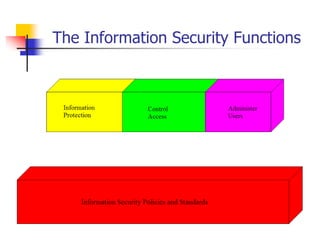
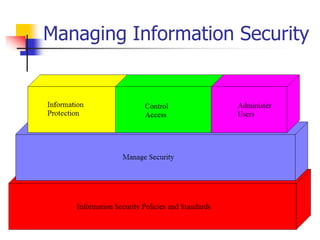
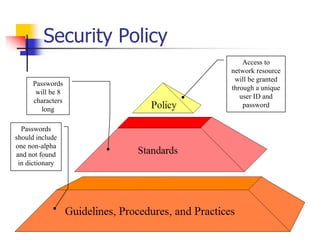
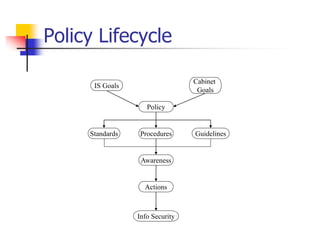
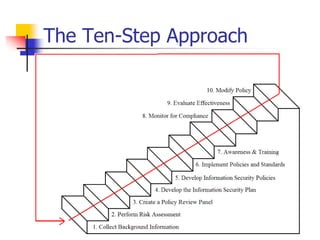
This document discusses information security policies and standards. It defines a security policy as a set of rules that define what it means to be secure for a system or organization. An information security policy sets rules to ensure all users and networks follow security prescriptions for digitally stored data. The challenges are to define policies and standards, measure against them, report violations, correct violations, and ensure compliance. It then discusses the key elements of developing an information security program, including performing risk assessments, creating review boards, developing plans, implementing policies and standards, providing awareness training, monitoring compliance, evaluating effectiveness, and modifying policies over time.