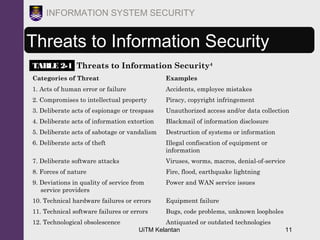
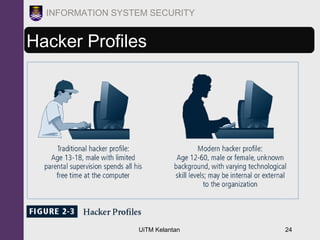
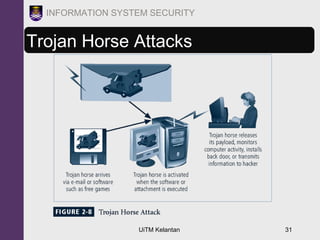
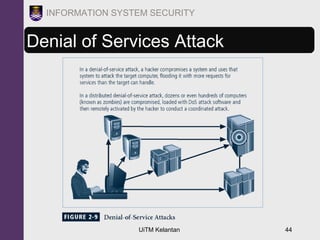
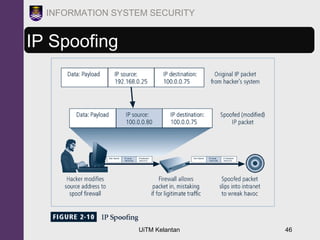
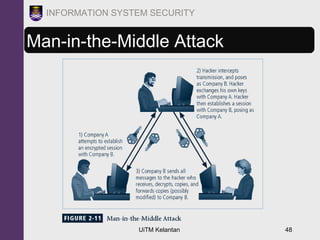
The document discusses information security threats and attacks. It provides examples of different types of threats including human error, intellectual property theft, espionage, service disruptions, natural disasters, hardware and software failures, and obsolescence. It also describes different categories of attacks such as malware, password cracking, denial of service, and how multi-vector worms can use various techniques like IP scanning, web browsing, file shares, and email to replicate. The document emphasizes that management must understand security threats in order to implement proper controls and safeguard the organization's data, systems, and ability to operate.