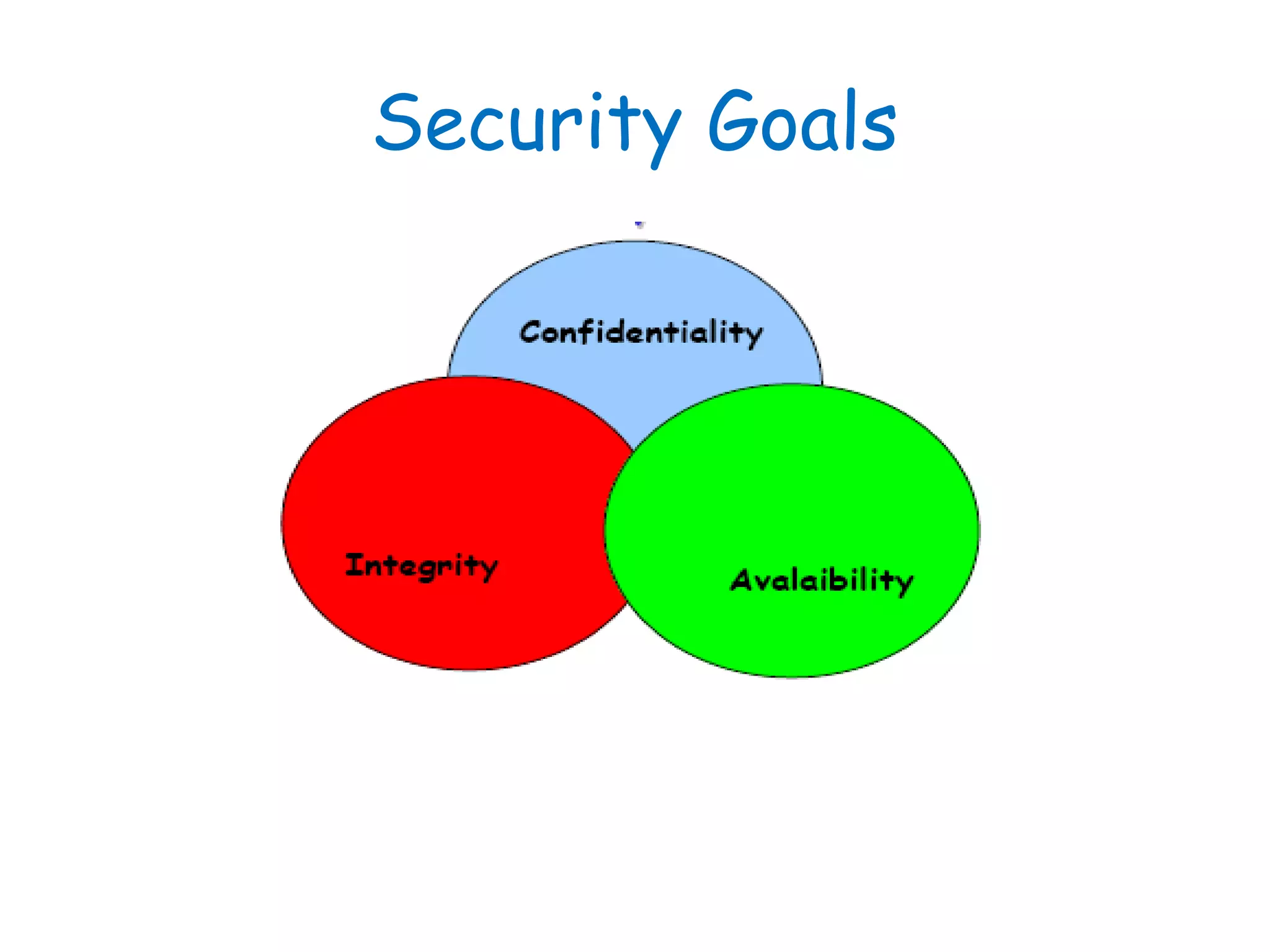
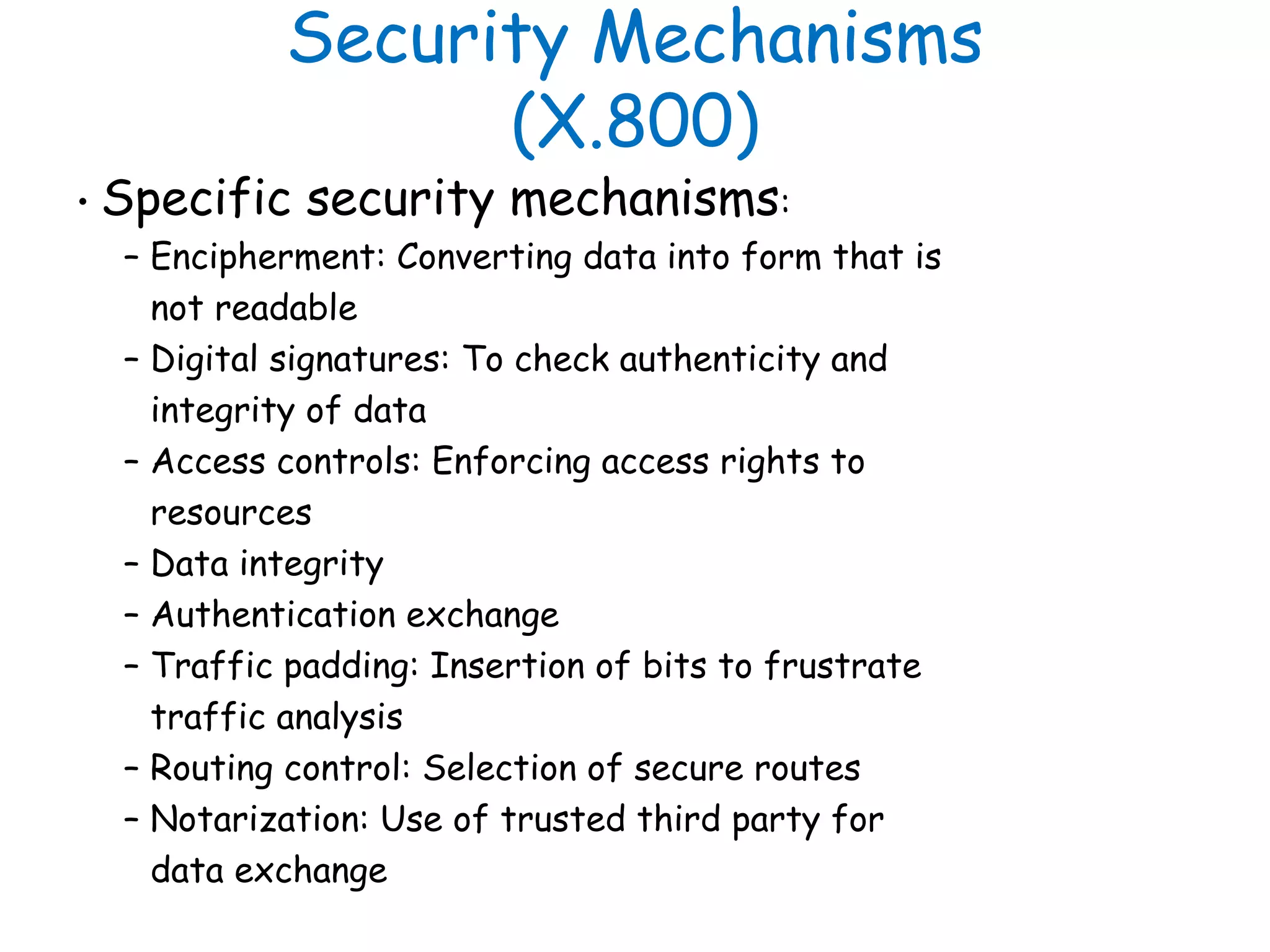
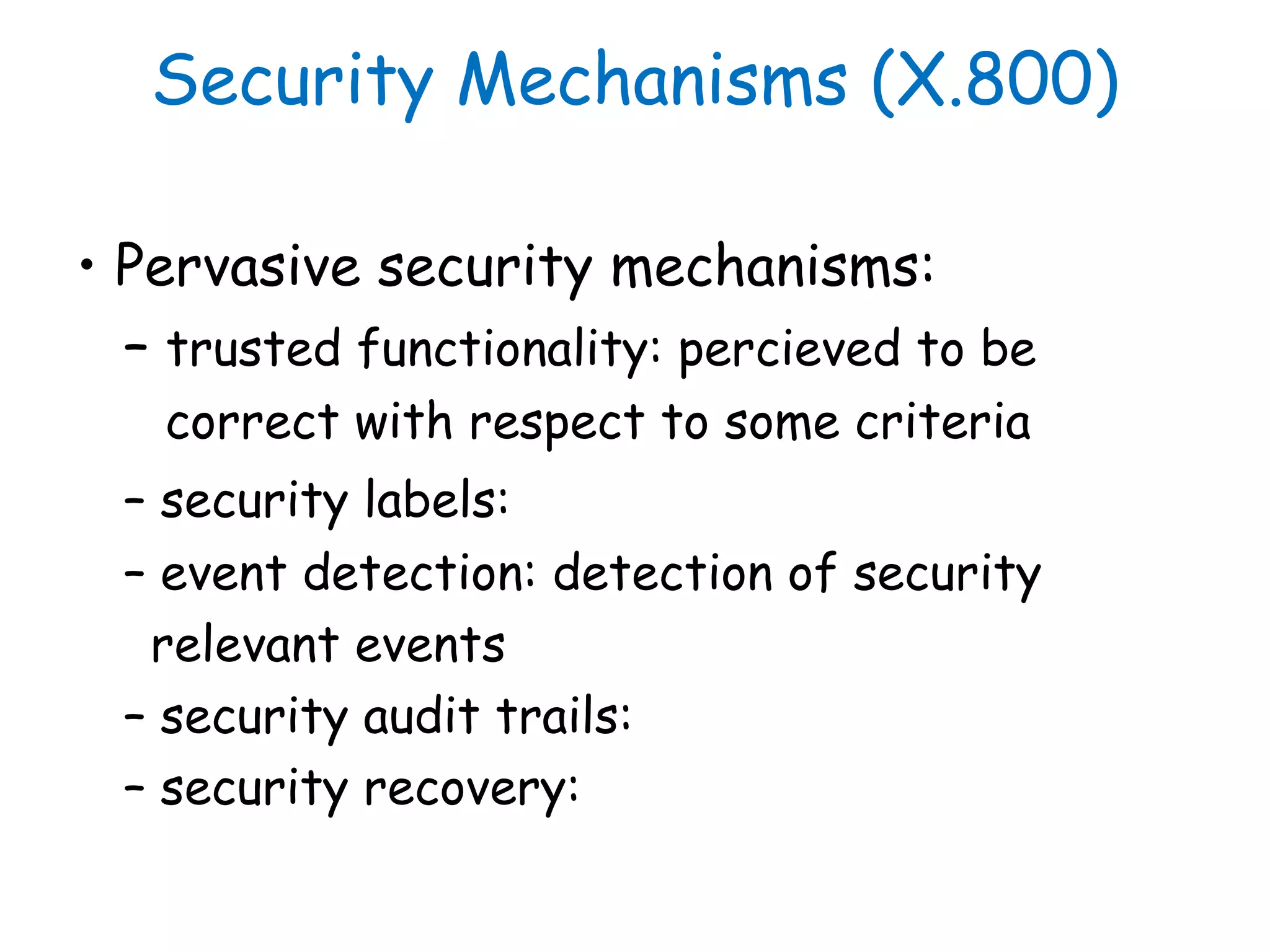
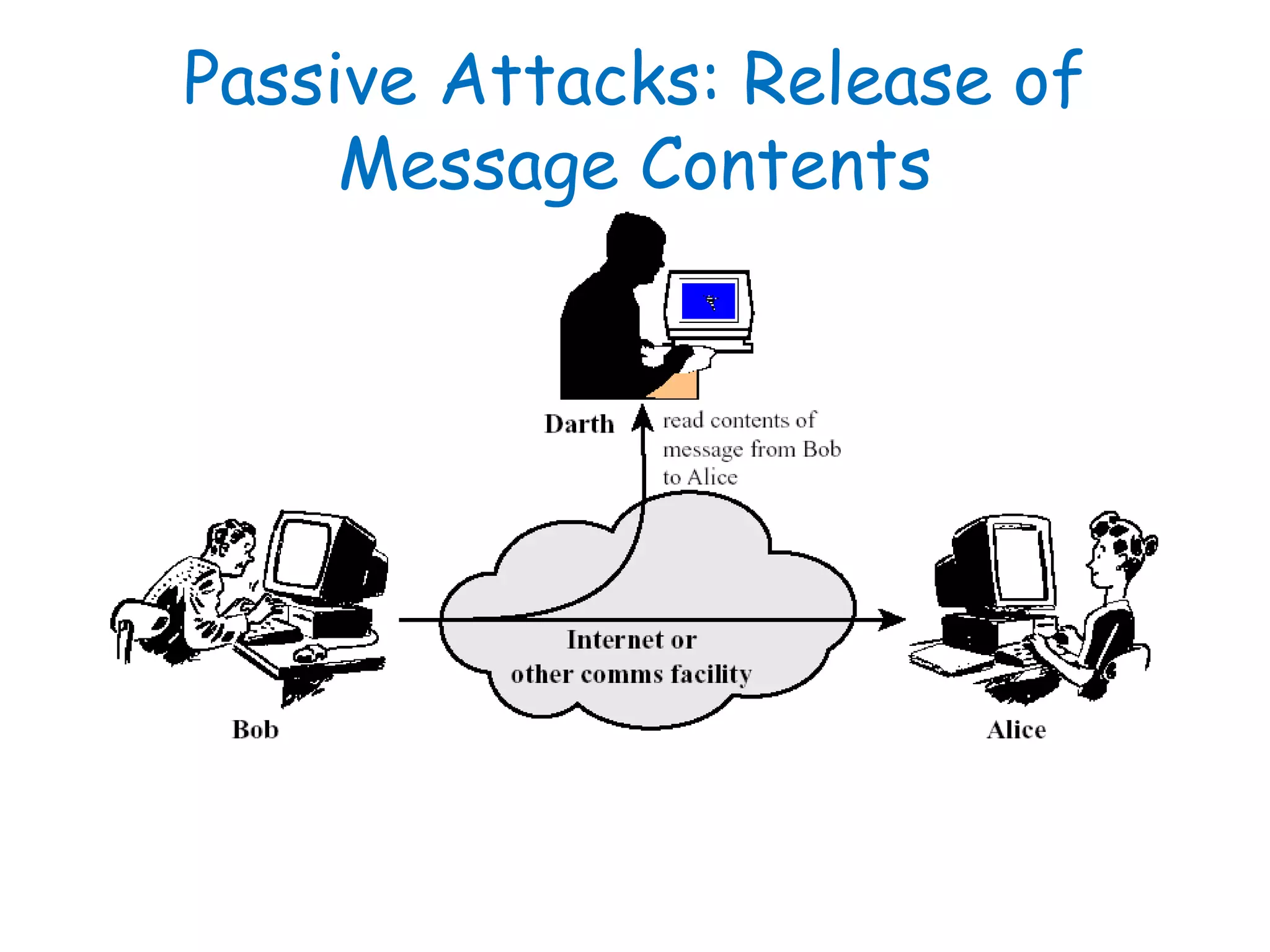
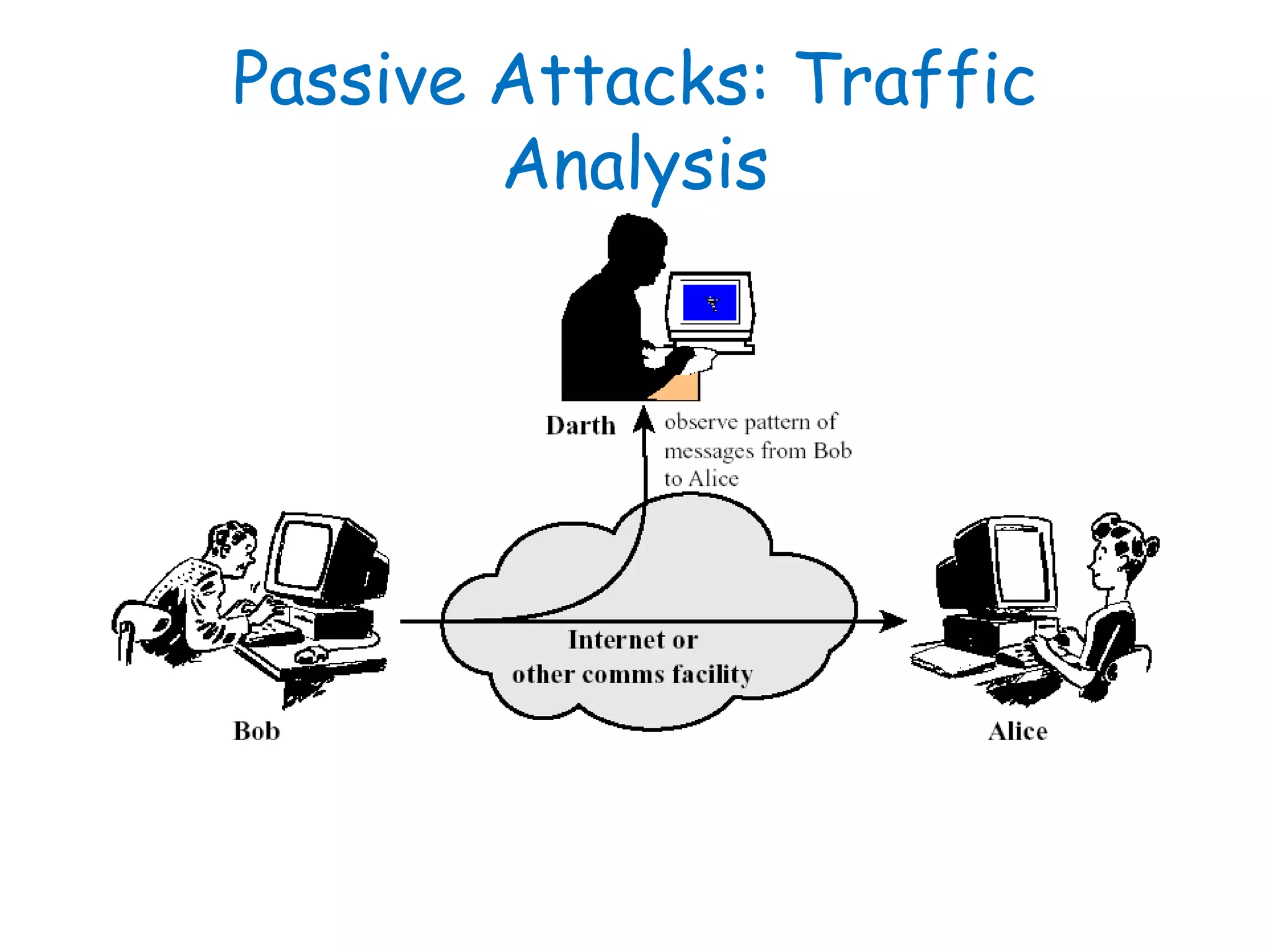
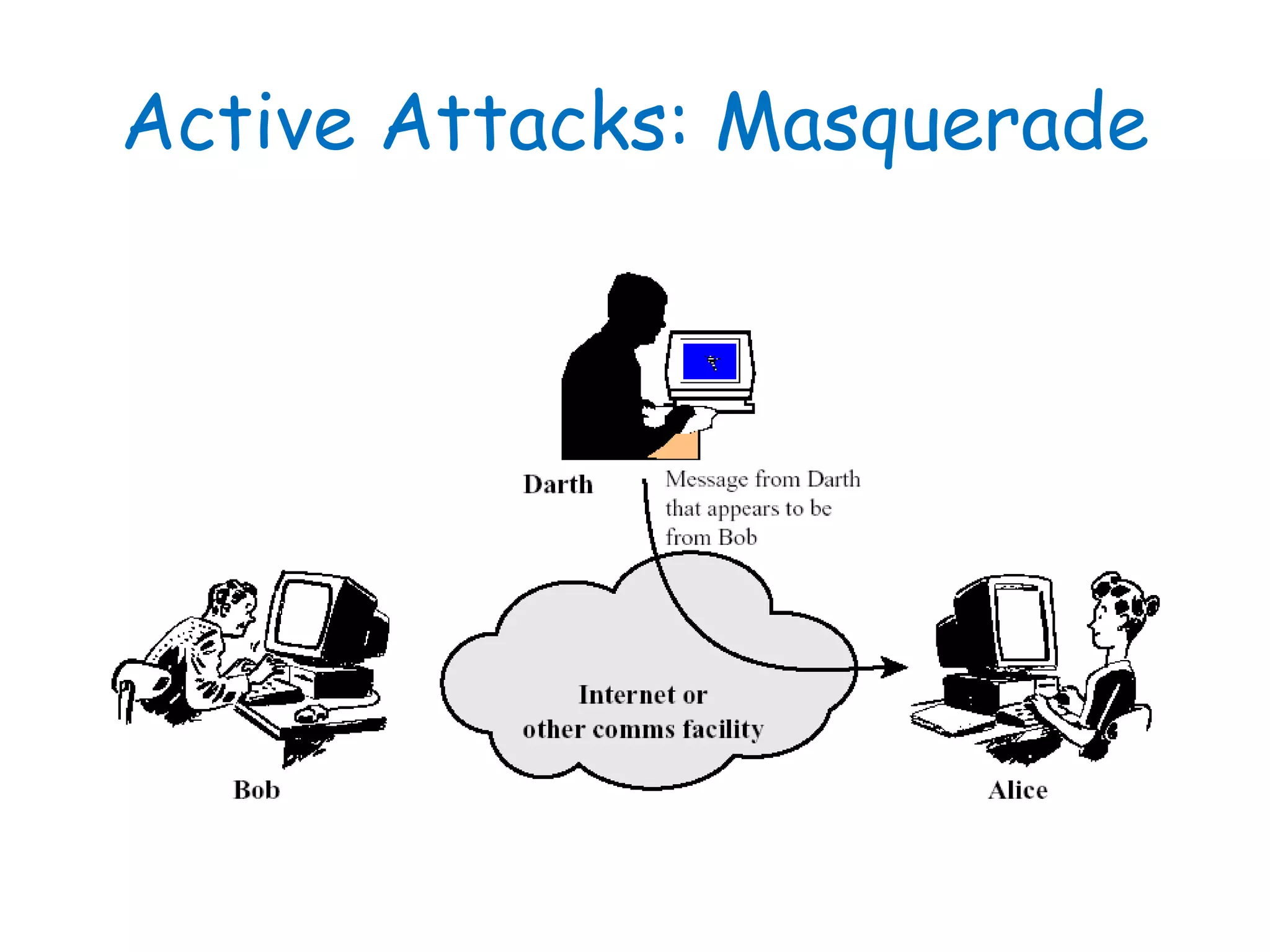
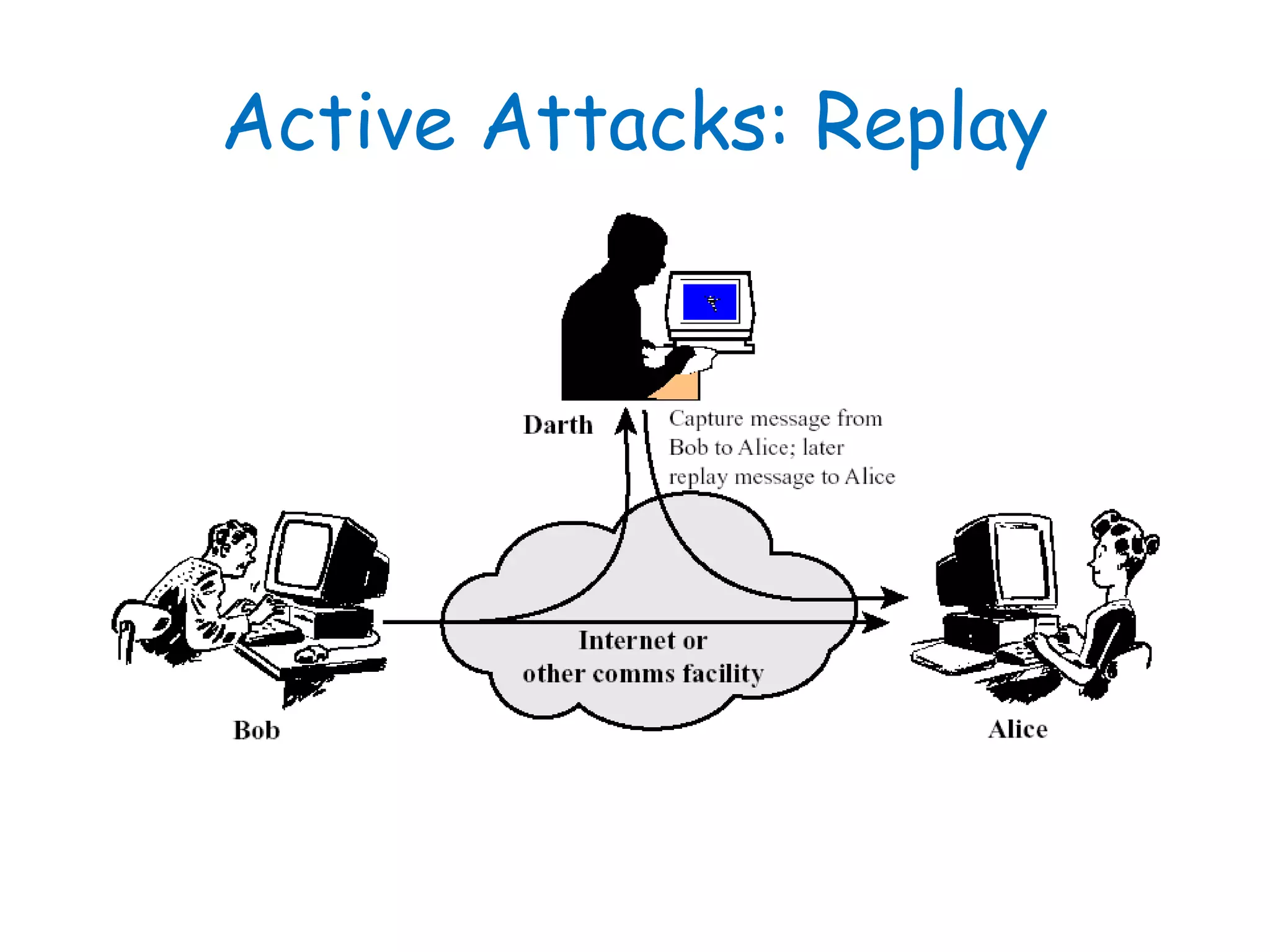
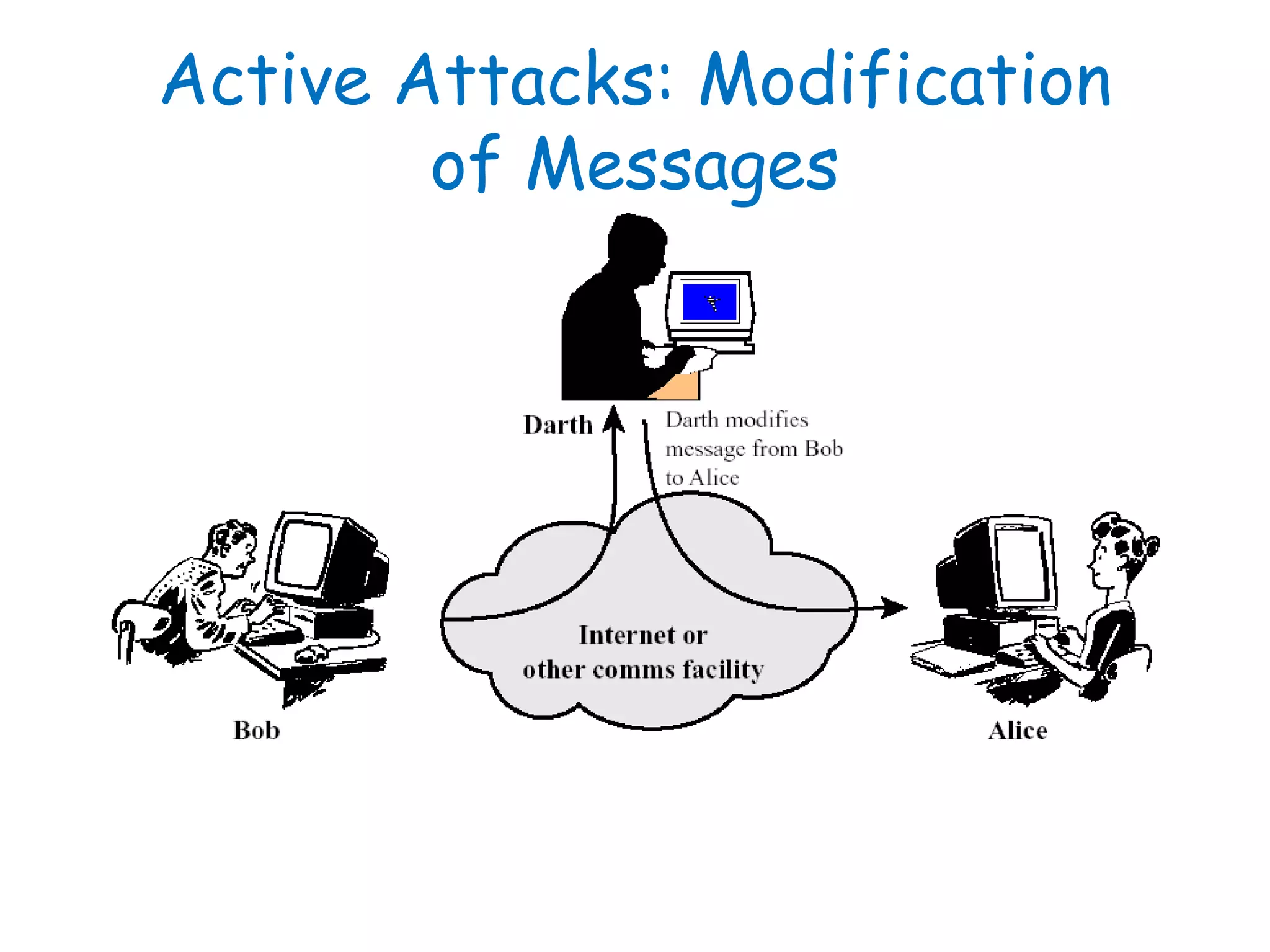
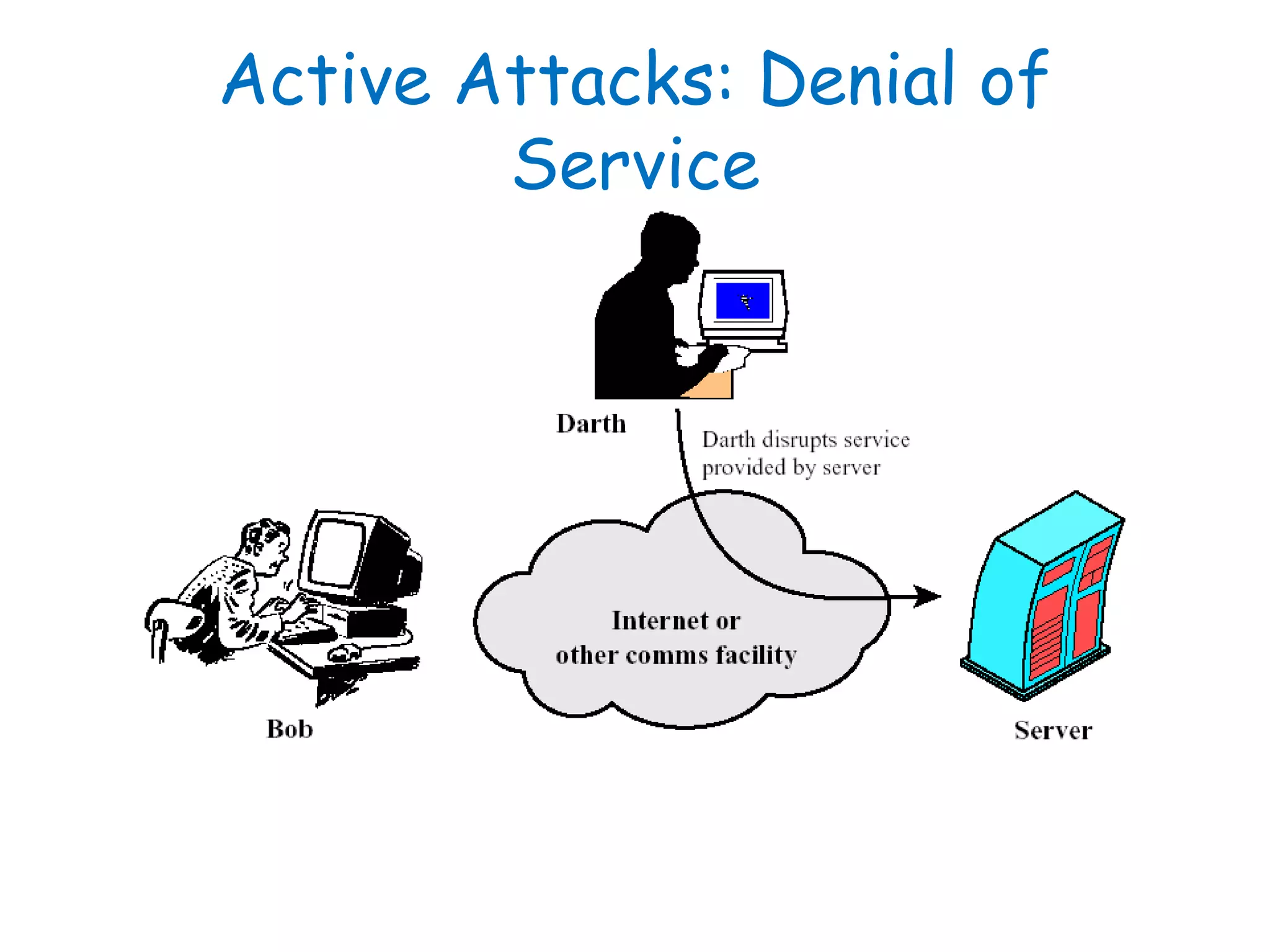
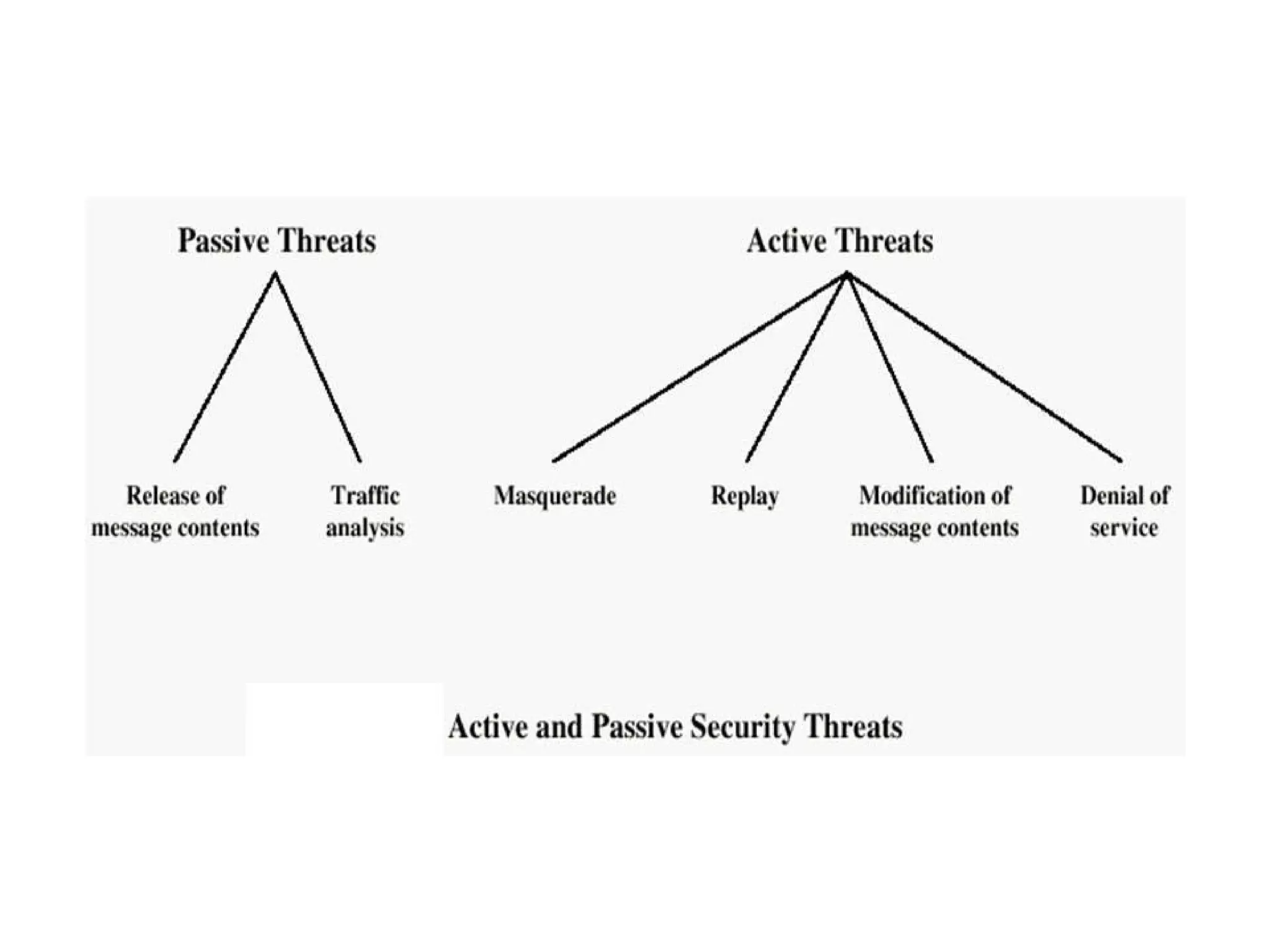
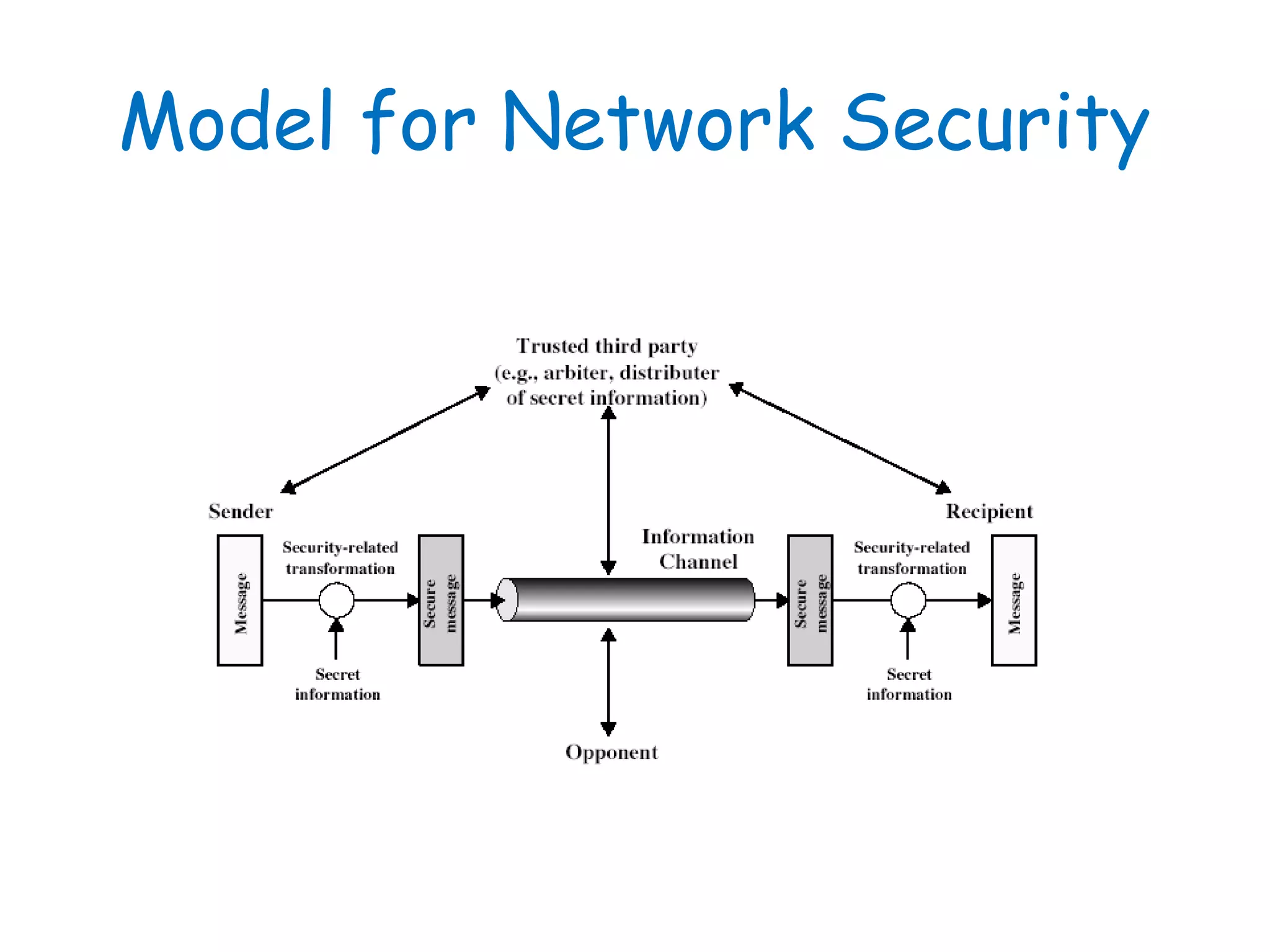
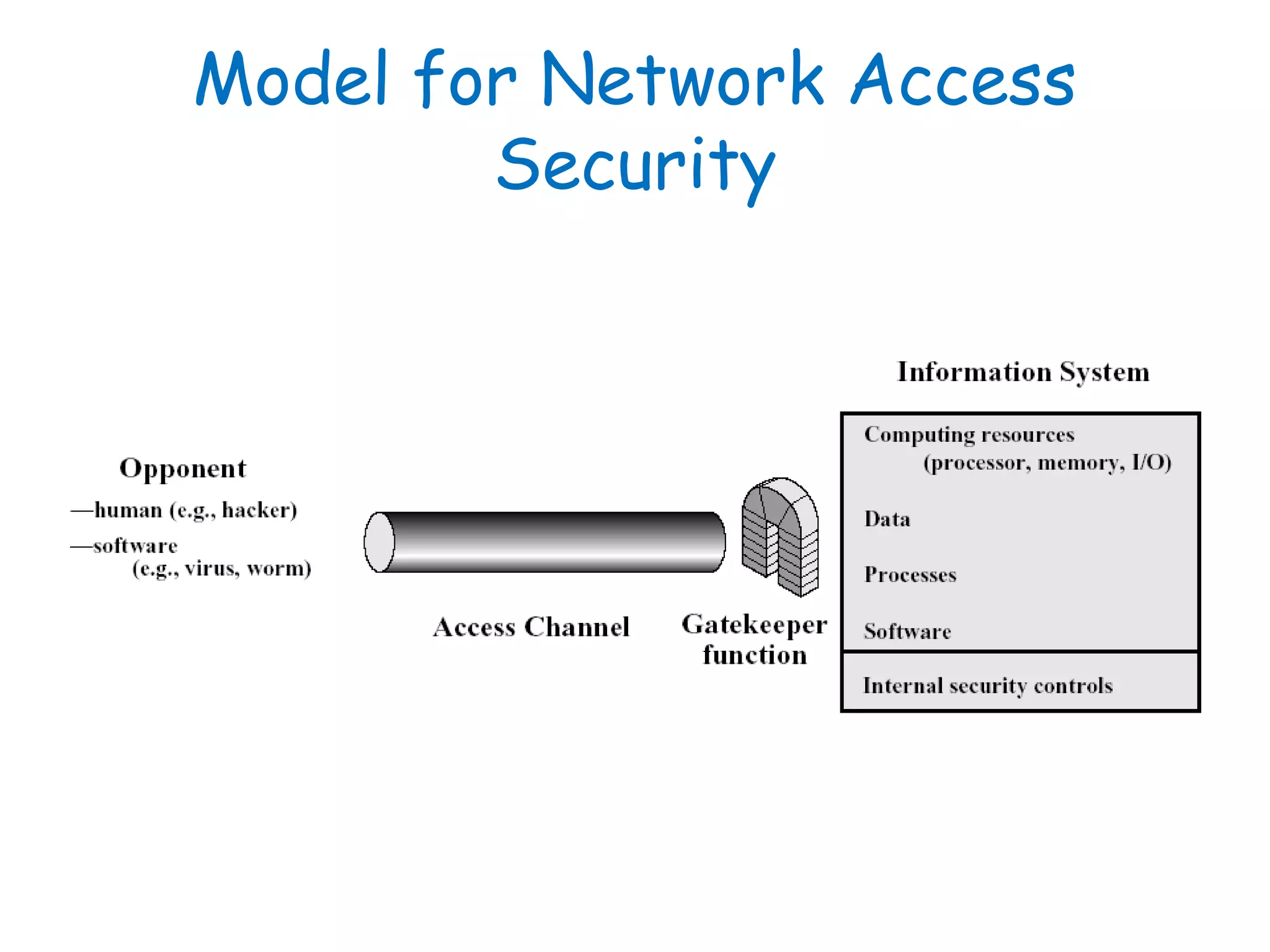
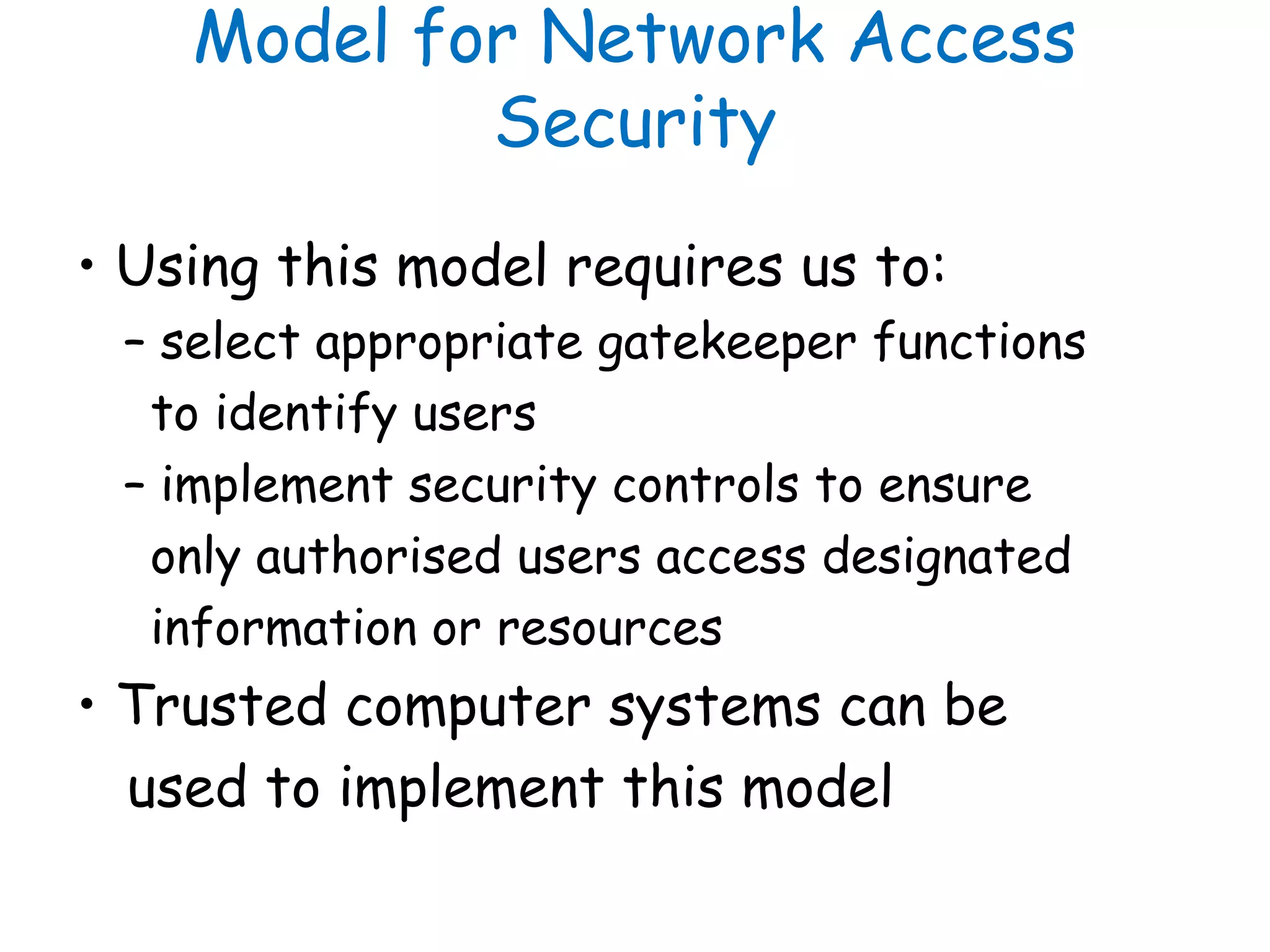
This document provides information about a network security course, including the instructor's contact details, course schedule, grading policy, reference materials, expectations, and course contents. The course will cover topics such as cryptography, network security applications, system security, and intrusion detection. Students will learn about network security principles, cryptography, authentication and encryption techniques, and security practices and applications.