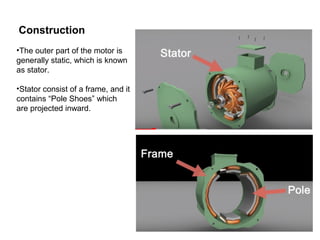
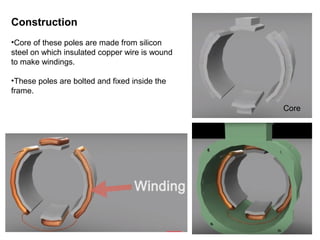
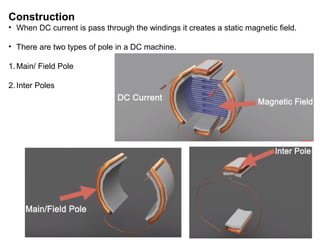
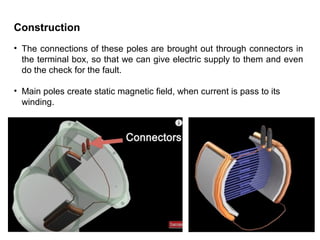
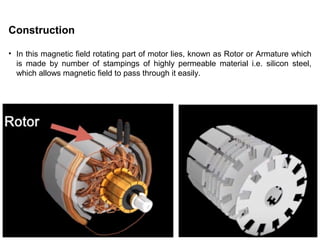
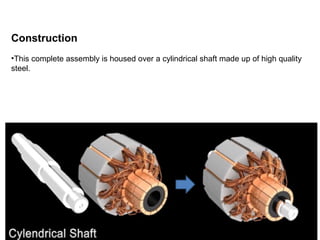
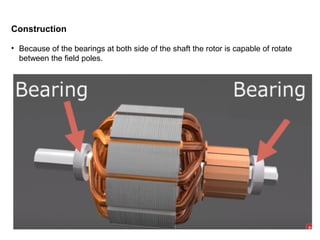
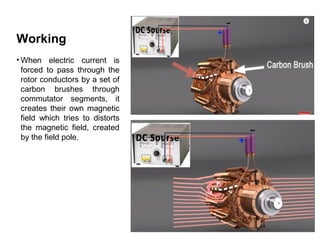
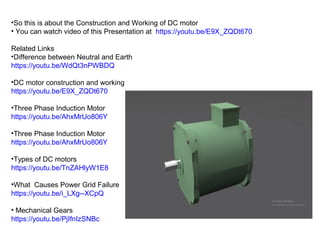
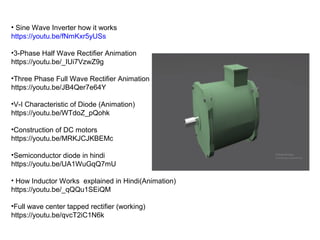
1. DC motors have a stationary stator that contains electromagnets and a rotating armature.
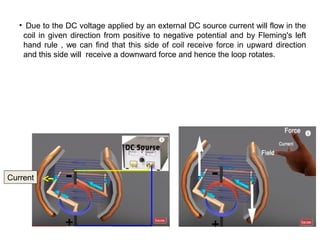
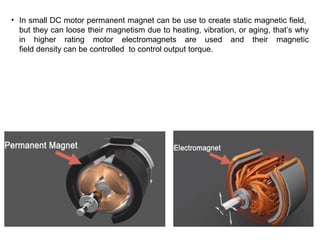
2. When DC current passes through the electromagnets, it creates a magnetic field that interacts with the magnetic field of the armature coils, producing rotational force.
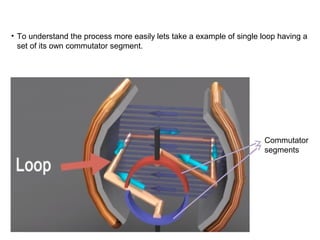
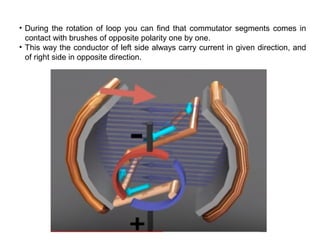
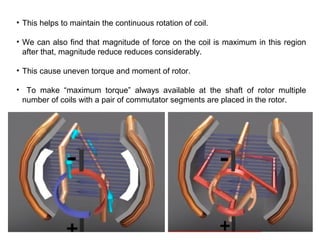
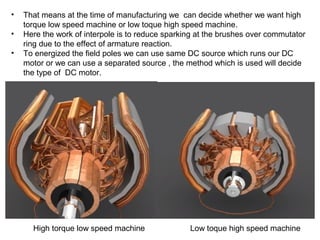
3. The commutator and brushes ensure that the direction of current in each armature coil remains constant, causing continuous rotation of the armature as each coil's magnetic field switches poles.