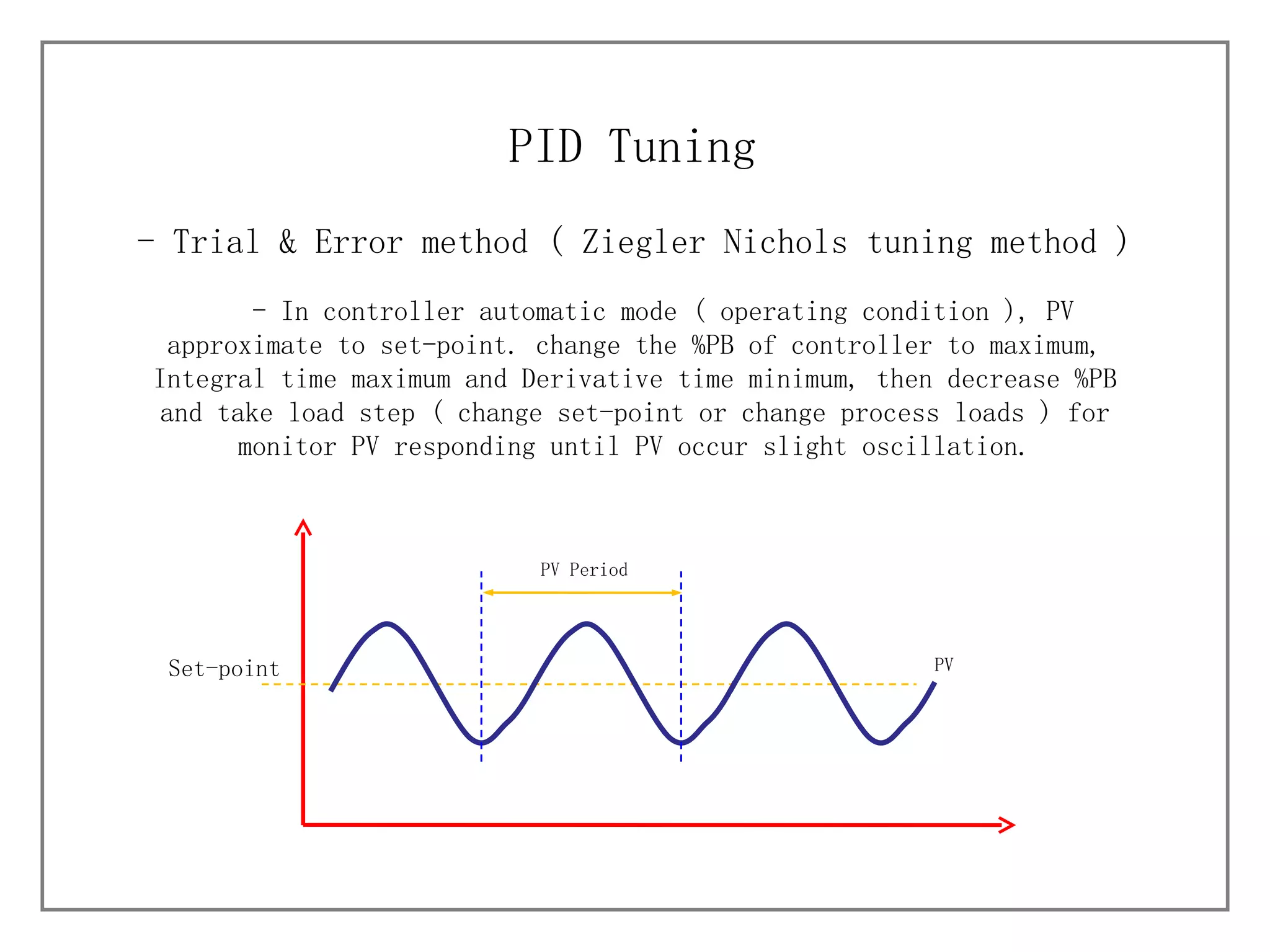
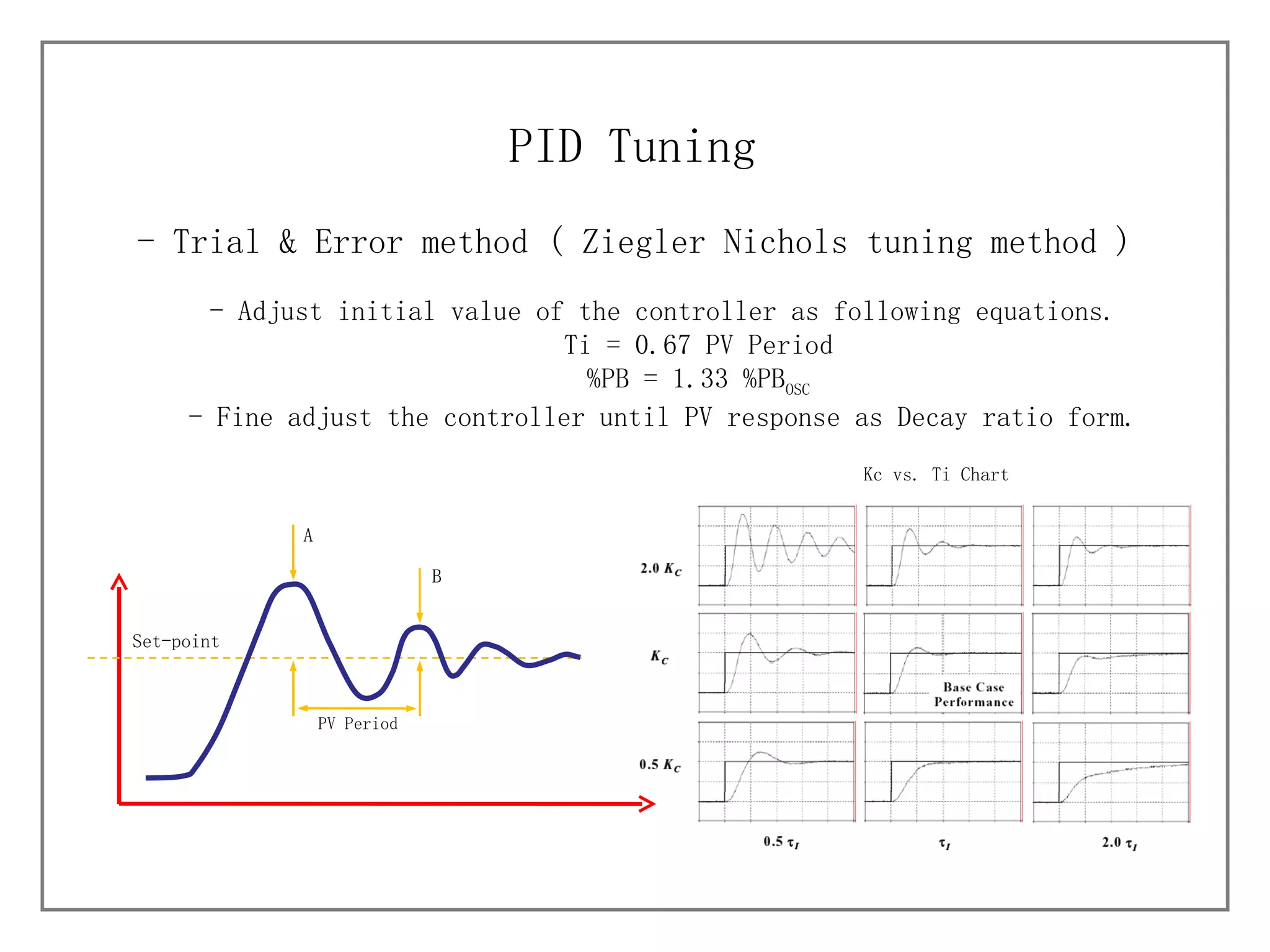
3) It details different tuning methods like open-loop, closed-loop, and trial and error, and provides equations and tables for initially setting PID parameters based on these methods.