This document provides an overview of the topics covered in the course CS8792 - Cryptography and Network Security. The topics include:
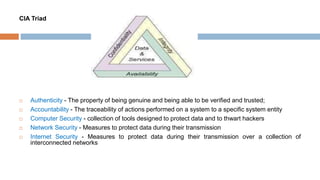
1. An introduction to security trends, including the CIA triad of confidentiality, integrity and availability. It also discusses legal, ethical and professional aspects of security.
2. The need for security at multiple levels and the role of security policies in protecting systems and setting access protocols.
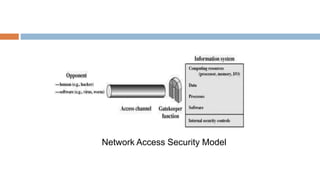
3. A model of network security which includes encryption, encryption keys, algorithm design, secret information distribution and security protocols.
4. The OSI security architecture and how it provides a systematic approach to security, organizing tasks like protecting information, key management and recovery procedures. It also discusses security