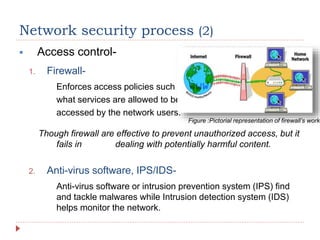
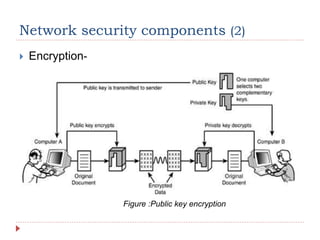
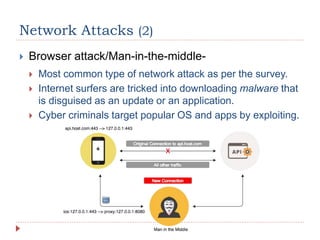
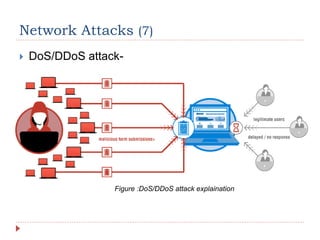
The document discusses network security, including its processes, components, and common attacks. It covers authentication methods, access control measures, and encryption techniques to protect networks from unauthorized access and threats. Additionally, it highlights various network attack types like man-in-the-middle, brute force, and DoS/DDoS attacks, along with prevention strategies.