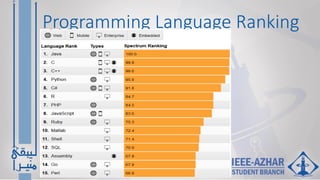
This document provides an overview of the C programming language, including:
- Why software is needed for embedded systems and choosing an appropriate programming language
- Key features of C like being easier/faster to develop with, portability, and efficient pointer usage
- Differences between embedded C and desktop C like writing low-level and inline assembly code
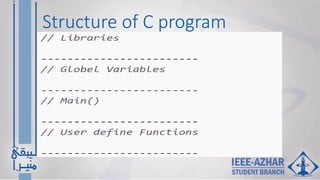
- The structure of a basic C program and a "Hello, World!" example
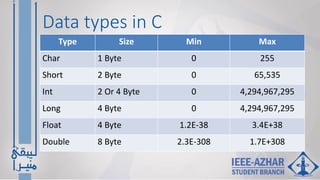
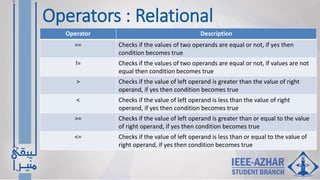
- C programming basics like constants, variables, data types, and arithmetic, relational, logical, and bitwise operators
- Control flow statements in C like if, if/else, and switch