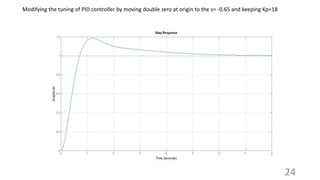
This document discusses different types of PID controllers including proportional (P), integral (I), derivative (D), PI, PD, and PID controllers. It provides the transfer functions and describes the basic functionality of each type. Tuning methods for PID controllers are presented, including Ziegler-Nichols tuning when the dynamic plant model is known or unknown. Examples are given to illustrate tuning a PID controller to achieve approximately 25% overshoot for a control system.


![3
Problem 1.1- For the system shown in Fig. 1.1 draw the open loop step response.
1
𝑠2 + 10𝑠 + 20
Fig. 1.1
input output
Solution- with the help of following command in MATLAB response is obtained.
G= tf(1,[1 10 20]);
step(G);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pid-180705094834/85/PID-Controllers-3-320.jpg)