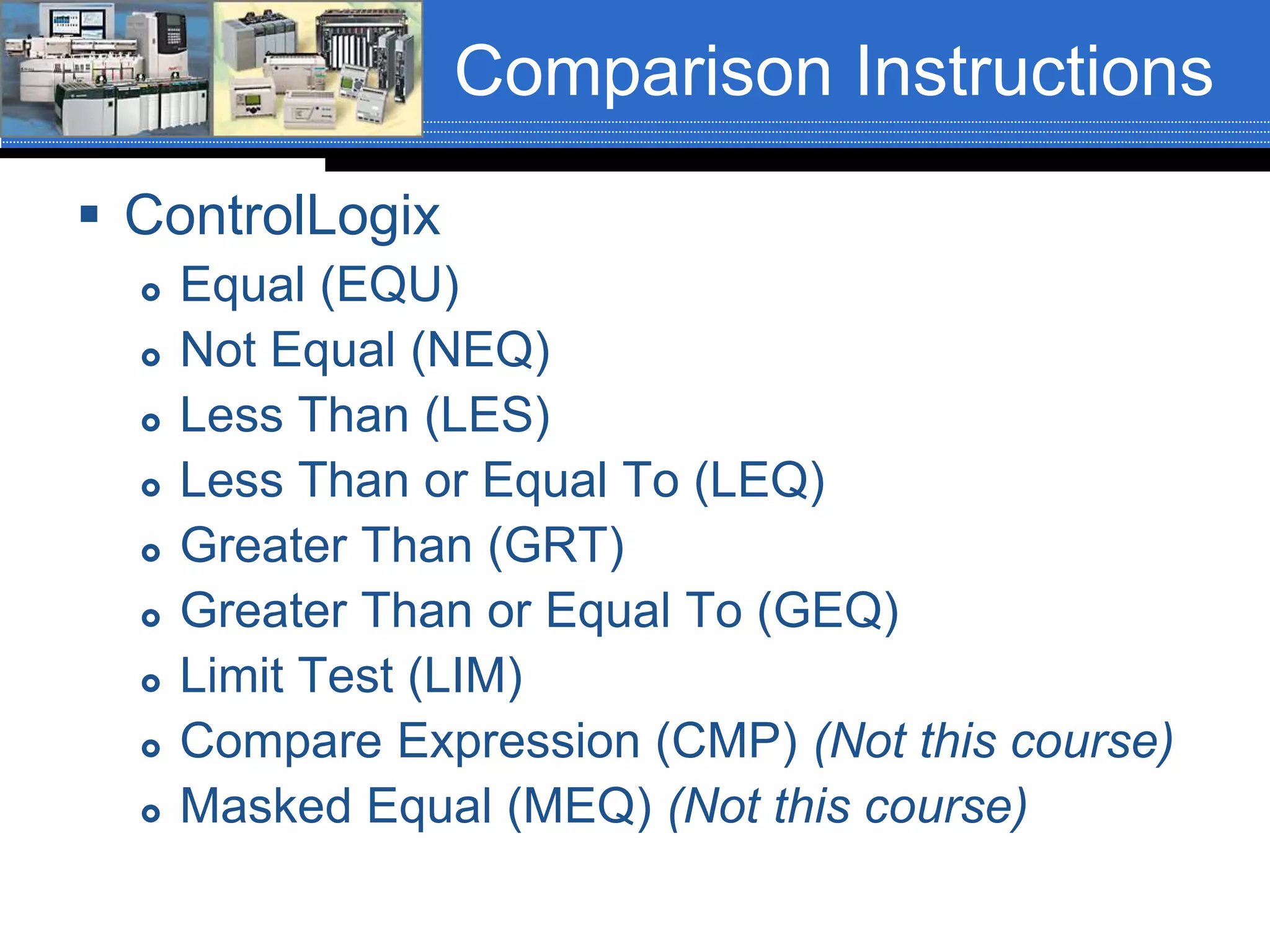
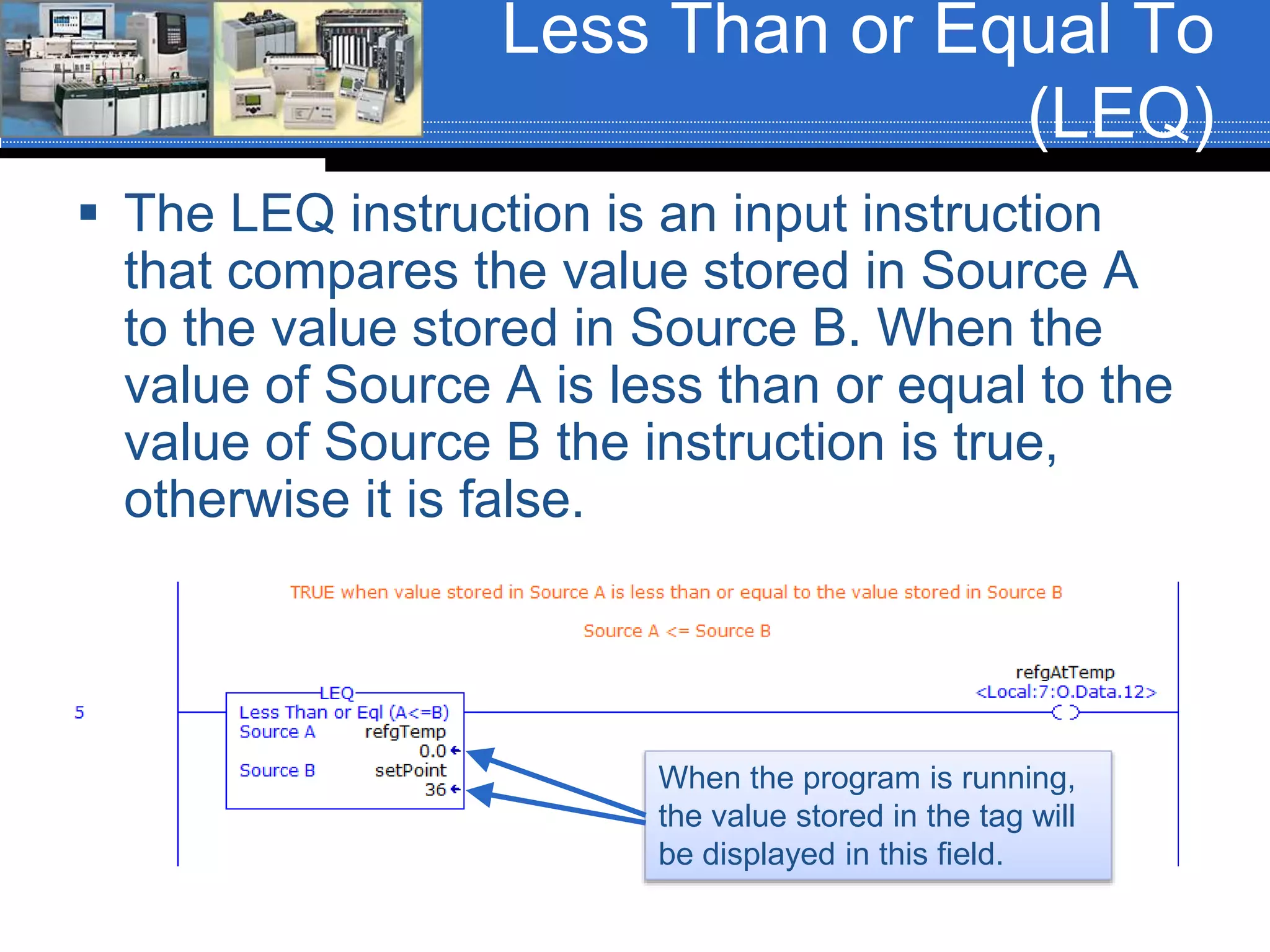
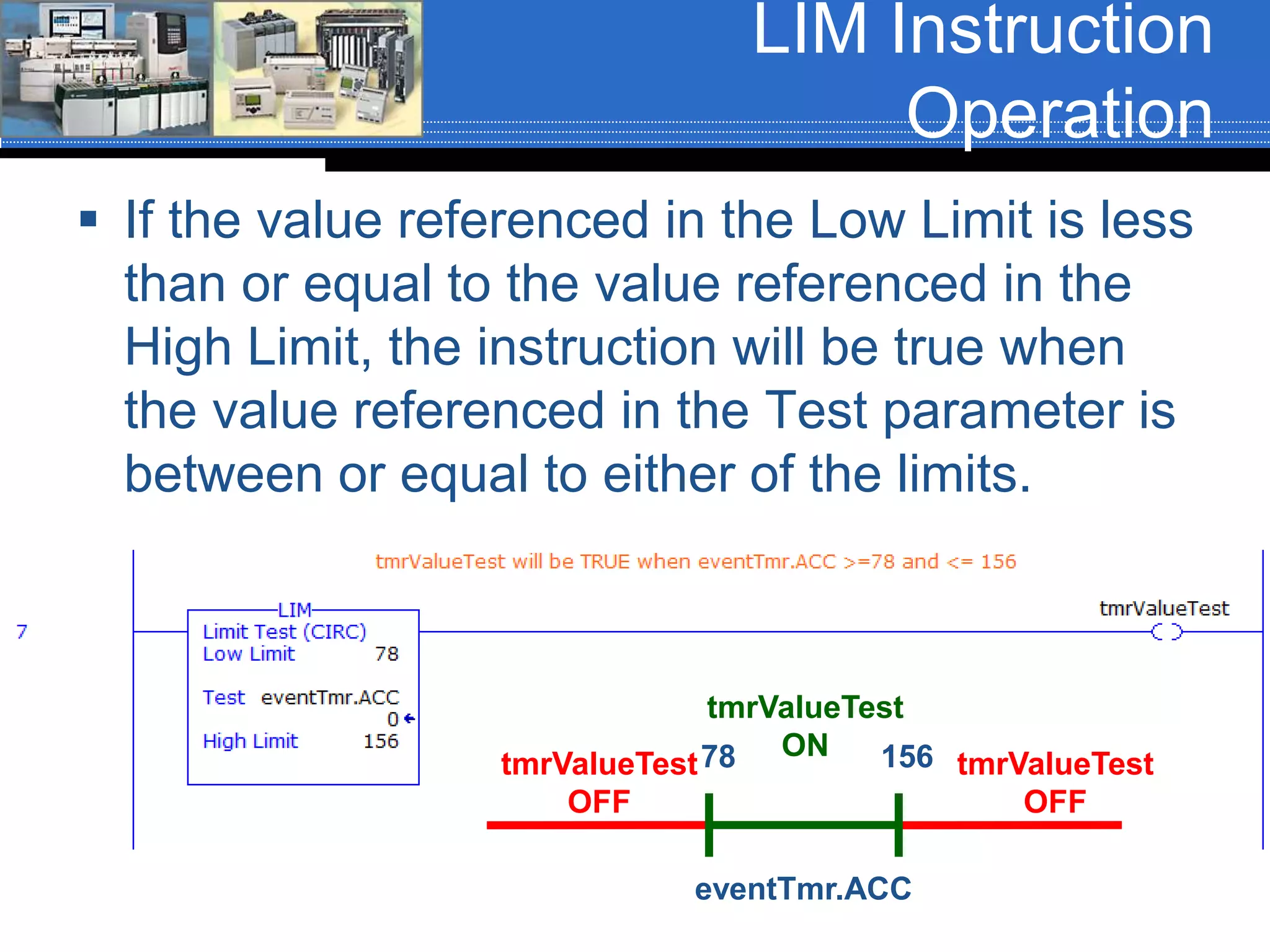
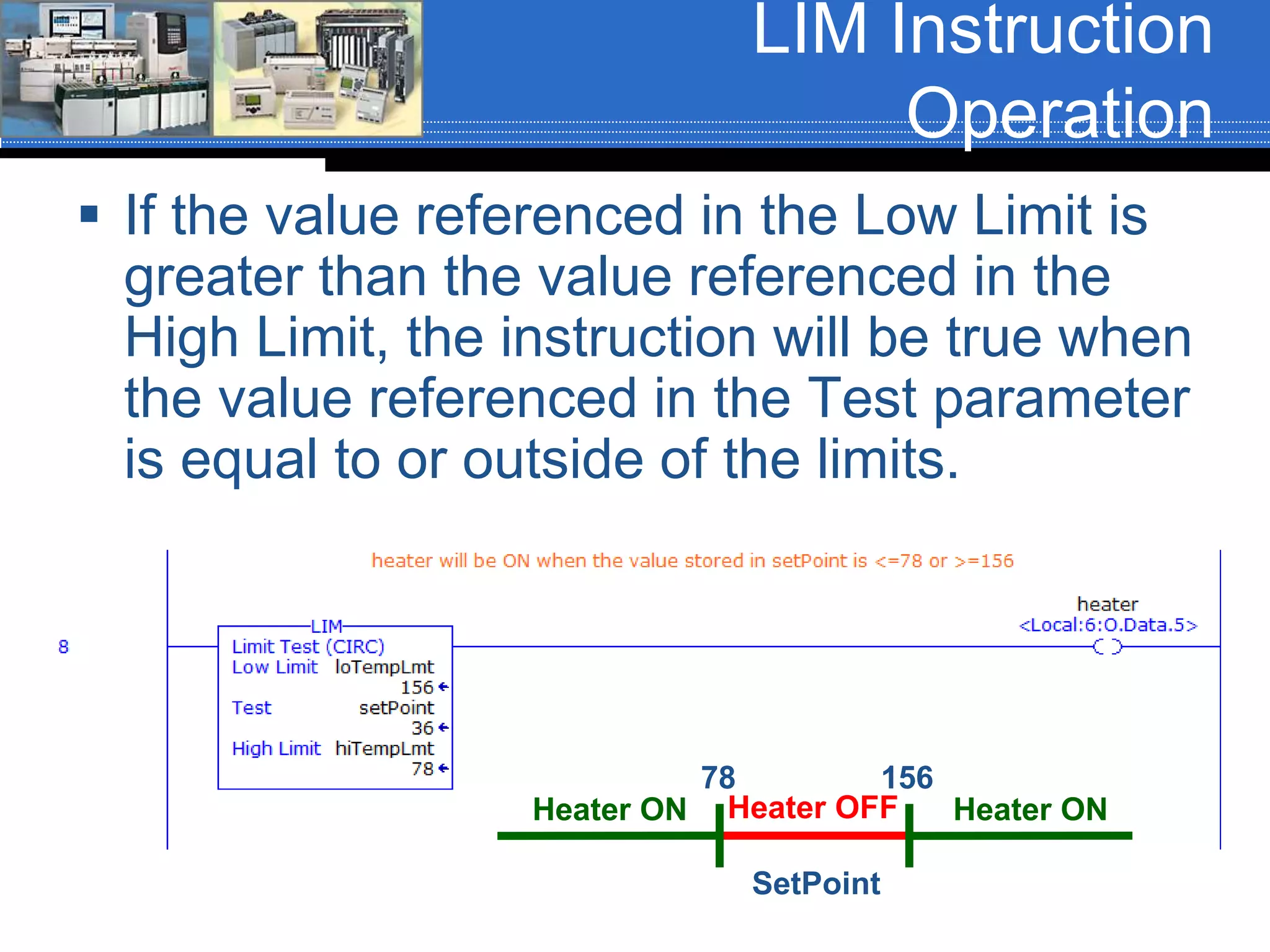
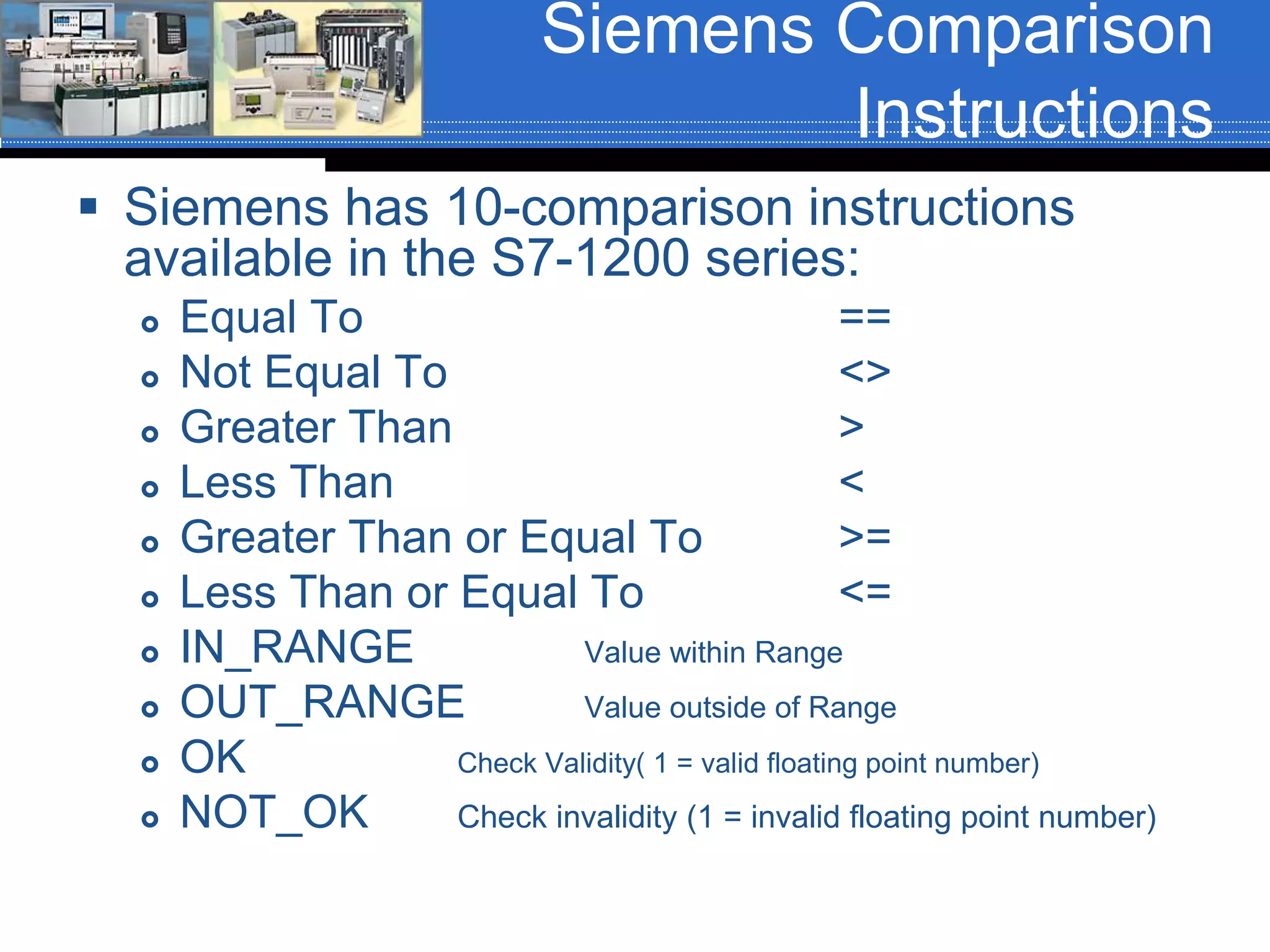
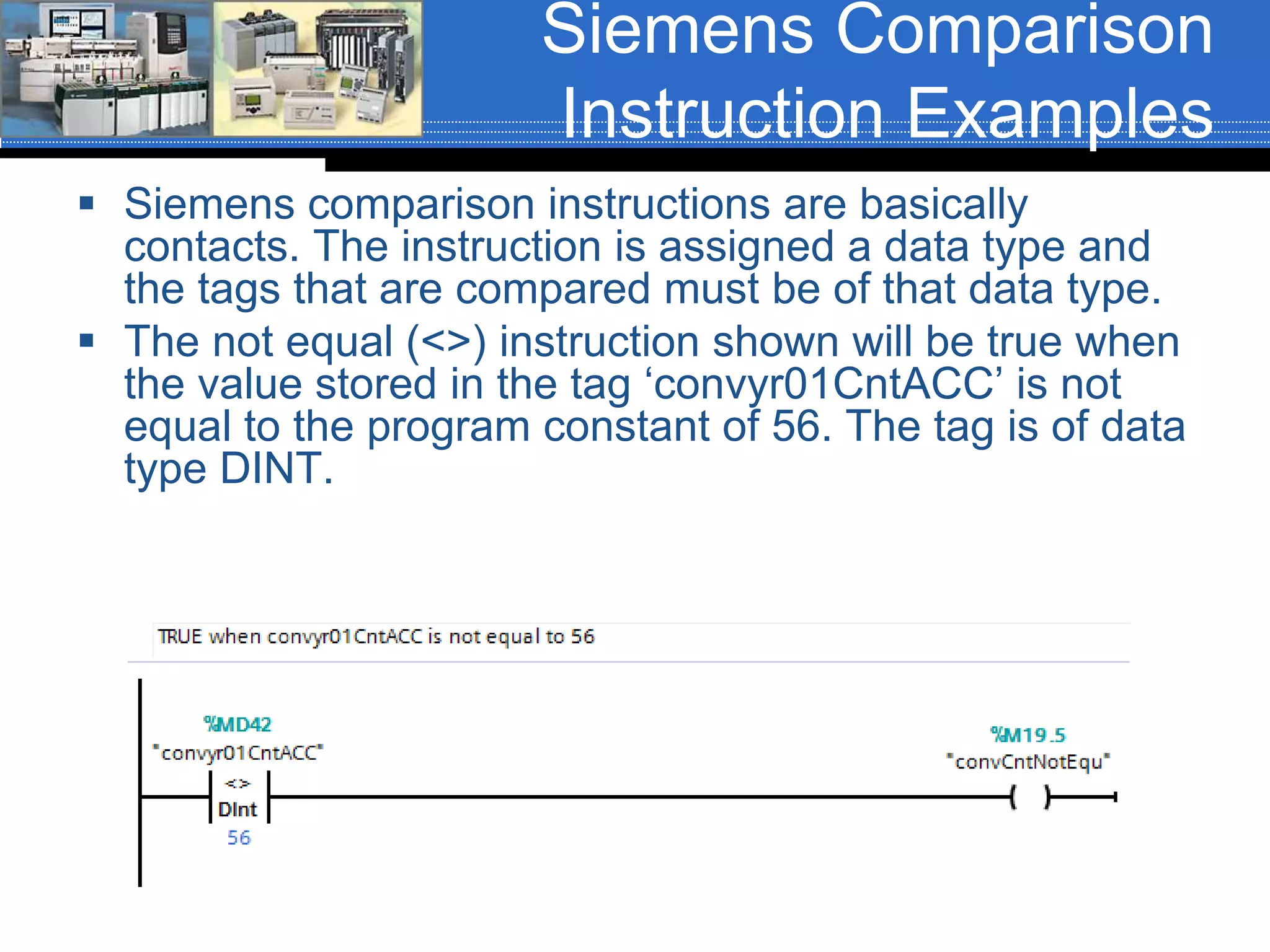
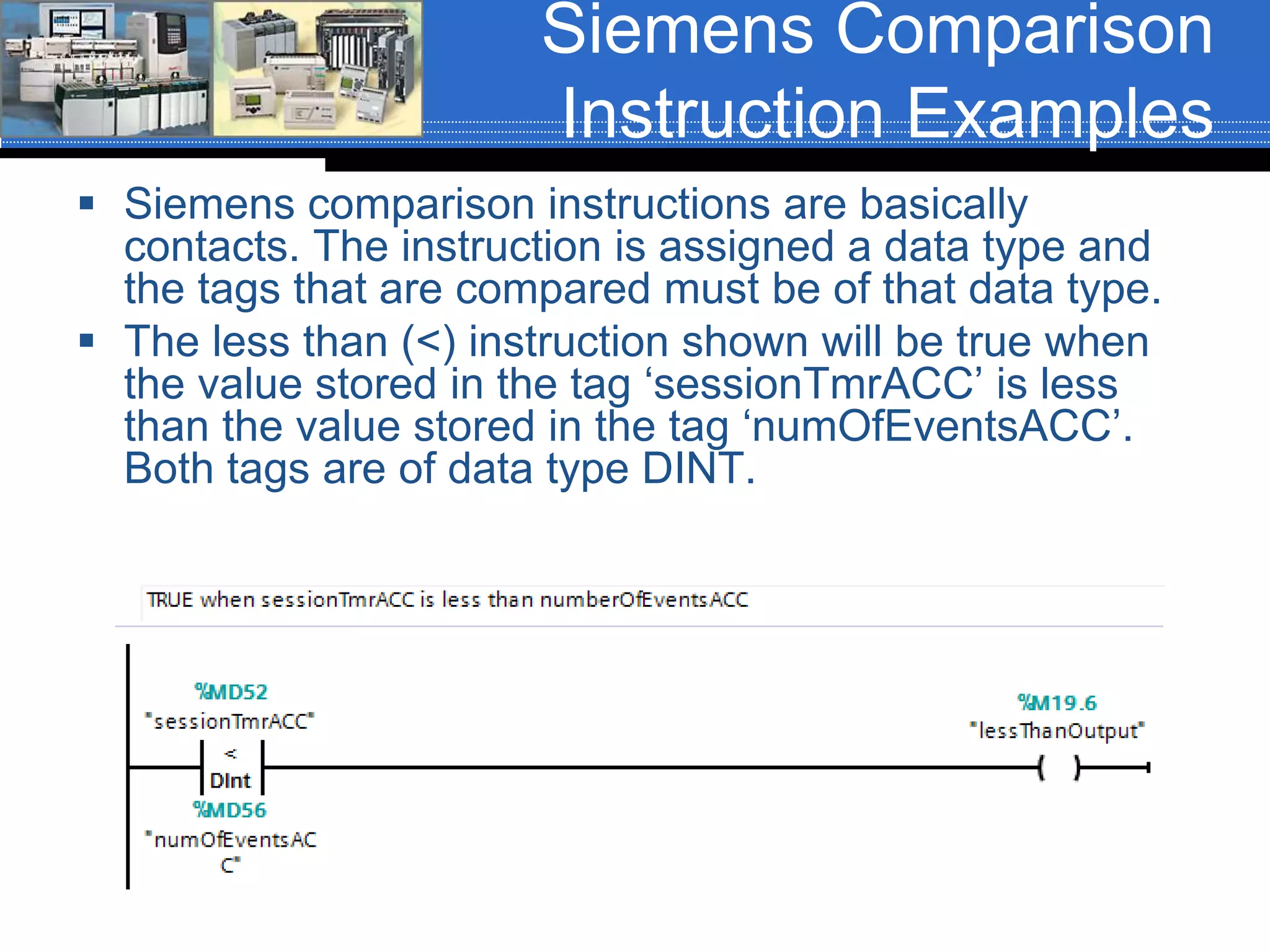
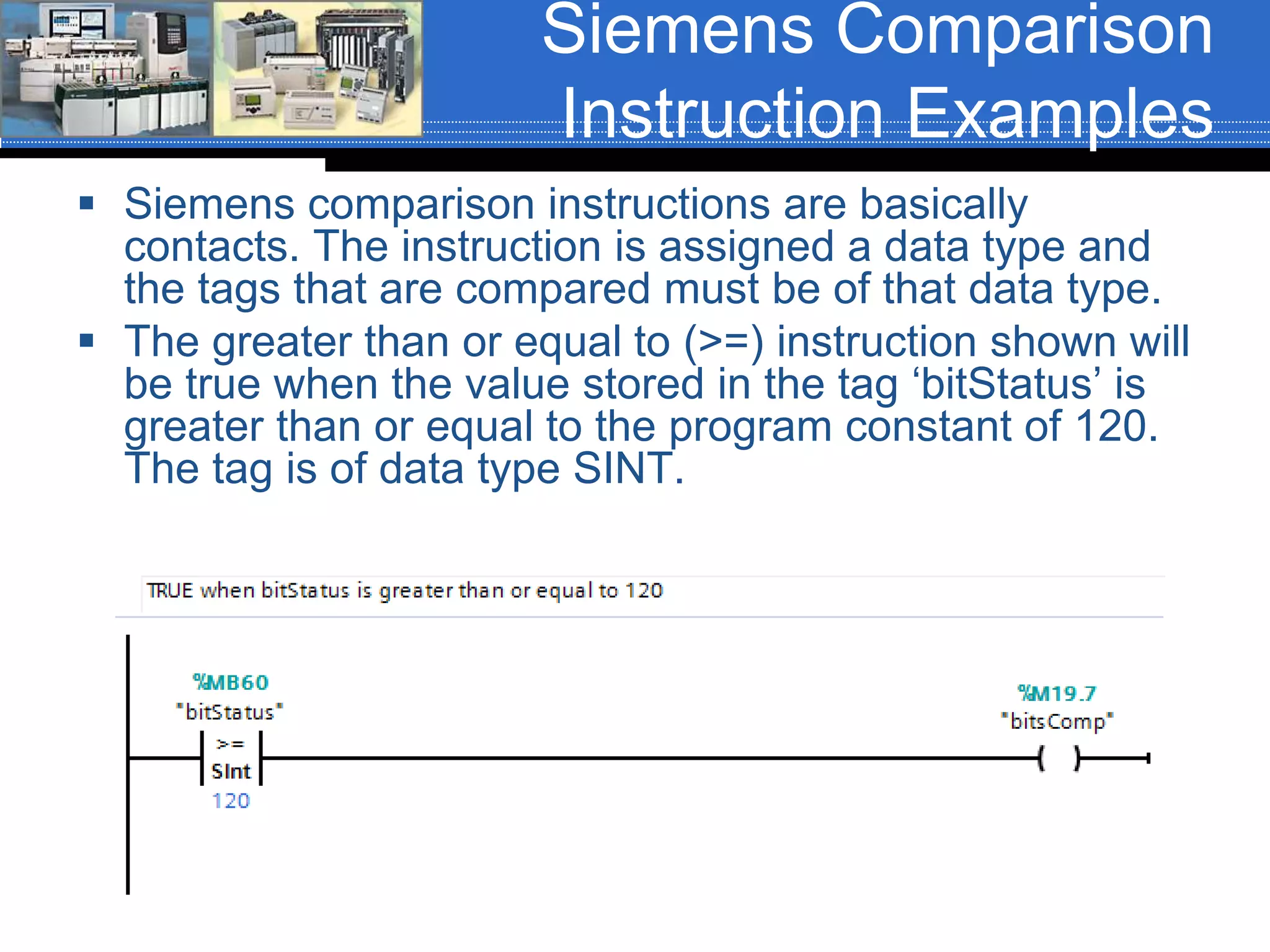
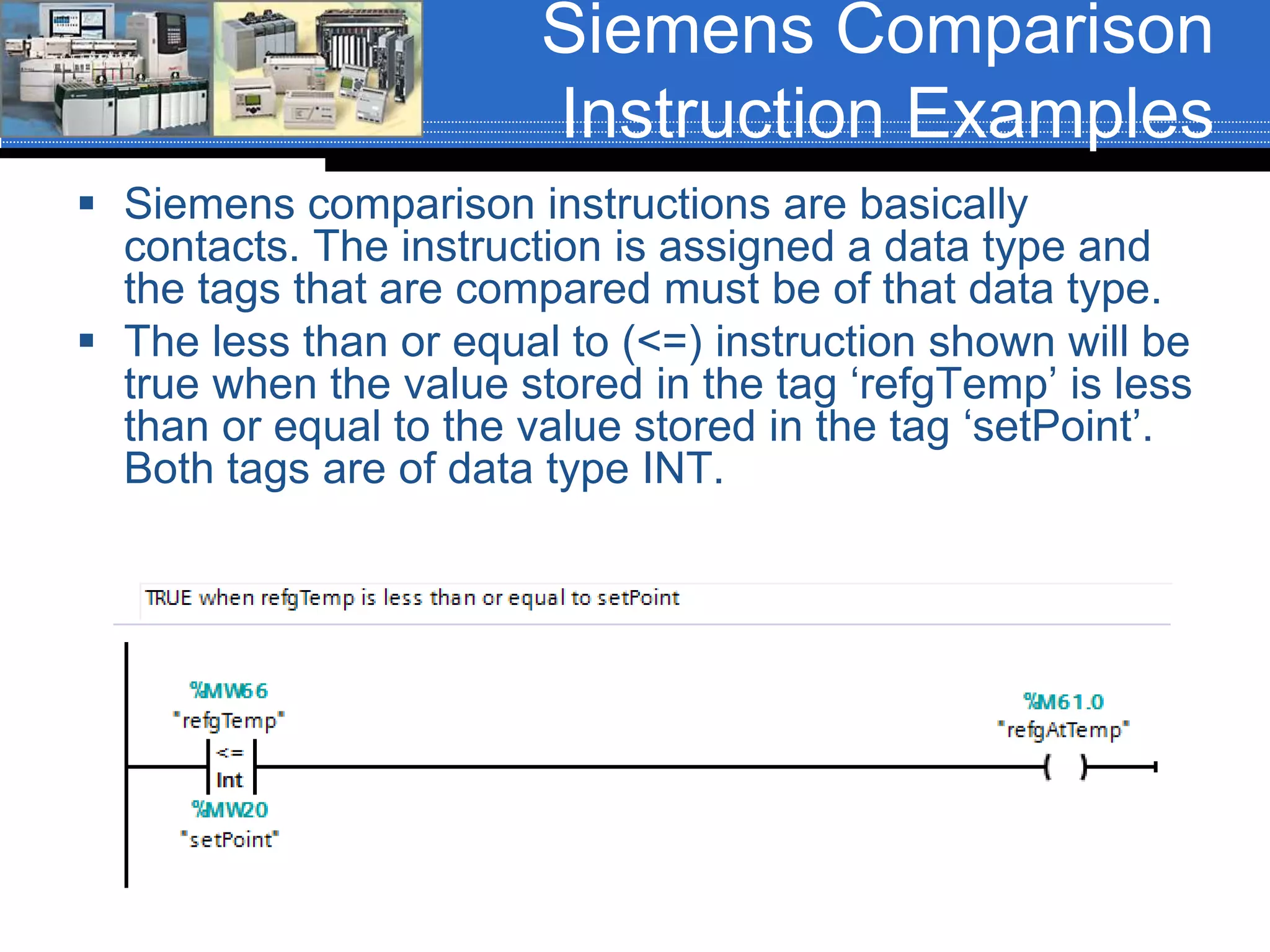
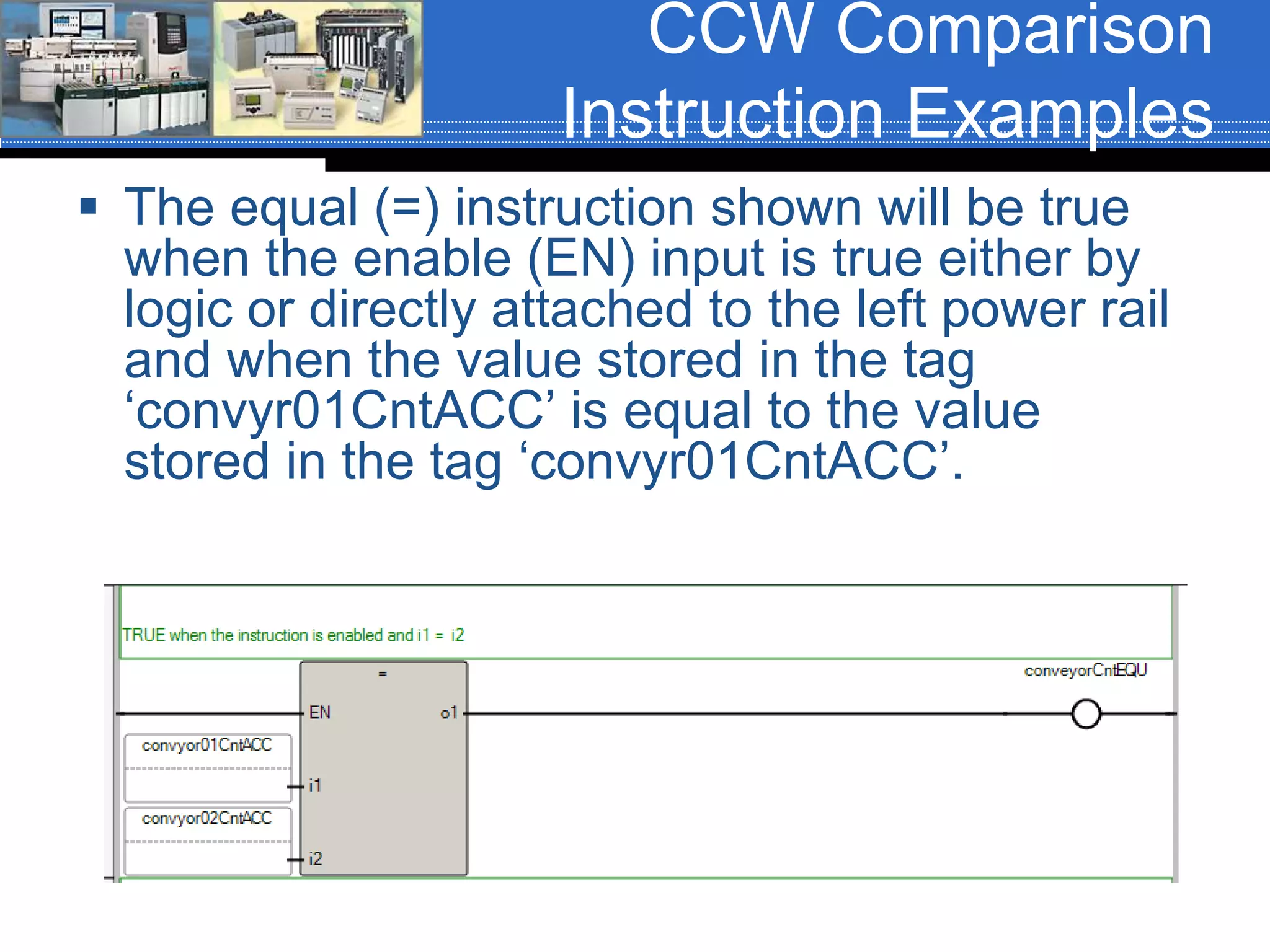
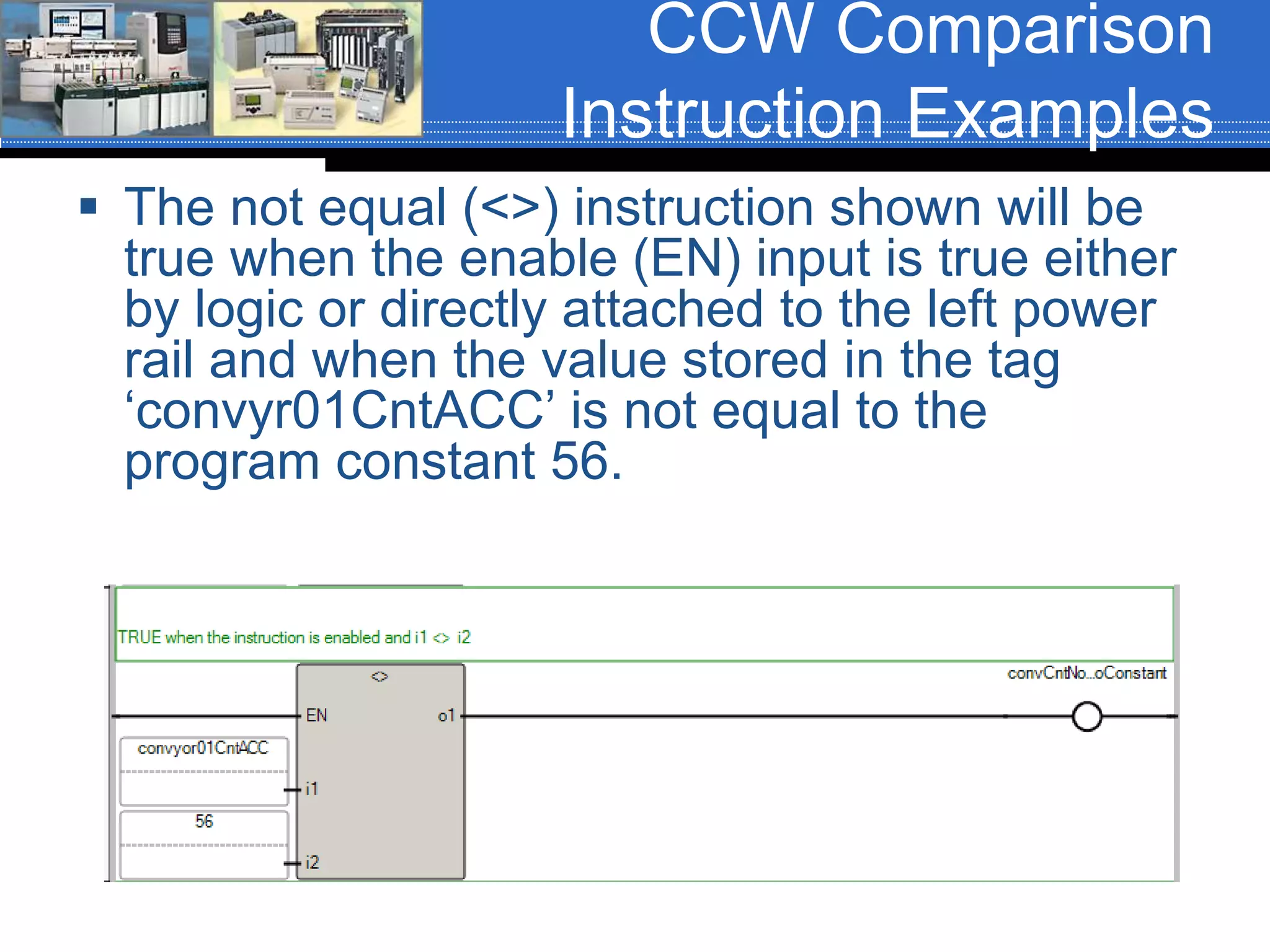
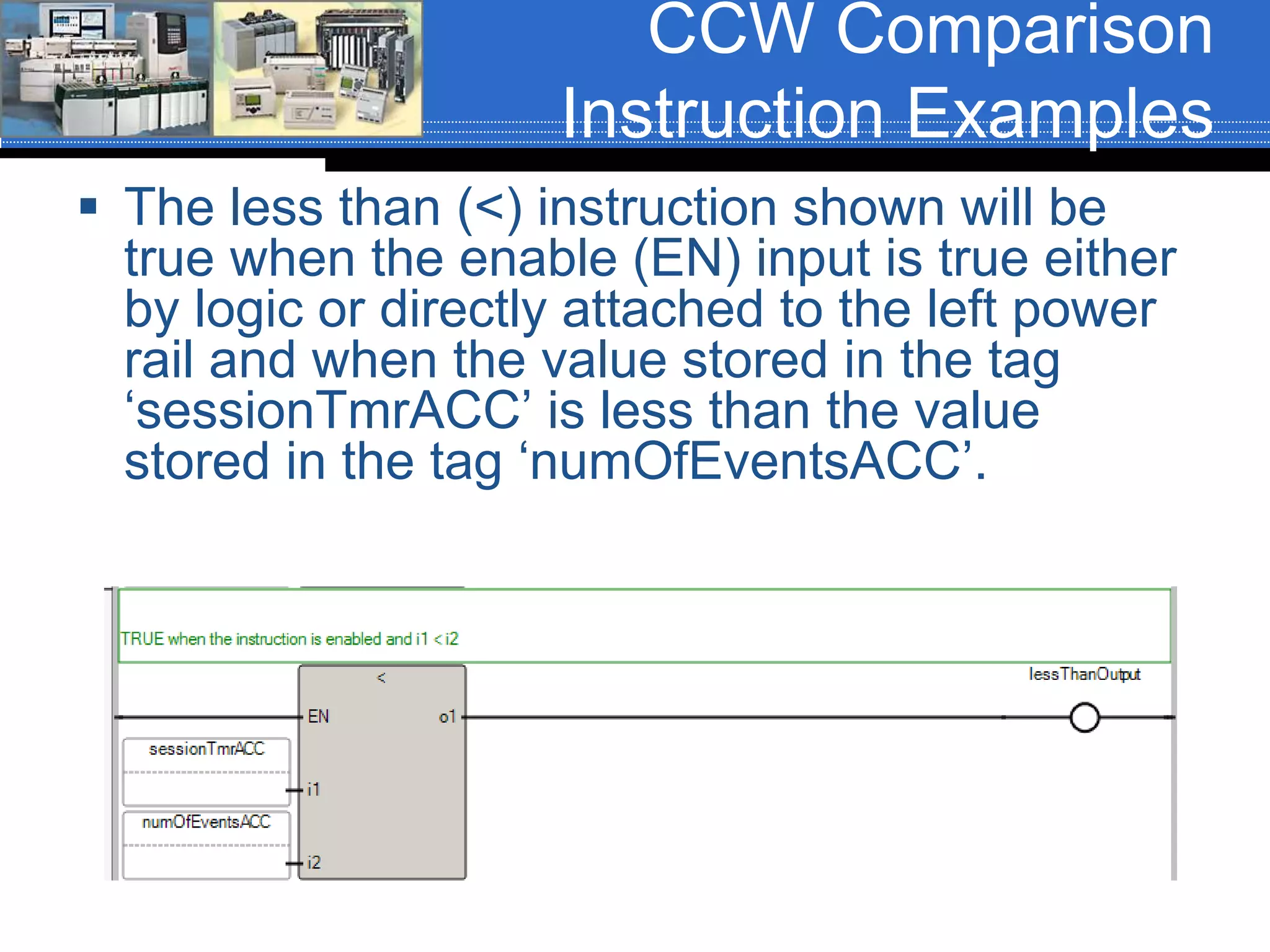
Chapter 07 discusses conversion and comparison instructions used for data comparisons in programming, detailing different types such as equal (equ), not equal (neq), greater than (grt), and less than (les). It highlights the rules for parameters involving word-level data types and describes how to implement instructions for setting conditions based on the results of comparisons. Additionally, the document provides specific examples of comparison instructions in ControlLogix, Siemens, and Connected Components Workbench environments.