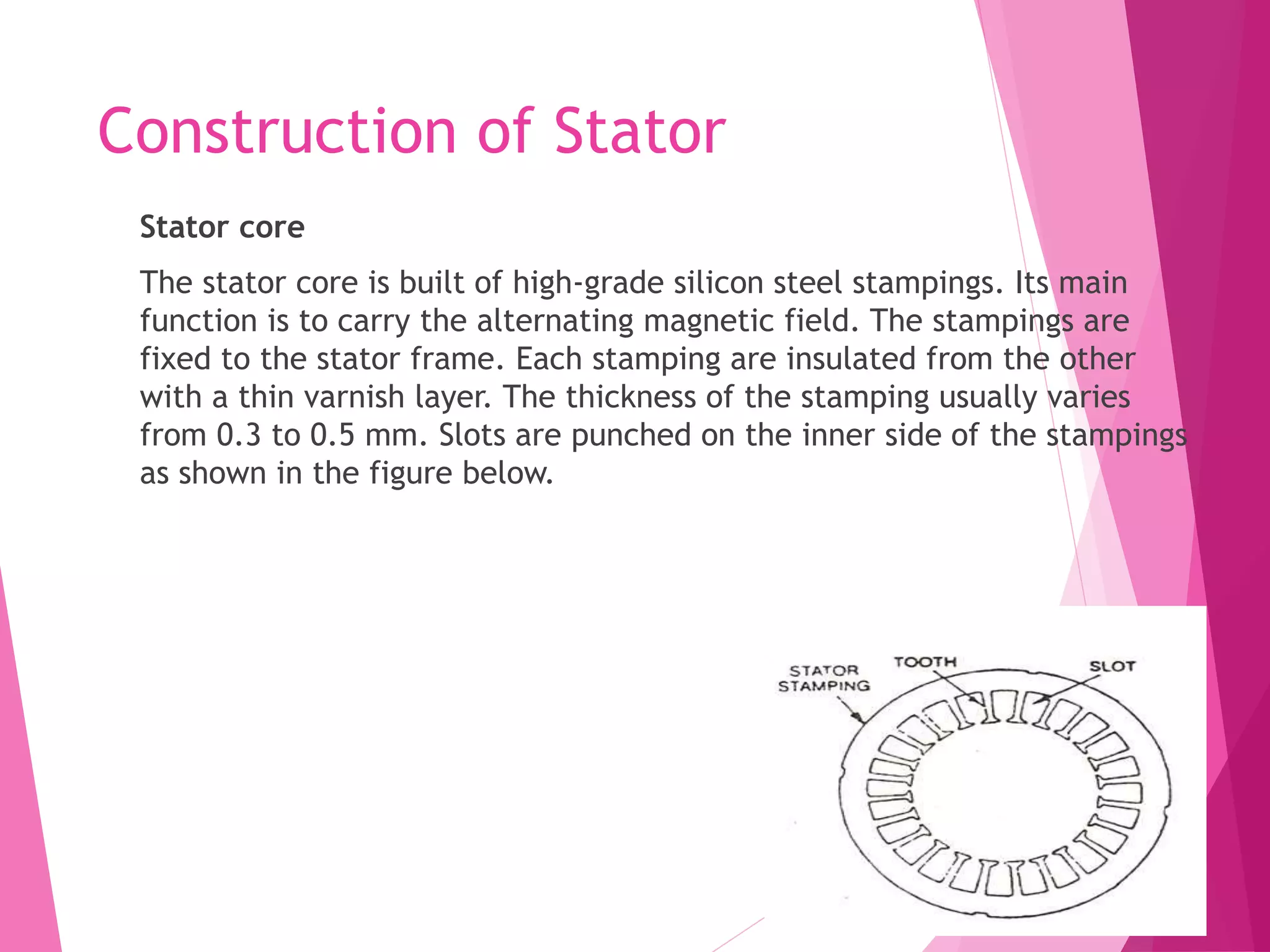
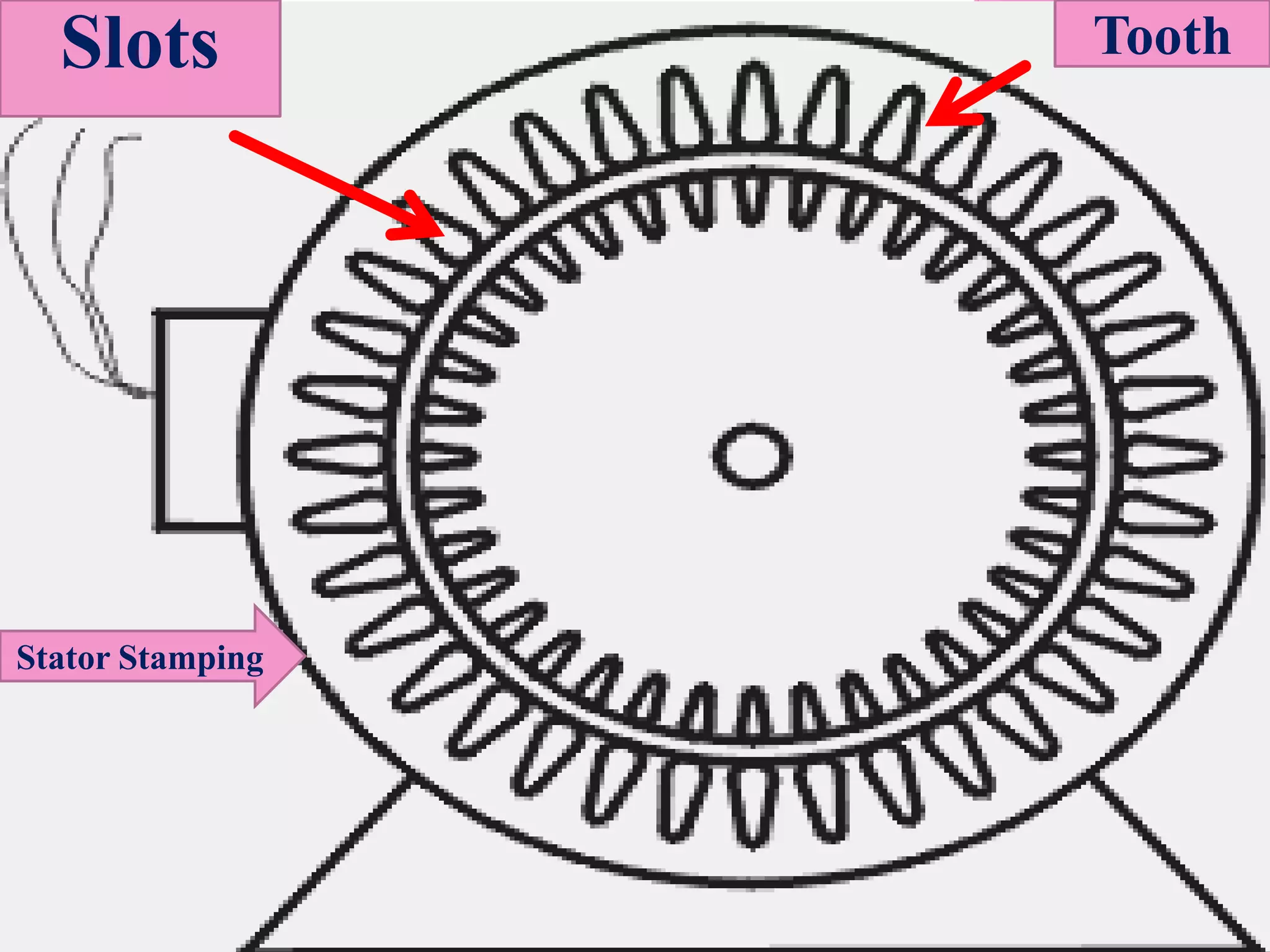
The document discusses induction motors, which are asynchronous AC motors that operate below synchronous speed. It describes the two main types - single phase and three phase induction motors. Three phase induction motors are commonly used in industry due to their ability to provide bulk power conversion from electrical to mechanical power. The document then discusses the construction and working principles of three phase induction motors in detail, including their stator, rotor, and how rotational motion is induced in the rotor via electromagnetic induction from the rotating stator magnetic field.