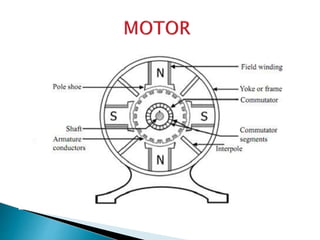
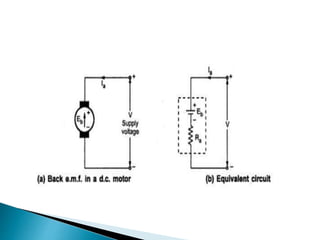
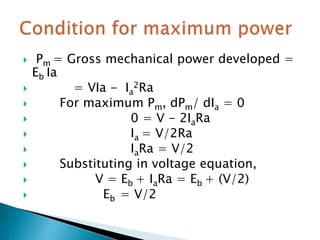
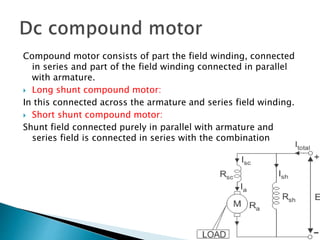
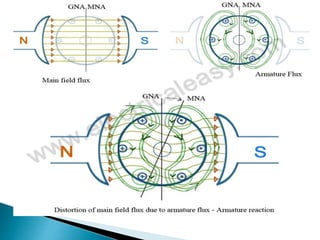
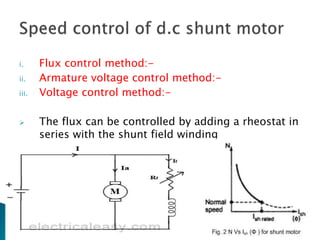
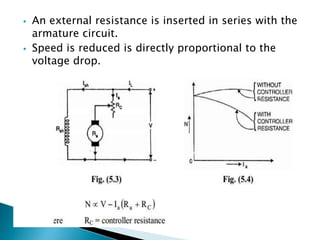
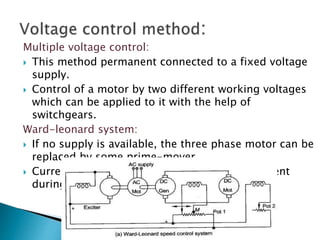
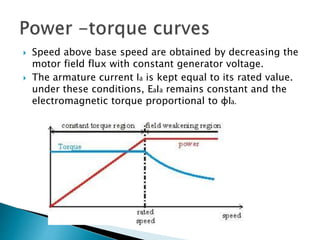
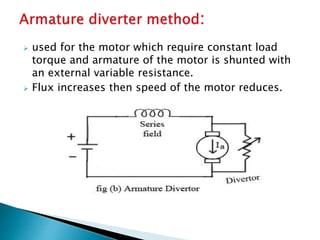
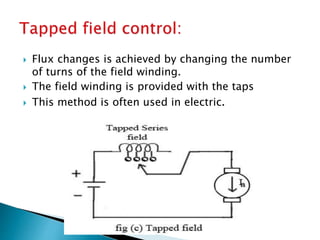
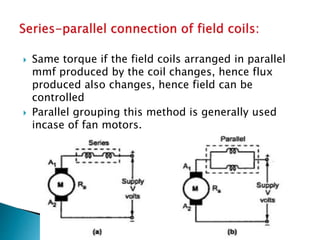
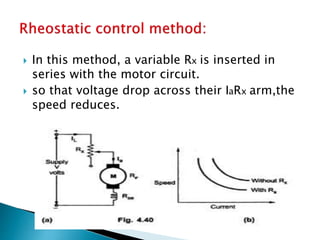
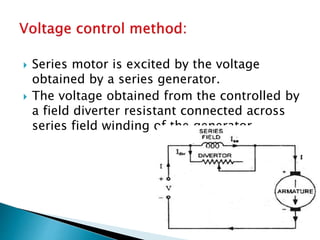
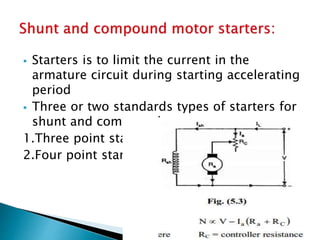
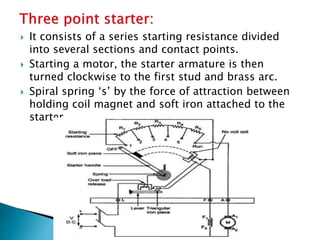
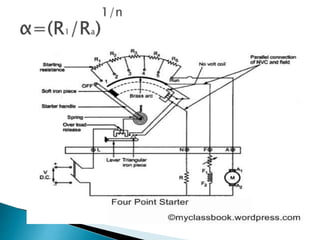
A DC motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy through electromagnetic induction. When a current-carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a mechanical force. In a DC motor, this force causes the armature conductors to rotate, producing torque. The motor's magnetic field is produced by a field winding and direct current is supplied by an external DC power source. A three-point starter is used to gradually reduce armature current and limit sparking during startup as motor speed increases and back EMF rises.